Abstract
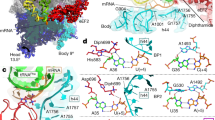
One key question in protein biosynthesis is how the ribosome couples mRNA and tRNA movements to prevent disruption of weak codon-anticodon interactions and loss of the translational reading frame during translocation. Here we report the complete path of mRNA on the 70S ribosome at the atomic level (3.1-Å resolution), and we show that one of the conformational rearrangements that occurs upon transition from initiation to elongation is a narrowing of the downstream mRNA tunnel. This rearrangement triggers formation of a network of interactions between the mRNA downstream of the A-site codon and the elongating ribosome. Our data elucidate the mechanism by which hypermodified nucleoside 2-methylthio-N6 isopentenyl adenosine at position 37 (ms2i6A37) in tRNAPheGAA stabilizes mRNA-tRNA interactions in all three tRNA binding sites. Another network of contacts is formed between this tRNA modification and ribosomal elements surrounding the mRNA E/P kink, resulting in the anchoring of P-site tRNA. These data allow rationalization of how modification deficiencies of ms2i6A37 in tRNAs may lead to shifts of the translational reading frame.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurland, C.G., Hughes, D. & Ehrenberg, M. Limitation of translation accuracy. in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Cellular and Molecular Biology (ed. Neidhardt, F.C.) 979–1004 (American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, 1996).
Jorgensen, F. & Kurland, C.G. Processivity errors of gene expression in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 511–521 (1990).
Bouadloun, F., Srichaiyo, T., Isaksson, L.A. & Bjork, G.R. Influence of modification next to the anticodon in tRNA on codon context sensitivity of translational suppression and accuracy. J. Bacteriol. 166, 1022–1027 (1986).
Konevega, A.L., Soboleva, N.G., Makhno, V.I., Peshekhonov, A.V. & Katunin, V.I. The effect of modification of tRNA nucleotide-37 on the tRNA interaction with the P- and A-site of the 70S ribosome Escherichia coli. Mol. Biol. (Mosk.) 40, 669–683 (2006).
Urbonavicius, J., Qian, Q., Durand, J.M., Hagervall, T.G. & Bjork, G.R. Improvement of reading frame maintenance is a common function for several tRNA modifications. EMBO J. 20, 4863–4873 (2001).
Gustilo, E.M., Vendeix, F.A. & Agris, P.F. tRNA's modifications bring order to gene expression. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 11, 134–140 (2008).
Rozenski, J., Crain, P.F. & McCloskey, J.A. The RNA modification database: 1999 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 196–197 (1999).
Murphy, F.V. IV, Ramakrishnan, V., Malkiewicz, A. & Agris,, P.F. The role of modifications in codon discrimination by tRNA(Lys)UUU. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11, 1186–1191 (2004).
Weixlbaumer, A. et al. Mechanism for expanding the decoding capacity of transfer RNAs by modification of uridines. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 498–502 (2007).
Vacher, J., Grosjean, H., Houssier, C. & Buckingham, R.H. The effect of point mutations affecting Escherichia coli tryptophan tRNA on anticodon-anticodon interactions and on UGA suppression. J. Mol. Biol. 177, 329–342 (1984).
Yanofsky, C. Mutations affecting tRNATrp and its charging and their effect on regulation of transcription termination at the attenuator of the tryptophan operon. J. Mol. Biol. 113, 663–677 (1977).
Petrullo, L.A., Gallagher, P.J. & Elseviers, D. The role of 2-methylthio-N6-isopentenyladenosine in readthrough and suppression of nonsense codons in Escherichia coli. Mol. Gen. Genet. 190, 289–294 (1983).
Wilson, R.K. & Roe, B.A. Presence of the hypermodified nucleotide N6-(δ 2-isopentenyl)-2-methylthioadenosine prevents codon misreading by Escherichia coli phenylalanyl-transfer RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 409–413 (1989).
Urbonavicius, J. et al. Transfer RNA modifications that alter +1 frameshifting in general fail to affect −1 frameshifting. RNA 9, 760–768 (2003).
Yusupov, M.M. et al. Crystal structure of the ribosome at 5.5 Å resolution. Science 292, 883–896 (2001).
Korostelev, A., Trakhanov, S., Laurberg, M. & Noller, H.F. Crystal structure of a 70S ribosome-tRNA complex reveals functional interactions and rearrangements. Cell 126, 1065–1077 (2006).
Selmer, M. et al. Structure of the 70S ribosome complexed with mRNA and tRNA. Science 313, 1935–1942 (2006).
Ogle, J.M. et al. Recognition of cognate transfer RNA by the 30S ribosomal subunit. Science 292, 897–902 (2001).
Yusupova, G.Z., Yusupov, M.M., Cate, J.H. & Noller, H.F. The path of messenger RNA through the ribosome. Cell 106, 233–241 (2001).
Jenner, L. et al. Translational operator of mRNA on the ribosome: how repressor proteins exclude ribosome binding. Science 308, 120–123 (2005).
Yusupova, G., Jenner, L., Rees, B., Moras, D. & Yusupov, M. Structural basis for messenger RNA movement on the ribosome. Nature 444, 391–394 (2006).
Gogia, Z.V., Yusupov, M.M. & Spirina, T.N. Structure of Thermus thermophilus ribosomes. Method of isolation and purification of the ribosomes. Molekul. Biol. 20, 519–526 (1986).
Jukes, T.H. Possibilities for the evolution of the genetic code from a preceding form. Nature 246, 22–26 (1973).
Jenner, L., Rees, B., Yusupov, M. & Yusupova, G. Messenger RNA conformations in the ribosomal E site revealed by X-ray crystallography. EMBO Rep. 8, 846–850 (2007).
Lill, R. & Wintermeyer, W. Destabilization of codon-anticodon interaction in the ribosomal exit site. J. Mol. Biol. 196, 137–148 (1987).
Shine, J. & Dalgarno, L. The 3′-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71, 1342–1346 (1974).
Weixlbaumer, A. et al. Crystal structure of the ribosome recycling factor bound to the ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 733–737 (2007).
Weixlbaumer, A. et al. Insights into translational termination from the structure of RF2 bound to the ribosome. Science 322, 953–956 (2008).
Laurberg, M. et al. Structural basis for translation termination on the 70S ribosome. Nature 454, 852–857 (2008).
Korostelev, A. et al. Crystal structure of a translation termination complex formed with release factor RF2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 19684–19689 (2008).
Schurr, T., Nadir, E. & Margalit, H. Identification and characterization of E. coli ribosomal binding sites by free energy computation. Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 4019–4023 (1993).
Geigenmuller, U. & Nierhaus, K.H. Significance of the third tRNA binding site, the E site, on E. coli ribosomes for the accuracy of translation: an occupied E site prevents the binding of non-cognate aminoacyl-tRNA to the A site. EMBO J. 9, 4527–4533 (1990).
Menichi, B. & Heyman, T. Study of tyrosine transfer ribonucleic acid modification in relation to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 127, 268–280 (1976).
Hoburg, A., Aschhoff, H.J., Kersten, H., Manderschied, U. & Gassen, H.G. Function of modified nucleosides 7-methylguanosine, ribothymidine, and 2-thiomethyl-N6-(isopentenyl)adenosine in procaryotic transfer ribonucleic acid. J. Bacteriol. 140, 408–414 (1979).
Klein, D.J., Moore, P.B. & Steitz, T.A. The contribution of metal ions to the structural stability of the large ribosomal subunit. RNA 10, 1366–1379 (2004).
Pyle, A.M. Metal ions in the structure and function of RNA. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 7, 679–690 (2002).
Ogle, J.M., Murphy, F.V., Tarry, M.J. & Ramakrishnan, V. Selection of tRNA by the ribosome requires a transition from an open to a closed form. Cell 111, 721–732 (2002).
Valle, M. et al. Locking and unlocking of ribosomal motions. Cell 114, 123–134 (2003).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Domain movements of elongation factor eEF2 and the eukaryotic 80S ribosome facilitate tRNA translocation. EMBO J. 23, 1008–1019 (2004).
Zhang, W., Dunkle, J.A. & Cate, J.H. Structures of the ribosome in intermediate states of ratcheting. Science 325, 1014–1017 (2009).
Kabsch, W. Automatic indexing of rotation diffraction patterns. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 21, 67–72 (1988).
Kabsch, W. Evaluation of single-crystal X-ray diffraction data from a position-sensitive detector. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 21, 916–924 (1988).
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004).
Brunger, A.T. Version 1.2 of the Crystallography and NMR system. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2728–2733 (2007).
Brunger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 54, 905–921 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Schulze-Briese and the staff at the Swiss Light Source, Switzerland, for help during synchrotron X-ray data collection, D. Moras for discussions and scientific support, M. Iskakova for assisting during X-ray data collection, S. Duclaud for technical assistance in ribosome preparation and crystallization as well as the staff of the Structural Biology Department core facility at IGBMC and S. Melnikov for helpful discussions. This work was supported by ANR BLANC07-3_190451 (M.Y.), ANR-07-PCVI-0015-01 (G.Y.) and by the European Commission SPINE2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.B.J. performed ribosome purification, data collection, model building, refinement, data analysis and writing of the manuscript; N.D. performed data collection and model building; G.Y. performed crystallization; G.Y. and M.Y. initiated the project, performed model building and writing of the manuscript and acted as project leaders.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 1681 kb)
Supplementary Movie 1
30S domain closure. This animation shows the 30S subunit domain closure upon transition from the initiation to elongation state. (GIF 2578 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenner, L., Demeshkina, N., Yusupova, G. et al. Structural aspects of messenger RNA reading frame maintenance by the ribosome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17, 555–560 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1790
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1790
This article is cited by
-
mRNA reading frame maintenance during eukaryotic ribosome translocation
Nature (2023)
-
Specific length and structure rather than high thermodynamic stability enable regulatory mRNA stem-loops to pause translation
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Cryo-EM study of an archaeal 30S initiation complex gives insights into evolution of translation initiation
Communications Biology (2020)
-
A steric gate controls P/E hybrid-state formation of tRNA on the ribosome
Nature Communications (2020)
-
ArfB can displace mRNA to rescue stalled ribosomes
Nature Communications (2020)