Abstract
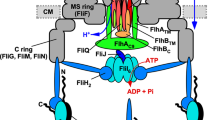
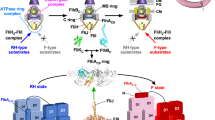
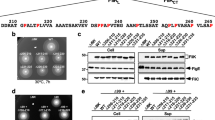
The proteins that form the bacterial flagellum are translocated to its distal end through the central channel of the growing flagellum by the flagellar-specific protein export apparatus, a family of the type III protein secretion system. FliI and FliJ are soluble components of this apparatus. FliI is an ATPase that has extensive structural similarity to the α and β subunits of FoF1-ATP synthase. FliJ is essential for export, but its function remains obscure. Here we show that the structure of FliJ derived from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is remarkably similar to that of the two-stranded α-helical coiled-coil part of the γ subunit of FoF1-ATP synthase and that FliJ promotes the formation of FliI hexamer rings by binding to the center of the ring. These results suggest that the type III protein export system and F- and V-type ATPases share a similar mechanism and an evolutionary relationship.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Minamino, T., Imada, K. & Namba, K. Mechanisms of type III protein export for bacterial flagellar assembly. Mol. Biosyst. 4, 1105–1115 (2008).
Macnab, R.M. How bacteria assemble flagella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57, 77–100 (2003).
Minamino, T. & Macnab, R.M. Components of the Salmonella flagellar export apparatus and classification of export substrates. J. Bacteriol. 181, 1388–1394 (1999).
Minamino, T. & Namba, K. Distinct roles of the FliI ATPase and proton motive force in bacterial flagellar protein export. Nature 451, 485–488 (2008).
Paul, K., Erhardt, M., Hirano, T., Blair, D.F. & Hughes, K.T. Energy source of flagellar type III secretion. Nature 451, 489–492 (2008).
Minamino, T., Yoshimura, S.D.J., Morimoto, Y.V., González-Pedrajo, B., Kami-ike, N. & Namba, K. Roles of the extreme N-terminal region of FliH for efficient localization of the FliH-FliI complex to the bacterial flagellar type III export apparatus. Mol. Microbiol. 74, 1471–1483 (2009).
Vogler, A.P., Homma, M., Irikura, V.M. & Macnab, R.M. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in flagellar filament regrowth and sequence similarity of FliI to F0F1, vacuolar, and archaebacterial ATPase subunits. J. Bacteriol. 173, 3564–3572 (1991).
Fan, F. & Macnab, R.M. Enzymatic characterization of FliI: an ATPase involved in flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 31981–31988 (1996).
Imada, K., Minamino, T., Tahara, A. & Namba, K. Structural similarity between the flagellar type III ATPase FliI and F1-ATPase subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 485–490 (2007).
Claret, L., Susannah, C.R., Higgins, M. & Hughes, C. Oligomerisation and activation of the FliI ATPase central to bacterial flagellum assembly. Mol. Microbiol. 48, 1349–1355 (2003).
Minamino, T. et al. Oligomerization of the bacterial flagellar ATPase FliI is controlled by its extreme N-terminal region. J. Mol. Biol. 360, 510–519 (2006).
Minamino, T. & Macnab, R.M. FliH, a soluble component of the type III flagellar export apparatus of Salmonella, forms a complex with FliI and inhibits its ATPase activity. Mol. Microbiol. 37, 1494–1503 (2000).
Lane, M.C., O'Toole, P.W. & Moore, S.A. Molecular basis of the interaction between the flagellar export proteins FliH and FliI from Helicobacter pylori. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 508–517 (2006).
Minamino, T., González-Pedrajo, B., Kihara, M., Namba, K. & Macnab, R.M. The ATPase FliI can interact with the type III flagellar protein export apparatus in the absence of its regulator FliH. J. Bacteriol. 185, 3983–3988 (2003).
Minamino, T., Chu, R., Yamaguchi, S. & Macnab, R.M. Role of FliJ in flagellar protein export in Salmonella. J. Bacteriol. 182, 4207–4215 (2000).
Minamino, T. & Macnab, R.M. Interactions among components of the Salmonella flagellar export apparatus and its substrates. Mol. Microbiol. 35, 1052–1064 (2000).
Fraser, G.M., González-Pedrajo, B., Tame, J.R. & Macnab, R.M. Interactions of FliJ with the Salmonella type III flagellar export apparatus. J. Bacteriol. 185, 5546–5554 (2003).
González-Pedrajo, B., Minamino, T., Kihara, M. & Namba, K. Interactions between C ring proteins and export apparatus components: a possible mechanism for facilitating type III protein export. Mol. Microbiol. 60, 984–998 (2006).
Evans, L.D., Stafford, G.P., Ahmed, S., Fraser, G.M. & Hughes, C. An escort mechanism for cycling of export chaperones during flagellum assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 17474–17479 (2006).
Imada, K., Minamino, T., Kinoshita, M., Furukawa, Y. & Namba, K. Structural insight into the regulatory mechanisms of interactions of the flagellar type III chaperone FliT with its binding partners. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 8812–8817 (2010).
Bange, G. et al. FlhA provides the adaptor for coordinated delivery of late flagella building blocks to the type III secretion system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 11295–11300 (2010).
Saijo-Hamano, Y. et al. Structure of the cytoplasmic domain of FlhA and implication for flagellar type III protein export. Mol. Microbiol. 76, 260–268 (2010).
Ibuki, T., Shimada, M., Minamino, T., Namba, K. & Imada, K. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of FliJ, a cytoplasmic component of the flagellar type III protein-export apparatus from Salmonella sp. Acta Crystallogr. F65, 47–50 (2009).
Holm, L., Kääriäinen, S., Rosenström, P. & Schenkel, A. Searching protein structure databases with DaliLite v.3. Bioinformatics 23, 2780–2781 (2008).
Abrahams, J.P., Leslie, A.G., Lutter, R. & Walker, J.E. Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature 370, 621–628 (1994).
Gibbons, C., Montgomery, M.G., Leslie, A.G. & Walker, J.E. The structure of the central stalk in bovine F1-ATPase at 2.4 Å resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7, 1055–1061 (2000).
Numoto, N., Hasegawa, Y., Takeda, K. & Miki, K. Inter-subunit interaction and quaternary rearrangement defined by the central stalk of prokaryotic V1-ATPase. EMBO Rep. 10, 1228–1234 (2009).
Kazetani, K., Minamino, T., Miyata, T., Kato, T. & Namba, K. ATP-induced FliI hexamerization facilitates bacterial flagellar protein export. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 388, 323–327 (2009).
Pallen, M.J., Bailey, C.M. & Beatson, S.A. Evolutionary links between FliH/YscL-like proteins from bacterial type III secretion systems and second-stalk components of the FoF1 and vacuolar ATPases. Protein Sci. 15, 935–941 (2006).
Yoshida, M., Muneyuki, E. & Hisabori, T. ATP synthase—a marvellous rotary engine of the cell. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 669–677 (2001).
Noji, H., Yasuda, T., Yoshida, M. & Kinoshita, K. Direct observation of the rotation of F1-ATPase. Nature 386, 299–302 (1997).
Zarivach, R., Vuckovic, M., Deng, W., Finlay, B.B. & Strynadka, N.C.J. Structural analysis of a prototypical ATPase from the type III secretion system. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 131–137 (2007).
Lorenzini, E. et al. Structure and protein-protein interaction studies on Chlamydia trachomatis protein CT670 (YscO homolog). J. Bacteriol. 192, 2746–2756 (2010).
Payne, P.L. & Straley, S.C. YscO of Yersinia pestis is a mobile core component of the Yop secretion system. J. Bacteriol. 180, 3882–3890 (1998).
Stock, D., Leslie, A.G.W. & Walker, J.E. Molecular architecture of the rotary motor in ATP synthase. Science 286, 1700–1705 (1999).
Ashkenazy, H., Erez, E., Martz, E., Pupko, T. & Ben-Tal, N. ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, W529–W533 (2010).
Leslie, A.G.W. Joint CCP4 and ESFEACMB newsletter on protein. Protein Crystallogr 26, 27–33 (1992).
Collaborative Computational Project. Number 4, The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760–763 (1994).
Terwilliger, T.C. & Berendzen, J. Automated MAD and MIR structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D55, 849–861 (1999).
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D60, 2126–2132 (2004).
Brünger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D54, 905–921 (1998).
Ludtke, S.J., Baldwin, P.R. & Chiu, W. EMAN: Semiautomated software for high-resolution single-particle reconstructions. J. Struct. Biol. 128, 82–97 (1999).
Ludtke, S.J. & Chiu, W. Focal pair merging for contrast enhancement of single particles. J. Struct. Biol. 144, 73–78 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Shimada and K. Kazetani for technical assistance and N. Shimizu, M. Kawamoto and K. Hasegawa at SPring-8 for technical help in use of beamlines. T.I. is a research fellow of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (18074006 to K.I., 22570161 to T. Minamino and 16087207 and 21227006 to K.N.) and the Targeted Proteins Research Program (TPRP) from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.I. prepared samples and carried out crystallization and X-ray structure analysis. K.I. helped and supervised T.I. in X-ray crystallography. T. Minamino prepared protein expression constructs and carried out pulldown assays. T.K. helped and supervised T.I. in cryo-EM image analysis. T. Miyata collected cryo-EM images. K.N. supervised the whole project. T.I., K.I., T. Minamino and K.N. wrote the paper based on discussions with T.K. and T. Miyata.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figure 1 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 319 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibuki, T., Imada, K., Minamino, T. et al. Common architecture of the flagellar type III protein export apparatus and F- and V-type ATPases. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18, 277–282 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1977
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1977
This article is cited by
-
Orf1B controls secretion of T3SS proteins and contributes to Edwardsiella piscicida adhesion to epithelial cells
Veterinary Research (2022)
-
The holobiont transcriptome of teneral tsetse fly species of varying vector competence
BMC Genomics (2021)
-
A positive charge region of Salmonella FliI is required for ATPase formation and efficient flagellar protein export
Communications Biology (2021)
-
FliI6-FliJ molecular motor assists with unfolding in the type III secretion export apparatus
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Novel insights into the mechanism of well-ordered assembly of bacterial flagellar proteins in Salmonella
Scientific Reports (2018)