Abstract
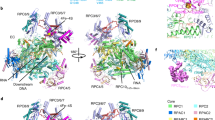
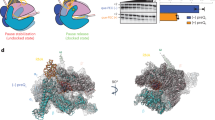
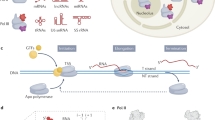
The noncoding RNA B2 and the RNA aptamer FC bind RNA polymerase (Pol) II and inhibit messenger RNA transcription initiation, but not elongation. We report the crystal structure of FC*, the central part of FC RNA, bound to Pol II. FC* RNA forms a double stem-loop structure in the Pol II active center cleft. B2 RNA may bind similarly, as it competes with FC* RNA for Pol II interaction. Both RNA inhibitors apparently prevent the downstream DNA duplex and the template single strand from entering the cleft after DNA melting and thus interfere with open-complex formation. Elongation is not inhibited, as nucleic acids prebound in the cleft would exclude the RNA inhibitors. The structure also indicates that A-form RNA could interact with Pol II similarly to a B-form DNA promoter, as suggested for the bacterial transcription inhibitor 6S RNA.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, T.A., Von Kaenel, S., Goodrich, J.A. & Kugel, J.F. The SINE-encoded mouse B2 RNA represses mRNA transcription in response to heat shock. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11, 816–821 (2004).
Espinoza, C.A., Allen, T.A., Hieb, A.R., Kugel, J.F. & Goodrich, J.A. B2 RNA binds directly to RNA polymerase II to repress transcript synthesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11, 822–829 (2004).
Trotochaud, A.E. & Wassarman, K.M. A highly conserved 6S RNA structure is required for regulation of transcription. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12, 313–319 (2005).
Wassarman, K.M. & Storz, G. 6S RNA regulates E. coli RNA polymerase activity. Cell 101, 613–623 (2000).
Barrick, J.E., Sudarsan, N., Weinberg, Z., Ruzzo, W.L. & Breaker, R.R. 6S RNA is a widespread regulator of eubacterial RNA polymerase that resembles an open promoter. RNA 11, 774–784 (2005).
Thomas, M. et al. Selective targeting and inhibition of yeast RNA polymerase II by RNA aptamers. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 27980–27986 (1997).
Cramer, P., Bushnell, D.A. & Kornberg, R.D. Structural basis of transcription: RNA polymerase II at 2.8 angstrom resolution. Science 292, 1863–1876 (2001).
Westover, K.D., Bushnell, D.A. & Kornberg, R.D. Structural basis of transcription: nucleotide selection by rotation in the RNA polymerase II active center. Cell 119, 481–489 (2004).
Kettenberger, H., Armache, K.-J. & Cramer, P. Complete RNA polymerase II elongation complex structure and its interactions with NTP and TFIIS. Mol. Cell 16, 955–965 (2004).
Rasmussen, E.B. & Lis, J.T. In vitro transcriptional pausing and cap formation on three Drosophila heat shock genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 7923–7927 (1993).
Lis, J. Promoter-associated pausing in promoter architecture and postinitiation transcriptional regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 63, 347–356 (1998).
Chung, W.H. et al. RNA polymerase II/TFIIF structure and conserved organization of the initiation complex. Mol. Cell 12, 1003–1013 (2003).
Murakami, K.S., Masuda, S., Campbell, E.A., Muzzin, O. & Darst, S.A. Structural basis of transcription initiation: an RNA polymerase holoenzyme-DNA complex. Science 296, 1285–1290 (2002).
Armache, K.-J., Kettenberger, H. & Cramer, P. Architecture of the initiation-competent 12-subunit RNA polymerase II. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 6964–6968 (2003).
Chen, H.T. & Hahn, S. Mapping the location of TFIIB within the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex: a model for the structure of the PIC. Cell 119, 169–180 (2004).
Bushnell, D.A. & Kornberg, R.D. Complete RNA polymerase II at 4.1 Å resolution: implications for the initiation of transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 6969–6972 (2003).
Bushnell, D.A., Westover, K.D., Davis, R.E. & Kornberg, R.D. Structural basis of transcription: an RNA polymerase II-TFIIB cocrystal at 4.5 Angstroms. Science 303, 983–988 (2004).
Buratowski, S. & Zhou, H. Functional domains of transcription factor TFIIB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 5633–5637 (1993).
Pardee, T.S., Bangur, C.S. & Ponticelli, A.S. The N-terminal region of yeast TFIIB contains two adjacent functional domains involved in stable RNA polymerase II binding and transcription start site selection. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 17859–17864 (1998).
Kettenberger, H. & Cramer, P. Fluorescence detection of nucleic acids and proteins in multicomponent crystals. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr (in the press).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1996).
Armache, K.-J., Mitterweger, S., Meinhart, A. & Cramer, P. Structures of complete RNA polymerase II and its subcomplex Rpb4/7. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 7131–7134 (2005).
McCoy, A.J., Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W., Storoni, L.C. & Read, R.J. Likelihood-enhanced fast translation functions. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 61, 458–464 (2005).
Brunger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 54, 905–921 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Schulze-Briese and the staff of beamline X06SA at the Swiss Light Source for help. We thank O. Weichenrieder for advice on cloning and in vitro transcription of B2 RNA. M.F. and P.C. are supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the European Union and the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kettenberger, H., Eisenführ, A., Brueckner, F. et al. Structure of an RNA polymerase II–RNA inhibitor complex elucidates transcription regulation by noncoding RNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 44–48 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1032
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1032
This article is cited by
-
Mechanistic insights into chromosome-wide silencing in X inactivation
Human Genetics (2011)
-
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting for aptamer SELEX with cell mixtures
Nature Protocols (2010)
-
Merging the RNA and DNA worlds
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2007)
-
Molecular basis of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase II activity
Nature (2007)
-
Synthetic RNA circuits
Nature Chemical Biology (2007)