Abstract
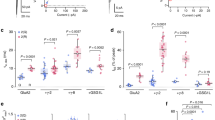
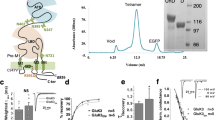
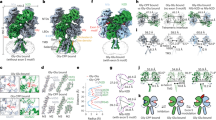
Desensitization is a universal feature of ligand-gated ion channels. Using the crystal structure of the GluR2 L483Y mutant channel as a guide, we attempted to build non-desensitizing kainate-subtype glutamate receptors. Success was achieved for GluR5, GluR6 and GluR7 with intermolecular disulfide cross-links but not by engineering the dimer interface. Crystallographic analysis of the GluR6 Y490C L752C dimer revealed relaxation from the active conformation, which functional studies reveal is not sufficient to trigger desensitization. The equivalent non-desensitizing cross-linked GluR2 mutant retained weak sensitivity to a positive allosteric modulator, which had no effect on GluR2 L483Y. These results establish that the active conformation of AMPA and kainate receptors is conserved and further show that their desensitization requires dimer rearrangements, that subtle structural differences account for their diverse functional properties and that the ligand-binding core dimer is a powerful regulator of ion-channel activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hille, B. Ionic channels of excitable membranes 3rd edn. (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA, 2001).
Jones, M.V. & Westbrook, G.L. The impact of receptor desensitization on fast synaptic transmission. Trends Neurosci. 19, 96–101 (1996).
Saviane, C. & Silver, R.A. Fast vesicle reloading and a large pool sustain high bandwidth transmission at a central synapse. Nature 439, 983–987 (2006).
Zorumski, C.F., Thio, L.L., Clark, G.D. & Clifford, D.B. Blockade of desensitization augments quisqualate excitotoxicity in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 5, 61–66 (1990).
David, J.C., Yamada, K.A., Bagwe, M.R. & Goldberg, M.P. AMPA receptor activation is rapidly toxic to cortical astrocytes when desensitization is blocked. J. Neurosci. 16, 200–209 (1996).
Sun, Y. et al. Mechanism of glutamate receptor desensitization. Nature 417, 245–253 (2002).
Horning, M.S. & Mayer, M.L. Regulation of AMPA receptor gating by ligand binding core dimers. Neuron 41, 379–388 (2004).
Partin, K.M., Patneau, D.K., Winters, C.A., Mayer, M.L. & Buonanno, A. Selective modulation of desensitization at AMPA versus kainate receptors by cyclothiazide and concanavlin A. Neuron 11, 1069–1082 (1993).
Partin, K.M., Bowie, D. & Mayer, M.L. Structural determinants of allosteric regulation in alternatively spliced AMPA receptors. Neuron 14, 833–843 (1995).
Stern-Bach, Y., Russo, S., Neuman, M. & Rosenmund, C. A point mutation in the glutamate binding site blocks desensitization of AMPA receptors. Neuron 21, 907–918 (1998).
Jin, R. et al. Mechanism of positive allosteric modulators acting on AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. 25, 9027–9036 (2005).
Lynch, G. Glutamate-based therapeutic approaches: ampakines. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 6, 82–88 (2006).
Hollmann, M. & Heinemann, S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 31–108 (1994).
Yelshansky, M.V., Sobolevsky, A.I., Jatzke, C. & Wollmuth, L.P. Block of AMPA receptor desensitization by a point mutation outside the ligand-binding domain. J. Neurosci. 24, 4728–4736 (2004).
Fleck, M.W., Cornell, E. & Mah, S.J. Amino-acid residues involved in glutamate receptor 6 kainate receptor gating and desensitization. J. Neurosci. 23, 1219–1227 (2003).
Smith, T.C. & Howe, J.R. Concentration-dependent substate behavior of native AMPA receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 992–997 (2000).
Bowie, D. & Lange, G.D. Functional stoichiometry of glutamate receptor desensitization. J. Neurosci. 22, 3392–3403 (2002).
Paternain, A.V., Cohen, A., Stern-Bach, Y. & Lerma, J. A role for extracellular Na+ in the channel gating of native and recombinant kainate receptors. J. Neurosci. 23, 8641–8648 (2003).
Armstrong, N. & Gouaux, E. Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: Crystal structures of the GluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron 28, 165–181 (2000).
Mayer, M.L., Olson, R. & Gouaux, E. Mechanisms for ligand binding to GluR0 ion channels: crystal structures of the glutamate and serine complexes and a closed apo state. J. Mol. Biol. 311, 815–836 (2001).
Nanao, M.H., Green, T., Stern-Bach, Y., Heinemann, S.F. & Choe, S. Structure of the kainate receptor subunit GluR6 agonist-binding domain complexed with domoic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 1708–1713 (2005).
Furukawa, H., Singh, S.K., Mancusso, R. & Gouaux, E. Subunit arrangement and function in NMDA receptors. Nature 438, 185–192 (2005).
Mayer, M.L., Ghosal, A., Dolman, N.P. & Jane, D.E. Crystal structures of the kainate receptor GluR5 ligand binding core dimer with novel GluR5-selective antagonists. J. Neurosci. 26, 2852–2861 (2006).
Hazes, B. & Dijkstra, B.W. Model building of disulfide bonds in proteins with known three-dimensional structure. Protein Eng. 2, 119–125 (1988).
Paternain, A.V., Rodriguez-Moreno, A., Villarroel, A. & Lerma, J. Activation and desensitization properties of native and recombinant kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology 37, 1249–1259 (1998).
Bowie, D. External anions and cations distinguish between AMPA and kainate receptor gating mechanisms. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 539, 725–733 (2002).
Armstrong, N., Mayer, M. & Gouaux, E. Tuning activation of the AMPA-sensitive GluR2 ion channel by genetic adjustment of agonist-induced conformational changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5736–5741 (2003).
Koike, M., Tsukada, S., Tsuzuki, K., Kijima, H. & Ozawa, S. Regulation of kinetic properties of GluR2 AMPA receptor channels by alternative splicing. J. Neurosci. 20, 2166–2174 (2000).
Hogner, A. et al. Structural basis for AMPA receptor activation and ligand selectivity: crystal structures of five agonist complexes with the GluR2 ligand-binding core. J. Mol. Biol. 322, 93 (2002).
Jin, R., Banke, T.G., Mayer, M.L., Traynelis, S.F. & Gouaux, E. Structural basis for partial agonist action at ionotropic glutamate receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 803–810 (2003).
Mayer, M.L. Crystal structures of the GluR5 and GluR6 ligand binding cores: molecular mechanisms underlying kainate receptor selectivity. Neuron 45, 539–552 (2005).
Tichelaar, W., Safferling, M., Keinanen, K., Stark, H. & Madden, D.R. The three-dimensional structure of an ionotropic glutamate receptor reveals a dimer-of-dimers assembly. J. Mol. Biol. 344, 435–442 (2004).
Nakagawa, T., Cheng, Y., Sheng, M. & Walz, T. Three-dimensional structure of an AMPA receptor without associated stargazin/TARP proteins. Biol. Chem. 387, 179–187 (2006).
Weston, M.C., Gertler, C., Mayer, M.L. & Rosenmund, C. Interdomain interactions in AMPA and kainate receptors regulate affinity for glutamate. J. Neurosci. 26, 7650–7658 (2006).
Nakagawa, T., Cheng, Y., Ramm, E., Sheng, M. & Walz, T. Structure and different conformational states of native AMPA receptor complexes. Nature 433, 545–549 (2005).
Armstrong, N., Jasti, J., Beich-Frandsen, M. & Gouaux, E. Structure of the desensitized state of ionotropic glutamate receptors. Cell 127, 85–97 (2006).
Mayer, M.L. & Armstrong, N. Structure and function of glutamate receptor ion channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 66, 161–181 (2004).
Vistica, J. et al. Sedimentation equilibrium analysis of protein interactions with global implicit mass conservation constraints and systematic noise decomposition. Anal. Biochem. 326, 234–256 (2004).
Schuck, P. Size-distribution analysis of macromolecules by sedimentation velocity ultracentrifugation and lamm equation modeling. Biophys. J. 78, 1606–1619 (2000).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. DENZO and SCALEPACK. Int. Tables Crystallogr. F, 226–235 (2001).
Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 50, 760–763 (1994).
Painter, J. & Merritt, E.A. Optimal description of a protein structure in terms of multiple groups undergoing TLS motion. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 62, 439–450 (2006).
Jones, T.A. & Kjeldgaard, M. Electron-density map interpretation. Methods Enzymol. 277, 173–208 (1997).
Kleywegt, G.J., Zou, J.Y., Kjeldgaard, M. & Jones, T.A. Around O. Int. Tables Crystallogr. F, 353–356 (2001).
Kraulis, P.J. MOLSCRIPT: A program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merritt, E.A. & Bacon, D.J. Raster3D: photorealistic molecular graphics. Methods Enzymol. 277, 505–524 (1997).
Chen, C. & Okayama, H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 2745–2752 (1987).
Clements, J.D. & Westbrook, G.L. Activation kinetics reveal the number of glutamate and glycine binding sites on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Neuron 7, 605–613 (1991).
Colquhoun, D., Jonas, P. & Sakmann, B. Action of brief pulses of glutamate on AMPA/kainate receptors in patches from different neurones of rat hippocampal slices. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 458, 261–287 (1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Glasser for technical assistance, P. Seeburg (Max Planck Institute for Medical Research, Heidelberg) and S. Heinemann (Salk Institute for Biological Studies) for the gift of the wild-type GluR plasmids, H. Deng for help with cell culture, M. Zhang for help with protein purification and crystallization, H. Jaffe (Protein/Peptide Sequencing Facility, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke) for mass spectral analysis, E. Gouaux for sharing results before publication and A. Plested for reading the manuscript. Nucleic acid sequencing was performed by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke DNA sequencing facility, Porter Neuroscience Research Center. This work was supported by the Brown foundation (C.R.), Neuroscience Training grant T32 GM008507 (M.C.W.) and the intramural research program of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, US National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services (M.L.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Electrophysiological experiments were performed by M.C.W., analytical ultracentrifugation by P.S., biochemistry and crystallography by M.L.M., molecular biology and biochemistry by A.G. Data was interpreted and the paper written by M.L.M., C.R. and M.C.W.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weston, M., Schuck, P., Ghosal, A. et al. Conformational restriction blocks glutamate receptor desensitization. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 1120–1127 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1178
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1178
This article is cited by
-
Damaging coding variants within kainate receptor channel genes are enriched in individuals with schizophrenia, autism and intellectual disabilities
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Structural mechanisms of activation and desensitization in neurotransmitter-gated ion channels
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2016)
-
Tethered ligands reveal glutamate receptor desensitization depends on subunit occupancy
Nature Chemical Biology (2014)
-
NMDA receptor structures reveal subunit arrangement and pore architecture
Nature (2014)
-
Net(o) excitement for kainate receptors
Nature Neuroscience (2011)