Abstract
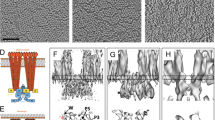
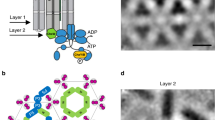
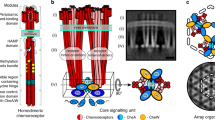
In bacterial chemotaxis, an assembly of transmembrane receptors, the CheA histidine kinase and the adaptor protein CheW processes environmental stimuli to regulate motility. The structure of a Thermotoga maritima receptor cytoplasmic domain defines CheA interaction regions and metal ion–coordinating charge centers that undergo chemical modification to tune receptor response. Dimeric CheA–CheW, defined by crystallography and pulsed ESR, positions two CheWs to form a cleft that is lined with residues important for receptor interactions and sized to clamp one receptor dimer. CheW residues involved in kinase activation map to interfaces that orient the CheW clamps. CheA regulatory domains associate in crystals through conserved hydrophobic surfaces. Such CheA self-contacts align the CheW receptor clamps for binding receptor tips. Linking layers of ternary complexes with close-packed receptors generates a lattice with reasonable component ratios, cooperative interactions among receptors and accessible sites for modification enzymes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wadhams, G.H. & Armitage, J.P. Making sense of it all: bacterial chemotaxis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 1024–1037 (2004).
Parkinson, J.S., Ames, P. & Studdert, C.A. Collaborative signaling by bacterial chemoreceptors. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 8, 116–121 (2005).
Sourjik, V. Receptor clustering and signal processing in E. coli chemotaxis. Trends Microbiol. 12, 569–576 (2004).
Falke, J.J. & Hazelbauer, G.L. Transmembrane signaling in bacterial chemoreceptors. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26, 257–265 (2001).
Falke, J.J. & Kim, S-H. Structure of a conserved receptor domain that regulates kinase activity: the cytoplasmic domain of bacterial taxis receptors. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 10, 462–469 (2000).
Chao, X. et al. A receptor-modifying deamidase in complex with a signaling phosphatase reveals reciprocal regulation. Cell 124, 561–571 (2006).
Szurmant, H. & Ordal, G.W. Diversity in chemotaxis mechanisms among the bacteria and archaea. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68, 301–319 (2004).
Ottemann, K.M., Xiao, W., Shin, Y-K. & Koshland, D.E., Jr. A piston model for transmembrane signaling of the aspartate receptor. Science 285, 1751–1754 (1999).
Bilwes, A.M., Park, S.Y., Quezada, C.M., Simon, M.I. & Crane, B.R. Structure and runction of CheA, the histidine kinase central to bacterial chemotaxis. in Histidine Kinases in Signal Transduction (eds. Inouye, M. & Dutta, R.) 48–74 (Academic Press, San Diego, 2003).
Bilwes, A.M., Alex, L.A., Crane, B.R. & Simon, M.I. Structure of CheA, a signal-transducing histidine kinase. Cell 96, 131–141 (1999).
Griswold, I.J. et al. The solution structure and interactions of CheW from Thermotoga maritima. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 121–125 (2002).
Stewart, R.C., Jahreis, K. & Parkinson, J.S. Rapid phosphotransfer to CheY from a CheA protein lacking the CheY-binding domain. Biochemistry 39, 13157–13165 (2000).
Quezada, C.M. et al. Structural and chemical requirements for histidine phosphorylation by the chemotaxis kinase CheA. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 30581–30585 (2005).
Lybarger, S.R. & Maddock, J.R. Polarity in action: asymmetric protein localization in bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 183, 3261–3267 (2001).
Gestwicki, J.E. & Kiessling, L.L. Inter-receptor communication through arrays of bacterial chemoreceptors. Nature 415, 81–84 (2002).
Lamanna, A.C., Ordal, G.W. & Kiessling, L.L. Large increases in attractant concentration disrupt the polar localization of bacterial chemoreceptors. Mol. Microbiol. 57, 774–785 (2005).
Studdert, C.A. & Parkinson, J.S. Crosslinking snapshots of bacterial chemoreceptor squads. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 2117–2122 (2004).
Ames, P., Studdert, C.A., Reiser, R.H. & Parkinson, J.S. Collaborative signaling by mixed chemoreceptor teams in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 7060–7065 (2002).
Li, M. & Hazelbauer, G.L. Adaptational assistance in clusters of bacterial chemoreceptors. Mol. Microbiol. 56, 1617–1626 (2005).
Kim, K.K., Yokota, H. & Kim, S.H. Four-helical-bundle structure of the cytoplasmic domain of a serine chemotaxis receptor. Nature 400, 787–792 (1999).
Kim, S.H., Wang, W. & Kim, K.K. Dynamic and clustering model of bacterial chemotaxis receptors: structural basis for signaling and high sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 11611–11615 (2002).
Coleman, M.D., Bass, R.B., Mehan, R.S. & Falke, J.J. Conserved glycine residues in the cytoplasmic domain of the aspartate receptor play essential roles in kinase coupling and on-off switching. Biochemistry 44, 7687–7695 (2005).
Starrett, D.J. & Falke, J.J. Adaptation mechanism of the aspartate receptor: electrostatics of the adaptation subdomain play a key role in modulating kinase activity. Biochemistry 44, 1550–1560 (2005).
Boukhvalova, M., Dahlquist, F.W. & Stewart, R.C. CheW binding interactions with CheA and Tar—importance for chemotaxis signaling in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22251–22259 (2002).
Bourret, R.B., Davagnino, J. & Simon, M.I. The carboxy-terminal portion of the CheA kinase mediates regulation of autophosphorylation by transducer and CheW. J. Bacteriol. 175, 2097–2101 (1993).
Zhao, J. & Parkinson, J.S. Mutational analysis of the chemoreceptor-coupling domain of the E. coli chemotaxis signaling kinase CheA. J. Bacteriol. (in the press).
Hamel, D.J. & Dahlquist, F.W. The contact interface of a 120 kD CheA-CheW complex by methyl TROSY interaction spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 9676–9677 (2005).
Park, S.Y., Quezada, C.M., Bilwes, A.M. & Crane, B.R. Subunit exchange by CheA histidine kinases from the mesophile Escherichia coli and the thermophile Thermotoga maritima. Biochemistry 43, 2228–2240 (2004).
Liu, J.D. & Parkinson, J.S. Genetic evidence for interaction between the CheW and Tsr proteins during chemoreceptor signaling by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 173, 4941–4951 (1991).
Zhou, J. & Parkinson, J.S. Cysteine-scanning analysis of the chemoreceptor-coupling domain of the E. coli chemotaxis signaling kinase CheA. J. Bacteriol. (in the press).
Boukhvalova, M., VanBruggen, R. & Stewart, R.C. CheA kinase and chemoreceptor interactions on CheW. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23596–23603 (2002).
Gegner, J.A., Graham, D.R., Roth, A.F. & Dahlquist, F.W. Assembly of an MCP receptor, CheW, and kinase CheA complex in the bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction pathway. Cell 70, 975–982 (1992).
Levit, M.N. & Stock, J.B. Receptor methylation controls the magnitude of stimulus-response coupling in bacterial chemotaxis. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 36760–36765 (2002).
Li, M. & Hazelbauer, G.L. Cellular stoichiometry of the components of the chemotaxis signaling complex. J. Bacteriol. 186, 3687–3694 (2004).
Li, G. & Weis, R.M. Covalent modification regulates ligand binding to receptor complexes in the chemosensory system of Escherichia coli. Cell 100, 357–365 (2000).
Bornhorst, J.A. & Falke, J.J. Attractant regulation of the aspartate receptor-kinase complex: limited cooperative interactions between receptors and effects of the receptor modification state. Biochemistry 39, 9486–9493 (2000).
Liu, Y., Levit, M., Lurz, R., Surette, M.G. & Stock, J.B. Receptor-mediated protein kinase activation and the mechanism of transmembrane signaling in bacterial chemotaxis. EMBO J. 16, 7231–7240 (1997).
Francis, N.R., Wolanin, P.M., Stock, J.B., Derosier, D.J. & Thomas, D.R. Three-dimensional structure and organization of a receptor/signaling complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 17480–17485 (2004).
Shimizu, T.S. et al. Molecular model of a lattice of signalling proteins involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 792–796 (2000).
Rao, C.V., Frenklach, M. & Arkin, A.P. An allosteric model for transmembrane signaling in bacterial chemotaxis. J. Mol. Biol. 343, 291–303 (2004).
Studdert, C.A. & Parkinson, J.S. Insights into the organization and dynamics of bacterial chemoreceptor clusters through in vivo crosslinking studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15623–15628 (2005).
Levit, M.N., Liu, Y. & Stock, J.B. Mechanism of CheA protein kinase activation in receptor signaling complexes. Biochemistry 38, 6651–6658 (1999).
Otwinowski, A. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–325 (1997).
Brunger, A.T. et al. Crystallography and NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 54, 905–921 (1998).
Borbat, P.P. & Freed, J.H. Multiple-quantum ESR and distance measurements. Chem. Phys. Lett. 313, 145–154 (1999).
Borbat, P.P. & Freed, J.H. in Biological Magnetic Resonance Vol. 21 (eds. Berliner, L.J., Eaton, G.R. & Eaton, S.S.) 383–459 (Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, USA, 2001).
Borbat, P.P., Mchaourab, H.S. & Freed, J.H. Protein structure determination using long-distance constraints from double-quantum coherence ESR: study of T4 lysozyme. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 5304–5314 (2002).
Milov, A.D., Maryasov, A.G. & Tsvetkov, Y.D. Pulsed electron double resonance (PELDOR) and its applications in free-radicals research. Appl. Magn. Reson. 15, 107–143 (1998).
Pfannebecker, V. et al. Determination of end-to-end distances in oligomers by pulsed EPR. J. Phys. Chem. 100, 13428–13432 (1996).
Borbat, P.P., Crepeau, R.H. & Freed, J.H. Multifrequency two-dimensional Fourier transform ESR: an X/Ku-band spectrometer. J. Magn. Reson. 127, 155–167 (1997).
Pake, G.E. Nuclear resonance absorption in hydrated crystale—fine structure of the proton line. J. Chem. Phys. 16, 327–336 (1948).
Chiang, Y.W., Borbat, P.P. & Freed, J.H. The determination of pair distance distributions by pulsed ESR using Tikhonov regularization. J. Magn. Reson. 172, 279–295 (2005).
Glaser, F. et al. ConSurf: identification of functional regions in proteins by surface-mapping of phylogenetic information. Bioinformatics 19, 163–164 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Arango for help with distance-geometry calculations, C. Kim for advice on crystal growth, S. Oga and W. Hubbell for advice on nitroxide spin-labeling, J.S. Parkinson, R. Alexander, I.B. Zhulin and J.J. Falke for helpful discussions and NSLS, CHESS and NE-CAT at the Advanced Photon Source for access to data-collection facilities. This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health grants GM:R01066775 (to B.R.C.) and NCRR:P41-RR016292 (to J.H.F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Initial electron density map for the MCP1143c crystal structure (PDF 1026 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Omit electron density map for the CheAΔ354–CheW crystal structure (PDF 941 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
P4 domain orientations in the CheAΔ354–CheW crystallographic complex (PDF 579 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
The CheA–CheW–MCP array (PDF 424 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, SY., Borbat, P., Gonzalez-Bonet, G. et al. Reconstruction of the chemotaxis receptor–kinase assembly. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 400–407 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1085
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1085
This article is cited by
-
Orientational Selectivity in Pulsed-EPR Does Not Have to be Complicated
Applied Magnetic Resonance (2024)
-
Type 1 Fimbriae and Motility Play a Pivotal Role During Interactions of Salmonella typhimurium with Acanthamoeba castellanii (T4 Genotype)
Current Microbiology (2020)
-
Sequences, Domain Architectures, and Biological Functions of the Serine/Threonine and Histidine Kinases in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2019)
-
An Assessment of the Use of Mesoporous Silica Materials to Improve Pulsed Dipolar Spectroscopy
Applied Magnetic Resonance (2018)
-
Dynamic domain arrangement of CheA-CheY complex regulates bacterial thermotaxis, as revealed by NMR
Scientific Reports (2017)