Abstract
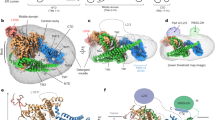
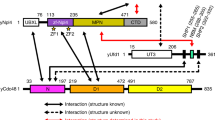
ESCRT-II, a complex that sorts ubiquitinated membrane proteins to lysosomes, localizes to endosomes through interaction between the Vps36 subunit's GLUE domain and phosphatidylinositides (PIs). In yeast, a ubiquitin (Ub)-interacting NZF domain is inserted in Vps36 GLUE, whereas its mammalian counterpart, Eap45 GLUE, lacks the NZF domain. In the Eap45 GLUE–Ub complex structure, Ub binds far from the proposed PI-binding site of Eap45 GLUE, suggesting their independent binding.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Fiore, P.P., Polo, S. & Hofmann, K. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 491–497 (2003).
Slagsvold, T., Pattni, K., Malerod, L. & Stenmark, H. Trends Cell Biol. 16, 317–326 (2006).
Schnell, J.D. & Hicke, L. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 35857–35860 (2003).
Raiborg, C., Rusten, T.E. & Stenmark, H. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 446–455 (2003).
Slagsvold, T. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 19600–19606 (2005).
Hurley, J.H. & Emr, S.D. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 35, 277–298 (2006).
Hirano, S. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 272–277 (2006).
Swanson, K.A., Kang, R.S., Stamenova, S.D., Hicke, L. & Radhakrishnan, I. EMBO J. 22, 4597–4606 (2003).
Teo, H., Veprintsev, D.B. & Williams, R.L. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 28689–28696 (2004).
Sundquist, W.I. et al. Mol. Cell 13, 783–789 (2004).
Alam, S.L. et al. EMBO J. 23, 1411–1421 (2004).
Teo, H. et al. Cell 125, 99–111 (2006).
Hicke, L., Schubert, H.L. & Hill, C.P. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 610–621 (2005).
Vijay-Kumar, S., Bugg, C.E. & Cook, W.J. J. Mol. Biol. 194, 531–544 (1987).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Protein 3000 project, by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and by the Norwegian Cancer Society, the Research Council of Norway and the Novo-Nordisk Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Sequence alignment of the GLUE domains. (PDF 162 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Electrostatic surface potential of the phosphoinositide-binding site of GLUE domains. (PDF 67 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Comparison of the ubiquitin-binding sites of mouse Eap45 and yeast Vps36. (PDF 71 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Schematic drawing of ESCRT-II binding to ubiquitinated cargo and endosomal membrane. (PDF 67 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Data collection and refinement statistics. (PDF 51 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Sequences of QuikChange primers for Eap45 GLUE mutants. (PDF 19 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirano, S., Suzuki, N., Slagsvold, T. et al. Structural basis of ubiquitin recognition by mammalian Eap45 GLUE domain. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 1031–1032 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1163
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1163
This article is cited by
-
Exosomal transmission of viruses, a two-edged biological sword
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Preferential phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate binding contributes to a destabilization of the VHS domain structure of Tom1
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Membrane budding and scission by the ESCRT machinery: it's all in the neck
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2010)
-
ESCRT-II coordinates the assembly of ESCRT-III filaments for cargo sorting and multivesicular body vesicle formation
The EMBO Journal (2010)
-
The ESCRT machinery in endosomal sorting of ubiquitylated membrane proteins
Nature (2009)