Abstract
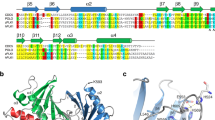
The forkhead-associated (FHA) domain of human Ki67 interacts with the human nucleolar protein hNIFK, recognizing a 44-residue fragment, hNIFK226–269, phosphorylated at Thr234. Here we show that high-affinity binding requires sequential phosphorylation by two kinases, CDK1 and GSK3, yielding pThr238, pThr234 and pSer230. We have determined the solution structure of Ki67FHA in complex with the triply phosphorylated peptide hNIFK226–2693P, revealing not only local recognition of pThr234 but also the extension of the β-sheet of the FHA domain by the addition of a β-strand of hNIFK. The structure of an FHA domain in complex with a biologically relevant binding partner provides insights into ligand specificity and potentially links the cancer marker protein Ki67 to a signaling pathway associated with cell fate specification.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerdes, J., Schwab, U., Lemke, H. & Stein, H. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int. J. Cancer 31, 13–20 (1983).
Gerdes, J. et al. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J. Immunol. 133, 1710–1715 (1984).
Brown, D.C. & Gatter, K.C. Ki67 protein: the immaculate deception? Histopathology 40, 2–11 (2002).
Scholzen, T. & Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J. Cell Physiol. 182, 311–22 (2000).
Schluter, C. et al. The cell proliferation-associated antigen of antibody Ki-67: a very large, ubiquitous nuclear protein with numerous repeated elements, representing a new kind of cell cycle-maintaining proteins. J. Cell Biol. 123, 513–522 (1993).
MacCallum, D.E. & Hall, P.A. The biochemical characterization of the DNA binding activity of pKi67. J. Pathol. 191, 286–298 (2000).
Endl, E. & Gerdes, J. Posttranslational modifications of the KI-67 protein coincide with two major checkpoints during mitosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 182, 371–380 (2000).
Scholzen, T. et al. The Ki-67 protein interacts with members of the heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) family: a potential role in the regulation of higher-order chromatin structure. J. Pathol. 196, 135–144 (2002).
Liao, H., Byeon, I.J. & Tsai, M.D. Structure and function of a new phosphopeptide-binding domain containing the FHA2 of Rad53. J. Mol. Biol. 294, 1041–1049 (1999).
Durocher, D., Henckel, J., Fersht, A.R. & Jackson, S.P. The FHA domain is a modular phosphopeptide recognition motif. Mol. Cell 4, 387–394 (1999).
Durocher, D. et al. The molecular basis of FHA domain:phosphopeptide binding specificity and implications for phospho-dependent signaling mechanisms. Mol. Cell 6, 1169–1182 (2000).
Liao, H. et al. Structure of the FHA1 domain of yeast Rad53 and identification of binding sites for both FHA1 and its target protein Rad9. J. Mol. Biol. 304, 941–951 (2000).
Li, J., Lee, G.I., Van Doren, S.R. & Walker, J.C. The FHA domain mediates phosphoprotein interactions. J. Cell Sci. 113, 4143–4149 (2000).
Lee, G.I., Ding, Z., Walker, J.C. & Van Doren, S.R. NMR structure of the forkhead-associated domain from the Arabidopsis receptor kinase-associated protein phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 11261–11266 (2003).
Schultz, J., Milpetz, F., Bork, P. & Ponting, C.P. SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 5857–5864 (1998).
Sueishi, M., Takagi, M. & Yoneda, Y. The forkhead-associated domain of Ki-67 antigen interacts with the novel kinesin-like protein Hklp2. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 28888–28892 (2000).
Takagi, M., Sueishi, M., Saiwaki, T., Kametaka, A. & Yoneda, Y. A novel nucleolar protein, NIFK, interacts with the forkhead associated domain of Ki-67 antigen in mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 25386–25391 (2001).
Li, H., Byeon, I.J., Ju, Y. & Tsai, M.D. Structure of human Ki67 FHA domain and its binding to a phosphoprotein fragment from hNIFK reveal unique recognition sites and new views to the structural basis of FHA domain functions. J. Mol. Biol. 335, 371–381 (2004).
Pike, B.L., Yongkiettrakul, S., Tsai, M.D. & Heierhorst, J. Mdt1, a novel Rad53 FHA1 domain-interacting protein, modulates DNA damage tolerance and G(2)/M cell cycle progression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 2779–2788 (2004).
Zhao, H., Tanaka, K., Nogochi, E., Nogochi, C. & Russell, P. Replication checkpoint protein Mrc1 is regulated by Rad3 and Tel1 in fission yeast. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 8395–8403 (2003).
Lee, S.J., Schwartz, M.F., Duong, J.K. & Stern, D.F. Rad53 phosphorylation site clusters are important for Rad53 regulation and signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 6300–6314 (2003).
Cerosaletti, K.M. & Concannon, P. Nibrin forkhead-associated domain and breast cancer C-terminal domain are both required for nuclear focus formation and phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 21944–21951 (2003).
Stavridi, E.S. et al. Crystal structure of the FHA domain of the Chfr mitotic checkpoint protein and its complex with tungstate. Structure 10, 891–899 (2002).
Li, J. et al. Structural and functional versatility of the FHA domain in DNA-damage signaling by the tumor suppressor kinase Chk2. Mol. Cell 9, 1045–1054 (2002).
Yuan, C., Yongkiettrakul, S., Byeon, I.J., Zhou, S. & Tsai, M.D. Solution structures of two FHA1-phosphothreonine peptide complexes provide insight into the structural basis of the ligand specificity of FHA1 from yeast Rad53. J. Mol. Biol. 314, 563–575 (2001).
Byeon, I.J., Yongkiettrakul, S. & Tsai, M.D. Solution structure of the yeast Rad53 FHA2 complexed with a phosphothreonine peptide pTXXL: comparison with the structures of FHA2-pYXL and FHA1-pTXXD complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 314, 577–588 (2001).
Skurat, A.V. & Roach, P.J. Phosphorylation of sites 3a and 3b (Ser640 and Ser644) in the control of rabbit muscle glycogen synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 12491–12497 (1995).
Wang, P. et al. II. Structure and specificity of the interaction between the FHA2 domain of Rad53 and phosphotyrosyl peptides. J. Mol. Biol. 302, 927–940 (2000).
Mahajan, A. et al. FHA domain-ligand interactions: importance of integrating chemical and biological approaches. J. Am. Chem. Soc. published online 30 September 2005 (10.1021/ja054538m).
Clore, G.M. & Gronenborn, A.M. Determining the structures of large proteins and protein complexes by NMR. Trends Biotechnol. 16, 22–34 (1998).
Bax, A. & Grzesiek, S. Methodological advances in protein NMR. Acc. Chem. Res. 26, 131–138 (1993).
Lee, W., Revington, M.J., Arrowsmith, C. & Kay, L.E. A pulsed field gradient isotope-filtered 3D 13C HMQC-NOESY experiment for extracting intermolecular NOE contacts in molecular complexes. FEBS Lett. 350, 87–90 (1994).
Ikura, M. & Bax, A. Isotope-filtered 2D NMR of a protein–peptide complex: study of a skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase fragment bound to calmodulin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114, 2433–2440 (1992).
Delaglio, F. et al. NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J. Biomol. NMR 6, 277–293 (1995).
Garrett, D.S., Powers, R., Gronenborn, A.M. & Clore, G.M.A. Common-sense approach to peak picking in 2-dimensional, 3-dimensional, and 4-dimensional spectra using automatic computer-analysis of contour diagrams. J. Magn. Reson. 95, 214–220 (1991).
Cornilescu, G., Delaglio, F. & Bax, A. Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J. Biomol. NMR 13, 289–302 (1999).
Bax, A. et al. Measurement of homo- and heteronuclear J couplings from quantitative J correlation. Methods Enzymol. 239, 79–105 (1994).
Ottiger, M., Delaglio, F. & Bax, A. Measurement of J and dipolar couplings from simplified two-dimensional NMR spectra. J. Magn. Reson. 131, 373–378 (1998).
Schwieters, C.D., Kuszewski, J.J., Tjandra, N. & Clore, G.M. The XPLOR-NIH NMR molecular structure determination package. J. Magn. Reson. 160, 65–73 (2003).
Brünger, A.T. X-PLOR: a System for X-ray Crystallography and NMR, xvii, 382 (Yale University Press, New Haven, Connecticut, 1992).
Koradi, R., Billeter, M. & Wuthrich, K. MolMol: a program for display and analysis of macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Graph 14, 29–32, 51–55 (1996).
Laskowski, R.A., Rullmann, J.A.C., MacArthur, M.W., Kaptein, R. & Thornton, J.M. AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J. Biomol. NMR 8, 477–486 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank Y. Yoneda (Osaka University, Osaka, Japan) for providing the hNIFK gene. This work was supported by NIH grants CA87031 and CA69472, by the Genomics Research Center, Taiwan (M.-D.T.) and the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, and in part by the Intramural AIDS Targeted Antiviral Program of the Office of the Director (A.M.G.). We thank D. Garrett and F. Delaglio for software, J. Baber for technical support, the MS and Proteomics Facility of OSU for MS analyses and D. Vandre of OSU for help in growing HeLa cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Phosphorylation by cell lysate supports biological relevance. (PDF 220 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Binding of hNIFK(226-269) to Ki67FHA probed by 31P NMR spectroscopy. (PDF 57 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Titration of Ki67FHA with the hNIFK(260-266) heptapeptide. (PDF 78 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Influence of proline residues on the phosphorylation of hNIFK(226-269). (PDF 58 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Byeon, IJ., Li, H., Song, H. et al. Sequential phosphorylation and multisite interactions characterize specific target recognition by the FHA domain of Ki67. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12, 987–993 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1008
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1008
This article is cited by
-
The Greatwall kinase safeguards the genome integrity by affecting the kinome activity in mitosis
Oncogene (2020)
-
Augmented expression of Ki-67 is correlated with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis for lung cancer patients: an up-dated systematic review and meta-analysis with 108 studies and 14,732 patients
Respiratory Research (2018)
-
TRIB2 regulates normal and stress-induced thymocyte proliferation
Cell Discovery (2016)
-
The unique role of the hepatitis virus B X protein on HEK 293 cell morphology and cellular change
Archives of Virology (2016)
-
Cell signaling, post-translational protein modifications and NMR spectroscopy
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2012)