Abstract
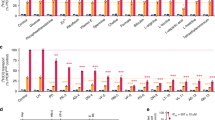
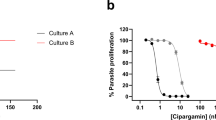
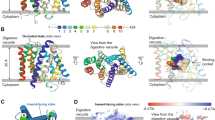
Artemisinins are the most important class of antimalarial drugs. They specifically inhibit PfATP6, a SERCA-type ATPase of Plasmodium falciparum. Here we show that a single amino acid in transmembrane segment 3 of SERCAs can determine susceptibility to artemisinin. An L263E replacement of a malarial by a mammalian residue abolishes inhibition by artemisinins. Introducing residues found in other Plasmodium spp. also modulates artemisinin sensitivity, suggesting that artemisinins interact with the thapsigargin-binding cleft of susceptible SERCAs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klayman, D.L. Science 228, 1049–1055 (1985).
Arrow, K.J., Panosian, C.B. & Geltband, H. (eds.). Saving Lives, Buying Time: Economics of Malaria Drugs in an Age of Resistance (National Academic Press, Washington, DC, 2004).
Krishna, S., Uhlemann, A.C. & Haynes, R.K. Drug Resist. Updat. 7, 233–244 (2004).
Eckstein-Ludwig, U. et al. Nature 424, 957–961 (2003).
Toyoshima, C., Nakasako, M., Nomura, H. & Ogawa, H. Nature 405, 647–655 (2000).
Toyoshima, C. & Nomura, H. Nature 418, 605–611 (2002).
Toyoshima, C. & Mizutani, T. Nature 430, 529–535 (2004).
Toyoshima, C., Nomura, H. & Tsuda, T. Nature 432, 361–368 (2004).
Janse, C.J., Waters, A.P., Kos, J. & Lugt, C.B. Int. J. Parasitol. 24, 589–594 (1994).
Russell, B.M. et al. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47, 170–173 (2003).
Chotivanich, K. et al. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 70, 395–397 (2004).
Brockman, A. et al. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 94, 537–544 (2000).
Ngo, T. et al. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 68, 350–356 (2003).
Noedl, H. et al. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 68, 140–142 (2003).
Gu, H.M., Warhurst, D.C. & Peters, W. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 78, 265–270 (1984).
Yu, M. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 3542–3546 (1998).
Kremsner, P.G. & Krishna, S. Lancet 364, 285–294 (2004).
Price, R.N. et al. Lancet 364, 438–447 (2004).
Woodrow, C.J., Penny, J.I. & Krishna, S. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 7272–7277 (1999).
Thompson, J.D., Higgins, D.G. & Gibson, T.J. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4673–4680 (1994).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Wellcome Trust (grant 074395). We thank D. Fidock for invaluable discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uhlemann, AC., Cameron, A., Eckstein-Ludwig, U. et al. A single amino acid residue can determine the sensitivity of SERCAs to artemisinins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12, 628–629 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb947
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb947
This article is cited by
-
Artemisinin inhibits neutrophil and macrophage chemotaxis, cytokine production and NET release
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Prevalence of potential mediators of artemisinin resistance in African isolates of Plasmodium falciparum
Malaria Journal (2021)
-
Molecular detection of drug resistant polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Southwest, Nigeria
BMC Research Notes (2020)
-
Current scenario and future strategies to fight artemisinin resistance
Parasitology Research (2019)
-
Profiling of the anti-malarial drug candidate SC83288 against artemisinins in Plasmodium falciparum
Malaria Journal (2018)