Abstract
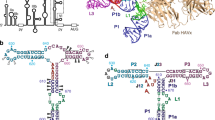
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) internal ribosome entry site (IRES) RNA drives internal initiation of viral protein synthesis during host cell infection. In the tertiary structure of the IRES RNA, two helical junctions create recognition sites for direct binding of the 40S ribosomal subunit and eukaryotic initiation factor 3 (eIF3). The 2.8 Å resolution structure of the IIIabc four-way junction, which is critical for binding eIF3, reveals how junction nucleotides interact with an adjacent helix to position regions directly involved in eIF3 recognition. Two of the emergent helices stack to form a nearly continuous A-form duplex, while stacking of the other two helices is interrupted by the insertion of junction residues into the helix minor groove. This distorted stack probably serves as an important recognition surface for the translational machinery.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pestova, T.V. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 7029–7036 (2001).
Hellen, C.U. & Sarnow, P. Genes Dev. 15, 1593–1612 (2001).
Tsukiyama-Kohara, K., Iizuka, N., Kohara, M. & Nomoto, A. J. Virol. 66, 1476–1483 (1992).
Lemon, S.M. & Honda, M. Semin. Virol. 8, 274–288 (1997).
Pestova, T.V., Shatsky, I.N., Fletcher, S.P., Jackson, R.J. & Hellen, C.U. Genes Dev. 12, 67–83 (1998).
Sizova, D.V., Kolupaeva, V.G., Pestova, T.V., Shatsky, I.N. & Hellen, C.U. J. Virol. 72, 4775–4782 (1998).
Hellen, C.U. & Pestova, T.V. J. Viral. Hepat. 6, 79–87 (1999).
Kolupaeva, V.G., Pestova, T.V. & Hellen, C.U. J. Virol. 74, 6242–6250 (2000).
Kieft, J.S., Zhou, K., Jubin, R. & Doudna, J.A. RNA 7, 194–206 (2001).
Kieft, J.S. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 292, 513–29 (1999).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Science 291, 1959–1962 (2001).
Klinck, R. et al. RNA 6, 1423–1431 (2000).
Lukavsky, P.J., Otto, G.A., Lancaster, A.M., Sarnow, P. & Puglisi, J.D. Nature Struct. Biol. 7, 1105–1110 (2000).
Buratti, E., Tisminetzky, S., Zotti, M. & Baralle, F.E. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 3179–3187 (1998).
Odreman-Macchioli, F.E., Tisminetzky, S.G., Zotti, M., Baralle, F.E. & Buratti, E. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 875–885 (2000).
Baugh, C., Grate, D. & Wilson, C. J. Mol. Biol. 301, 117–128 (2000).
Ban, N., Nissen, P., Hansen, J., Moore, P.B. & Steitz, T.A. Science 289, 905–920 (2000).
Lopez de Quinto, S., Lafuente, E. & Martinez-Salas, E. RNA 7, 1213–1226 (2001).
Ho, P.S. & Eichman, B.F. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 11, 302–308 (2001).
Leulliot, N. & Varani, G. Biochemistry 40, 7947–7956 (2001).
Otwinowski, V. & Minor, W. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Brünger, A. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998)
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Jubin, R. et al. J. Virol. 74, 10430–10437 (2000).
Carson, M. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 958–961 (1991).
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the NSLS X25 beamline staff and the Yale Center for Structural Biology staff for assistance in data collection and processing. We also thank L. Zhang, D.J. Battle and J.M. Murray for assistance in data collection and figure construction (DB), and A.R. Ferré-D'Amaré, R.T. Batey, R.P. Rambo and P.L. Adams for helpful discussions and advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kieft, J., Zhou, K., Grech, A. et al. Crystal structure of an RNA tertiary domain essential to HCV IRES-mediated translation initiation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 9, 370–374 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb781
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb781