Abstract
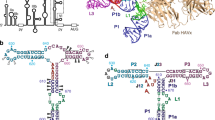
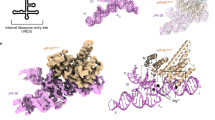
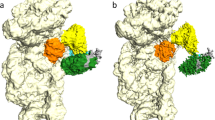
Internal ribosome entry sites (IRESs) facilitate an alternative, end-independent pathway of translation initiation. A particular family of dicistroviral IRESs can assemble elongation-competent 80S ribosomal complexes in the absence of canonical initiation factors and initiator transfer RNA. We present here a cryo-EM reconstruction of a dicistroviral IRES bound to the 80S ribosome. The resolution of the cryo-EM reconstruction, in the subnanometer range, allowed the molecular structure of the complete IRES in its active, ribosome-bound state to be solved. The structure, harboring three pseudoknot-containing domains, each with a specific functional role, shows how defined elements of the IRES emerge from a compactly folded core and interact with the key ribosomal components that form the A, P and E sites, where tRNAs normally bind. Our results exemplify the molecular strategy for recruitment of an IRES and reveal the dynamic features necessary for internal initiation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sonenberg, N. & Dever, T.E. Eukaryotic translation initiation factors and regulators. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 13, 56–63 (2003).
Dever, T.E. Gene-specific regulation by general translation factors. Cell 108, 545–556 (2002).
Hellen, C.U. & Sarnow, P. Internal ribosome entry sites in eukaryotic mRNA molecules. Genes Dev. 15, 1593–1612 (2001).
Vagner, S., Galy, B. & Pyronnet, S. Irresistible IRES: attracting the translation machinery to internal ribosome entry sites. EMBO Rep. 2, 893–898 (2001).
Stoneley, M. & Willis, A.E. Cellular internal ribosome entry segments: structures, trans-acting factors and regulation of gene expression. Oncogene 23, 3200–3207 (2004).
Jackson, R.J. Alternative mechanisms of initiating translation of mammalian mRNAs. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 33, 1231–1241 (2005).
Sasaki, J. & Nakashima, N. Methionine-independent initiation of translation in the capsid protein of an insect RNA virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 1512–1515 (2000).
Pestova, T.V. & Hellen, C.U. Translation elongation after assembly of ribosomes on the Cricket paralysis virus internal ribosomal entry site without initiation factors or initiator tRNA. Genes Dev. 17, 181–186 (2003).
Wilson, J.E., Pestova, T.V., Hellen, C.U. & Sarnow, P. Initiation of protein synthesis from the A site of the ribosome. Cell 102, 511–520 (2000).
Jan, E., Goss Kinzy, T. & Sarnow, P. Divergent tRNA-like element supports initiation, elongation and termination of protein biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 15410–15415 (2003).
Spahn, C.M.T. et al. Hepatitis C virus IRES RNA-induced changes in the conformation of the 40S ribosomal subunit. Science 291, 1962 (2001).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Cryo-EM visualization of a viral internal ribosome entry site bound to human ribosomes: the IRES functions as an RNA-based translation factor. Cell 118, 465–475 (2004).
Thompson, S.R., Gulyas, K.D. & Sarnow, P. Internal initiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mediated by an initiator tRNA/eIF2-independent internal ribosome entry site element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 12972–12977 (2001).
Halic, M., Becker, T., Frank, J., Spahn, C.M. & Beckmann, R. Localization and dynamic behavior of ribosomal protein L30e. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12, 467–468 (2005).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Domain movements of elongation factor eEF2 and the eukaryotic 80S ribosome facilitate tRNA translocation. EMBO J. 23, 1008–1019 (2004).
Jan, E. & Sarnow, P. Factorless ribosome assembly on the internal ribosome entry site of cricket paralysis virus. J. Mol. Biol. 324, 889–902 (2002).
Nishiyama, T. et al. Structural elements in the internal ribosome entry site of Plautia stali intestine virus responsible for binding with ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 2434–2442 (2003).
Kanamori, Y. & Nakashima, N. A tertiary structure model of the internal ribosome entry site (IRES) for methionine-independent initiation of translation. RNA 7, 266–274 (2001).
Pestova, T.V., Lomakin, I.B. & Hellen, C.U. Position of the CrPV IRES on the 40S subunit and factor dependence of IRES/80S ribosome assembly. EMBO Rep. 5, 906–913 (2004).
Hilbers, C.W., Michiels, P.J. & Heus, H.A. New developments in structure determination of pseudoknots. Biopolymers 48, 137–153 (1998).
Su, L., Chen, L., Egli, M., Berger, J.M. & Rich, A. Minor groove RNA triplex in the crystal structure of a ribosomal frameshifting viral pseudoknot. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6, 285–292 (1999).
Battle, D.J. & Doudna, J.A. Specificity of RNA-RNA helix recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 11676–11681 (2002).
Nissen, P., Ippolito, J.A., Ban, N., Moore, P.B. & Steitz, T.A. RNA tertiary interactions in the large ribosomal subunit: the A-minor motif. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4899–4903 (2001).
Costantino, D. & Kieft, J.S. A preformed compact ribosome-binding domain in the cricket paralysis-like virus IRES RNAs. RNA 11, 332–343 (2005).
Theimer, C.A., Blois, C.A. & Feigon, J. Structure of the human telomerase RNA pseudoknot reveals conserved tertiary interactions essential for function. Mol. Cell 17, 671–682 (2005).
Yusupov, M.M. et al. Crystal structure of the ribosome at 5.5 Å resolution. Science 292, 883–896 (2001).
Spahn, C.M.T. et al. Structure of the 80S ribosome from Saccharomyces cerevisiae—tRNA-ribosome and subunit-subunit interactions. Cell 107, 373–386 (2001).
Harms, J. et al. High resolution structure of the large ribosomal subunit from a mesophilic eubacterium. Cell 107, 679–688 (2001).
Valle, M. et al. Locking and unlocking of ribosomal motions. Cell 114, 123–134 (2003).
Ban, N., Nissen, P., Hansen, J., Moore, P.B. & Steitz, T.A. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science 289, 905–920 (2000).
Bottcher, B., Wynne, S.A. & Crowther, R.A. Determination of the fold of the core protein of hepatitis B virus by electron cryomicroscopy. Nature 386, 88–91 (1997).
Chiu, W., Baker, M.L., Jiang, W., Dougherty, M. & Schmid, M.F. Electron cryomicroscopy of biological machines at subnanometer resolution. Structure 13, 363–372 (2005).
Frank, J. et al. SPIDER and WEB: processing and visualization of images in 3D electron microscopy and related fields. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 190–199 (1996).
Massire, C. & Westhof, E. MANIP: an interactive tool for modelling RNA. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 16, 197–205 255–7 (1998).
Jones, T.A. & Kjeldgaard, M. Electron density map interpretation. Methods Enzymol. 277B, 173–207 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the VolkswagenStiftung (to C.M.T.S.), by US National Institutes of Health grant R01 GM60635 (to P.A.P.), by the sixth EU framework program 3DEM and by the European Union and Senatsverwaltung für Wissenschaft, Forschung und Kultur Berlin (UltraStructureNetwork and Anwenderzentrum). S.R.C. was supported with a grant from the Alexander von Humboldt Stiftung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Resolution curve. (PDF 462 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Comparison of the PKIII pseudoknot with the BWYV pseudoknot. (PDF 2493 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Annotated secondary structure diagram. (PDF 1382 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Comparison of the human telomerase pseudoknot with PKI of the CrPV IRES. (PDF 1981 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
Interactions of the CRPV IRES with the 80S ribosome. (PDF 2623 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schüler, M., Connell, S., Lescoute, A. et al. Structure of the ribosome-bound cricket paralysis virus IRES RNA. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 1092–1096 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1177
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1177
This article is cited by
-
The molecular basis of translation initiation and its regulation in eukaryotes
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2024)
-
IRESpy: an XGBoost model for prediction of internal ribosome entry sites
BMC Bioinformatics (2019)
-
Viral RNA structure-based strategies to manipulate translation
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2019)
-
A conserved RNA structural motif for organizing topology within picornaviral internal ribosome entry sites
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Advances in the field of single-particle cryo-electron microscopy over the last decade
Nature Protocols (2017)