Abstract
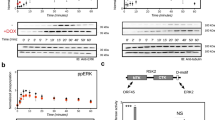
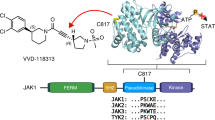
The V617F mutation in the Jak2 pseudokinase domain causes myeloproliferative neoplasms, and the equivalent mutation in Jak1 (V658F) is found in T-cell leukemias. Crystal structures of wild-type and V658F-mutant human Jak1 pseudokinase reveal a conformational switch that remodels a linker segment encoded by exon 12, which is also a site of mutations in Jak2. This switch is required for V617F-mediated Jak2 activation and possibly for physiologic Jak activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, S.J., Rane, S.G. & Reddy, E.P. Oncogene 26, 6724–6737 (2007).
Ghoreschi, K., Laurence, A. & O'Shea, J.J. Immunol. Rev. 228, 273–287 (2009).
Saharinen, P., Takaluoma, K. & Silvennoinen, O. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 3387–3395 (2000).
Ihle, J.N. & Gilliland, D.G. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 17, 8–14 (2007).
Haan, C., Behrmann, I. & Haan, S. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 14, 504–527 (2010).
James, C. et al. Nature 434, 1144–1148 (2005).
Kralovics, R. et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1779–1790 (2005).
Levine, R.L. et al. Cancer Cell 7, 387–397 (2005).
Baxter, E.J. et al. Lancet 365, 1054–1061 (2005).
Tefferi, A. & Vainchenker, W. J. Clin. Oncol. 29, 573–582 (2011).
Jeong, E.G. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 14, 3716–3721 (2008).
Staerk, J., Kallin, A., Demoulin, J.B., Vainchenker, W. & Constantinescu, S.N. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 41893–41899 (2005).
Scott, L.M. Am. J. Hematol. 86, 668–676 (2011).
Scott, L.M. et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 356, 459–468 (2007).
Bandaranayake, R.M. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 19, 754–759 (2012).
Wernig, G. et al. Blood 111, 3751–3759 (2008).
Gnanasambandan, K., Magis, A. & Sayeski, P.P. Biochemistry 49, 9972–9984 (2010).
Dusa, A., Mouton, C., Pecquet, C., Herman, M. & Constantinescu, S.N. PLoS ONE 5, e11157 (2010).
Zhao, L. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 26988–26998 (2009).
Ungureanu, D. et al. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 971–976 (2011).
Valiev, M., Yang, J., Adams, J.A., Taylor, S.S. & Weare, J.H. J. Phys. Chem. B 111, 13455–13464 (2007).
Flex, E. et al. J. Exp. Med. 205, 751–758 (2008).
Bercovich, D. et al. Lancet 372, 1484–1492 (2008).
Mullighan, C.G. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 9414–9418 (2009).
Kearney, L. et al. Blood 113, 646–648 (2009).
Ashkenazy, H., Erez, E., Martz, E., Pupko, T. & Ben-Tal, N. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, W529–W33 (2010).
Jin, J. & Pawson, T. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 367, 2540–2555 (2012).
Pawson, T. & Kofler, M. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 21, 147–153 (2009).
Manning, G., Whyte, D.B., Martinez, R., Hunter, T. & Sudarsanam, S. Science 298, 1912–1934 (2002).
Zhang, Z. & Marshall, A.G. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 9, 225–233 (1998).
Deshpande, A. et al. Leukemia 26, 708–715 (2011).
Acknowledgements
We thank beamline personnel at the Macromolecular Crystallography Resource at the Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (MacCHESS) and the Northeast Collaborative Access Team at the Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory (NE-CAT) for assistance with data collection and processing. We thank K. Arnett for generous help with Jak1 autophosphorylation experiments. MacCHESS and NE-CAT are supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH). This work was supported in part by NIH grant CA134660 (M.S.) and NIH training grants GM008313 (J.M.R.) and CA936132 (R.M.), and by funding from Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research (M.J.E.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.V.T., A.D., R.M. and J.M.R. designed and performed experiments and analyzed data. Y.J. carried out experiments. S.M.G. and C.U.K. contributed pressure cryocooling, and S.B.F. and J.A.M. contributed MS analysis. A.V.T., R.M., M.S., J.D.G. and M.J.E. designed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J.D.G. and M.J.E. are consultants for and receive research support from Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 2312 kb)
Supplementary Data Set 1
Consurf alignment (PDF 1856 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toms, A., Deshpande, A., McNally, R. et al. Structure of a pseudokinase-domain switch that controls oncogenic activation of Jak kinases. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20, 1221–1223 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2673
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2673
This article is cited by
-
Chromosome 21 gain is dispensable for transient myeloproliferative disorder driven by a novel GATA1 mutation
Leukemia (2020)
-
Prospects for pharmacological targeting of pseudokinases
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2019)
-
Are peptides a solution for the treatment of hyperactivated JAK3 pathways?
Inflammopharmacology (2019)
-
Rethinking JAK2 inhibition: towards novel strategies of more specific and versatile janus kinase inhibition
Leukemia (2017)
-
Mechanisms and consequences of Jak–STAT signaling in the immune system
Nature Immunology (2017)