Abstract
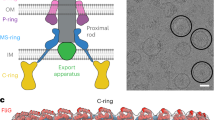
Type III secretion systems (T3SSs) mediate bacterial protein translocation into eukaryotic cells, a process essential for virulence of many Gram-negative pathogens. They are composed of a cytoplasmic secretion machinery and a base that bridges both bacterial membranes, into which a hollow, external needle is embedded. When isolated, the latter two parts are termed the 'needle complex'. An incomplete understanding of the structure of the needle complex has hampered studies of T3SS function. To estimate the stoichiometry of its components, we measured the mass of its subdomains by scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). We determined subunit symmetries by analysis of top and side views within negatively stained samples in low-dose transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Application of 12-fold symmetry allowed generation of a 21–25-Å resolution, three-dimensional reconstruction of the needle complex base, revealing many new features and permitting tentative docking of the crystal structure of EscJ, an inner membrane component.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
Change history
18 May 2009
In the version of this article initially published, the incorrect accession number for EM map deposition was provided. The correct accession number for data deposited in EmDep is EMD-1617. The error has been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions of the article.
References
Blocker, A., Komoriya, K. & Aizawa, S. Type III secretion systems and bacterial flagella: insights into their function from structural similarities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 3027–3030 (2003).
Hale, T.L. Bacilliary dysentery. in Topley and Wilson's Microbiology and Microbial Infections Vol. 3 (ed. Hansler, W.J., & Shuman, M.) 479–493 (Arnold, London, 1998).
Cossart, P. & Sansonetti, P.J. Bacterial invasion: the paradigms of enteroinvasive pathogens. Science 304, 242–248 (2004).
Blocker, A. et al. The tripartite type III secreton of Shigella flexneri inserts IpaB and IpaC into host membranes. J. Cell Biol. 147, 683–693 (1999).
Ghosh, P. Process of protein transport by the type III secretion system. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68, 771–795 (2004).
Veenendaal, A.K. et al. The type III secretion system needle tip complex mediates host cell sensing and translocon insertion. Mol. Microbiol. 63, 1719–1730 (2007).
Kubori, T. et al. Supramolecular structure of the Salmonella typhimurium type III protein secretion system. Science 280, 602–605 (1998).
Blocker, A. et al. Structure and composition of the Shigella flexneri “needle complex”, a part of its type III secreton. Mol. Microbiol. 39, 652–663 (2001).
Cordes, F.S. et al. Helical structure of the needle of the type III secretion system of Shigella flexneri. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 17103–17107 (2003).
Deane, J.E. et al. Molecular model of a type III secretion system needle: implications for host-cell sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12529–12533 (2006).
Cordes, F.S. et al. Helical packing of needles from functionally altered Shigella type III secretion systems. J. Mol. Biol. 354, 206–211 (2005).
Johnson, S. et al. Self-chaperoning of the type III secretion system needle tip proteins IpaD and BipD. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 4035–4044 (2007).
Kenjale, R. et al. The needle component of the type III secreton of Shigella regulates the activity of the secretion apparatus. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 42929–42937 (2005).
Blocker, A.J. et al. What's the point of the type III secretion system needle? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 6507–6513 (2008).
Kimbrough, T.G. & Miller, S.I. Contribution of Salmonella typhimurium type III secretion components to needle complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11008–11013 (2000).
Tamano, K. et al. Supramolecular structure of the Shigella type III secretion machinery: the needle part is changeable in length and essential for delivery of effectors. EMBO J. 19, 3876–3887 (2000).
Allaoui, A. et al. MxiG, a membrane protein required for secretion of Shigella spp. Ipa invasins: involvement in entry into epithelial cells and in intercellular dissemination. Mol. Microbiol. 17, 461–470 (1995).
Allaoui, A., Sansonetti, P.J. & Parsot, C. MxiJ, a lipoprotein involved in secretion of Shigella Ipa invasins, is homologous to YscJ, a secretion factor of the Yersinia Yop proteins. J. Bacteriol. 174, 7661–7669 (1992).
Yip, C.K. et al. Structural characterization of the molecular platform for type III secretion system assembly. Nature 435, 702–707 (2005).
Silva-Herzog, E., Ferracci, F., Jackson, M.W., Joseph, S.S. & Plano, G.V. Membrane localization and topology of the Yersinia pestis YscJ lipoprotein. Microbiology 154, 593–607 (2008).
Burghout, P. et al. Structure and electrophysiological properties of the YscC secretin from the type III secretion system of Yersinia enterocolitica. J. Bacteriol. 186, 4645–4654 (2004).
Allaoui, A., Sansonetti, P.J. & Parsot, C. MxiD, an outer membrane protein necessary for the secretion of the Shigella flexneri lpa invasins. Mol. Microbiol. 7, 59–68 (1993).
Marlovits, T.C. et al. Structural insights into the assembly of the type III secretion needle complex. Science 306, 1040–1042 (2004).
Sani, M. et al. Structural organization of the needle complex of the type III secretion apparatus of Shigella flexneri. Micron 38, 291–301 (2007).
Zenk, S.F., Stabat, D., Veenendaal, A.K.J., Johnson, S. & Blocker, A. Identification of minor inner membrane components of the Shigella T3SS “needle complex”. Microbiology 153, 2405–2415 (2007).
Bayan, N., Guilvout, I. & Pugsley, A.P. Secretins take shape. Mol. Microbiol. 60, 1–4 (2006).
Kocsis, E., Cerritelli, M.E., Trus, B.L., Cheng, N. & Steven, A.C. Improved methods for determination of rotational symmetries in macromolecules. Ultramicroscopy 60, 219–228 (1995).
Thomas, D.R., Francis, N.R., Xu, C. & DeRosier, D.J. The three-dimensional structure of the flagellar rotor from a clockwise-locked mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 188, 7039–7048 (2006).
Chami, M. et al. Structural insights into the secretin PulD and its trypsin-resistant core. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 37732–37741 (2005).
Opalka, N. et al. Structure of the filamentous phage pIV multimer by cryo-electron microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 325, 461–470 (2003).
Collins, R.F., Davidsen, L., Derrick, J.P., Ford, R.C. & Tonjum, T. Analysis of the PilQ secretin from Neisseria meningitidis by transmission electron microscopy reveals a dodecameric quaternary structure. J. Bacteriol. 183, 3825–3832 (2001).
Collins, R.F. et al. Three-dimensional structure of the Neisseria meningitidis secretin PilQ determined from negative-stain transmission electron microscopy. J. Bacteriol. 185, 2611–2617 (2003).
Nouwen, N., Stahlberg, H., Pugsley, A.P. & Engel, A. Domain structure of secretin PulD revealed by limited proteolysis and electron microscopy. EMBO J. 19, 2229–2236 (2000).
Berg, H.C. The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 19–54 (2003).
André, I., Bradley, P., Wang, C. & Baker, D. Prediction of the structure of symmetrical protein assemblies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 17656–17661 (2007).
Kleywegt, G.J. & Jones, T.A. xdlMAPMAN and xdlDATAMAN—programs for reformatting, analysis and manipulation of biomacromolecular electron-density maps and reflection data sets. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 52, 826–828 (1996).
Knutton, S. et al. A novel EspA-associated surface organelle of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli involved in protein translocation into epithelial cells. EMBO J. 17, 2166–2176 (1998).
Macnab, R.M. How bacteria assemble flagella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57, 77–100 (2003).
Burns, R.E., McDaniel-Craig, A. & Sukhan, A. Site-directed mutagenesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system protein PscJ reveals an essential role for surface-localized residues in needle complex function. Microb. Pathog. 45, 225–230 (2008).
Sosinsky, G.E. et al. Mass determination and estimation of subunit stoichiometry of the bacterial hook-basal body flagellar complex of Salmonella typhimurium by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 4801–4805 (1992).
Aizawa, S.I. Bacterial flagella and type III secretion systems. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 202, 157–164 (2001).
Jones, C.J., Macnab, R.M., Okino, H. & Aizawa, S. Stoichiometric analysis of the flagellar hook-(basal-body) complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Mol. Biol. 212, 377–387 (1990).
Nouwen, N. et al. Secretin PulD: association with pilot PulS, structure, and ion-conducting channel formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8173–8177 (1999).
Marlovits, T.C. et al. Assembly of the inner rod determines needle length in the type III secretion injectisome. Nature 441, 637–640 (2006).
Claret, L., Calder, S.R., Higgins, M. & Hughes, C. Oligomerization and activation of the FliI ATPase central to bacterial flagellum assembly. Mol. Microbiol. 48, 1349–1355 (2003).
Imada, K., Minamino, T., Tahara, A. & Namba, K. Structural similarity between the flagellar type III ATPase FliI and F1-ATPase subunits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 485–490 (2007).
Minamino, T. et al. Oligomerization of the bacterial flagellar ATPase FliI is controlled by its extreme N-terminal region. J. Mol. Biol. 360, 510–519 (2006).
Zarivach, R., Vuckovic, M., Deng, W., Finlay, B.B. & Strynadka, N.C. Structural analysis of a prototypical ATPase from the type III secretion system. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 131–137 (2007).
Wall, J.S., Simon, M.N., Lin, B.Y. & Vinogradov, S.N. Mass mapping of large globin complexes by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 436, 487–501 (2008).
Crowther, R.A., Henderson, R. & Smith, J.M. MRC image processing programs. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 9–16 (1996).
van Heel, M., Harauz, G., Orlova, E.V., Schmidt, R. & Schatz, M. A new generation of the IMAGIC image processing system. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 17–24 (1996).
Frank, J. et al. SPIDER and WEB: processing and visualization of images in 3D electron microscopy and related fields. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 190–199 (1996).
Pettersen, E.F. et al. UCSF Chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612 (2004).
Matthews, B.W. Solvent content of protein crystals. J. Mol. Biol. 33, 491–497 (1968).
Vagin, A. & Teplyakov, A. An approach to multi-copy search in molecular replacement. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 56, 1622–1624 (2000).
Moraes, T.F., Spreter, T. & Strynadka, N.C. Piecing together the type III injectisome of bacterial pathogens. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 18, 258–266 (2008).
Chami, M. et al. Structural insights into the secretin PulD and its trypsin-resistant core. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 37732–37741 (2005).
Burghout, P. et al. Structure and electrophysiological properties of the YscC secretin from the type III secretion system of Yersinia enterocolitica. J. Bacteriol. 186, 4645–4654 (2004).
Opalka, N. et al. Structure of the filamentous phage pIV multimer by cryo-electron microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 325, 461–470 (2003).
Collins, R.F., Davidsen, L., Derrick, J.P., Ford, R.C. & Tonjum, T. Analysis of the PilQ secretin from Neisseria meningitidis by transmission electron microscopy reveals a dodecameric quaternary structure. J. Bacteriol. 183, 3825–3832 (2001).
Korotkov, K.V., Pardon, E., Steyaert, J. & Hol, W.G. Crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of the secretin GspD from ETEC determined with the assistance of a nanobody. Structure 17, 255–265 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Lin (Brookhaven) for assistance with STEM sample preparation and P. Roversi (Oxford) for the script to run the program for statistical assessment of docking of atomic structures to EM maps. We are indebted to N. Strynadka and co-workers (British Columbia) for the EscJ ring coordinates and to D. DeRosier (Brandeis) and K. Namba (GSFBS, Osaka) for advice and encouragement at all key stages of this work. They, along with F. Booy (Bristol), S. Daniell (Bristol), A. Veenendaal (Utrecht) and W. Steffen (MHH, Hanover) are also thanked for critical comments on the manuscript. J.L.H. was funded by UK Medical Research Council project grant G0401595 to A.J.B. and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft grant BR 849/29-1 to B. Brenner. A.J.B. was supported by the Guy G. F. Newton Senior Research Fellowship. S.J. was funded by UK Medical Research Council project grant G0400389 to S.M.L. J.S.W.'s laboratory is supported by the US National Institutes of Health and Department of Energy. P.C.A.d.F. and E.P.M. received funding from Cancer Research UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.J.B. and J.L.H. designed the research; D.S. and A.J.B. purified the needle complexes; J.L.H. acquired the negative stain images; M.S. acquired the STEM images; J.S.W. adapted the STEM image analysis programme; J.L.H., A.H. and A.J.B. analyzed data; P.C.A.d.F. and E.P.M. provided advice on image analysis; S.J., J.L.H. and S.M.L. performed the EscJ docking; J.L.H. and A.J.B. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 1337 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodgkinson, J., Horsley, A., Stabat, D. et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the Shigella T3SS transmembrane regions reveals 12-fold symmetry and novel features throughout. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16, 477–485 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1599
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1599
This article is cited by
-
Inhibitory effect of obovatol from Magnolia obovata on the Salmonella type III secretion system
The Journal of Antibiotics (2017)
-
Assembly, structure, function and regulation of type III secretion systems
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2017)
-
The Architecture of the Cytoplasmic Region of Type III Secretion Systems
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Near-atomic-resolution cryo-EM analysis of the Salmonella T3S injectisome basal body
Nature (2016)
-
Secretion systems in Gram-negative bacteria: structural and mechanistic insights
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2015)