Abstract
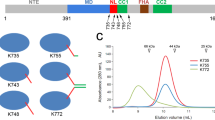
Crystal structures of the molecular motor kinesin show conformational variability in a structural element called the neck linker. Conformational change in the neck linker, initiated by ATP exchange, is thought to drive the movement of kinesin along the microtubule track. We use site-specific EPR measurements to show that when microtubules are absent, the neck linker exists in equilibrium between two structural states (disordered and 'docked'). The active site nucleotide does not control the position taken by the neck linker. However, we find that sulfate can specifically bind near the nucleotide site and stabilize the docked neck linker conformation, which we confirmed by solving a new crystal structure. Comparing the crystal structures of our construct with the docked or undocked neck linker reveals how microtubule binding may activate the nucleotide-sensing mechanism of kinesin, allowing neck linker transitions to power motility.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Goldstein, L.S. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 6999–7003 (2001).
Hirokawa, N. Science 279, 519–526 (1998).
Howard, J. Mechanics of Motor Proteins and the Cytoskeleton (Sinauer Associates, Sunderland; 2001).
Block, S.M. J. Cell. Biol. 140, 1281–1284 (1998).
Woehlke, G. & Schliwa, M. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1, 50–58 (2000).
Rice, S. et al. Nature 402, 778–784 (1999).
Case, R.B., Rice, S., Hart, C.L., Ly, B. & Vale, R.D. Curr. Biol. 10, 157–160 (2000).
Vale, R.D., Case, R., Sablin, E., Hart, C. & Fletterick, R. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 355, 449–457 (2000).
Rosenfeld, S.S., Jefferson, G.M. & King, P.H. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 40167–40174 (2001).
Kull, F.J., Sablin, E.P., Lau, R., Fletterick, R.J. & Vale, R.D. Nature 380, 550–555 (1996).
Kozielski, F. et al. Cell 91, 985–994 (1997).
Sack, S. et al. Biochemistry 36, 16155–16165. (1997).
Sablin, E.P., Kull, F.J., Cooke, R., Vale, R.D. & Fletterick, R.J. Nature 380, 555–559 (1996).
Muller, J., Marx, A., Sack, S., Song, Y.H. & Mandelkow, E. Biol. Chem. 380, 981–992 (1999).
Song, Y.H. et al. EMBO J. 20, 6213–6225 (2001).
Turner, J. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 25496–25502 (2001).
Kikkawa, M. et al. Nature 411, 439–445 (2001).
Xing, J. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 35413–35423 (2000).
Rosenfeld, S.S., Correia, J.J., Xing, J., Rener, B. & Cheung, H.C. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 30212–30221 (1996).
Rosenfeld, S.S., Rener, B., Correia, J.J., Mayo, M.S. & Cheung, H.C. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 9473–9482 (1996).
Vale, R.D. & Milligan, R.A. Science 288, 88–95 (2000).
Sablin, E.P. & Fletterick, R.J. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 11, 716–724 (2001).
Woehlke, G. et al. Cell 90, 207–216 (1997).
Sosa, H. et al. Cell 90, 217–224 (1997).
Baldwin, R.L. Biophys. J. 71, 2056–2063 (1996).
Naber, N., Cooke, R. & Pate, E. Biochemistry 36, 9681–9689 (1997).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Kissinger, C.R., Gehlhaar, D.K. & Fogel, D.B. Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 484–491 (1999).
Berman, H.M. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 235–242 (2000).
Brünger, A.T. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Vriend, G. J. Mol. Graph. 8, 52–56 (1990).
Guex, N. & Peitsch, M.C. Electrophoresis 18, 2714–2723 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to E. Sablin, who provided many insightful comments during the preparation of the manuscript. We also give our thanks to V. Minor for enthusiastic help in the indexing and scaling of diffraction data, and P. Fajer for helpful comments on the EPR analysis. The National Institutes of Health supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sindelar, C., Budny, M., Rice, S. et al. Two conformations in the human kinesin power stroke defined by X-ray crystallography and EPR spectroscopy. Nat Struct Mol Biol 9, 844–848 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb852
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb852
This article is cited by
-
Solution NMR assignments and structure for the dimeric kinesin neck domain
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2023)
-
High-resolution cryo-EM maps show the nucleotide binding pocket of KIF1A in open and closed conformations
The EMBO Journal (2006)