Abstract
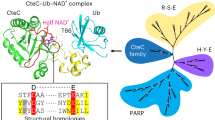
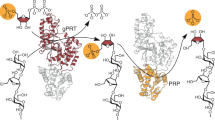
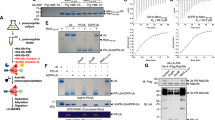
ADP ribosyl cyclase synthesizes the novel secondary messenger cyclic ADP ribose (cADPR) utilizing NAD as a substrate. The enzyme shares extensive sequence similarity with two lymphocyte antigens, CD38 and BST-1, which hydrolyse as well as synthesize cADPR. The crystal structure provides a model for these cell surface enzymes. Cyclase contains two spatially separated pockets composed of sequence conserved residues, suggesting that the cyclization reaction may entail use of distinct sites. The enzyme dimer encloses a cavity which may entrap the intermediate, ADP ribose.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee, H.C. Specific binding of cyclic ADP-ribose to calcium-storing microsomes from sea urchin eggs. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 2276–2281 (1991).
Lee, H.C. Cyclic ADP-ribose: a new member of a super family of signalling cyclic nucleotides. Cell. Signalling 6, 591–600 (1994).
Lee, H.C., Galione, A. & Walseth, T.F. Cyclic ADP-ribose: metabolism and calcium mobilizing function. Vitamins and Hormones 48, 199–258 (1994).
Lee, H.C., Aarhus, R. & Walseth, T.F. Calcium mobilization by dual receptors during fertilization of sea urchin eggs. Science 261, 352–355 (1993).
Lee, H.C., Aarhus, R., Graeff, R., Gurnack, M.E. & Walseth, T.F. Cyclic ADP ribose activation of the ryanodine receptor is mediated by calmodulin. Nature 370, 307–309 (1994).
Hellmich, M.R. & Strumwasser, F. Purification and characterization of a molluscan egg-specific NADase, a second-messenger enzyme. Cell Regul. 2, 193–202 (1991).
Lee, H.C. & Aarhus, R. ADP-ribosyl cyclase: an enzyme that cyclizes NAD+ into a calcium-mobilizing metabolite. Cell Regul. 2, 203–209 (1991).
Galione, A., White, A., Willmott, N., Turner, M., Potter, B.V.L. & Watson, S.P. cGMP mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ in sea urchin eggs by stimulating cyclic ADP-ribose synthesis. Nature 365, 456–459 (1993).
Walseth, T.F. & Lee, H.C. Synthesis and characterization of antagonists of cydic-ADP-ribose-induced Ca2+ release. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1178, 235–242 (1993).
Lee, H.C., Graeff, R. & Walseth, T.F. Cyclic ADP-ribose and its metabolic enzymes. Biochimie 77, 345–355 (1995).
Lee, H.C., Aarhus, R. & Levitt, D. The crystal structure of cyclic ADP–ribose. Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 143–144 (1994).
Howard, M. et al. Formation and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose catalyzed by lymphocyte antigen CD38. Science 262, 1056–1059 (1993).
Takasawa, S. et al. Synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose by human leukocyte antigen CD38 and inhibition of the hydrolysis by ATP. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 26052–26054 (1993).
Lund, F., Solvason, N., Grimaldi, J.C., Parkhouse, R.M.E. & Howard, M. Murine CD38: an immunoregulatory ectoenzyme. Immunol. Today 16, 469–473 (1995).
Kaisho, T. et al. BST-1, a surface molecule of bone marrow stromal cell lines that facilitates pre-B-cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 5325–5329 (1994).
Dong, C., Wang, J., Neame, P. & Cooper, M.D. The murine BP-3 gene encodes a relative of the CD38/NAD glycohydrolase family. Intnatl. Immunol. 6, 1353–1360 (1994).
Itoh, M. et al. Molecular cloning of murine BST-1 having homology with CD38 and Aplysia ADP-ribosyl cyclase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 203, 1309–1317 (1994).
Glick, D.L. et al. Primary structure of a molluscan egg-specific NADase, a second-messenger enzyme. Cell Regulation 2, 211–218 (1991).
States, D.J., Walseth, T.F. & Lee, H.C. Similarities in amino acid sequences of Aplysia ADP-ribosyl cyclase and human lymphocyte antigen CD38. Trends Biochem. Sci. 17, 495 (1992).
Jackson, D.G. & Bell, J.I. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the human CD38 (T10) molecule, a cell surface glycoprotein with an unusual discontinuous pattern of expression during lymphocyte differentiation. J. Immunol. 144, 2811–2815 (1990).
Harada, N. et al. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a novel murine B cell activation marker. J. Immunol. 151, 3111–3118 (1993).
Koguma, T. et al. Cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding rat ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase (homologueto human CD38) from islets of Langerhans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1223, 160–162 (1994).
Li, Q. et al. A cloned rat CD38-homologous protein and its expression in pancreatic islets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 202, 629–636 (1994).
Richardson, J.S. Describing patterns of protein tertiary structure. Meths. Enzymol. 115, 341–358 (1985).
Holm, L. & Sander, C. Families of structurally similar proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 233, 123–138 (1993).
Volz, K. & Matsumura, P. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli CheY refined at 1.7-Å resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 15511–15519 (1991).
Scapin, G., Grubmeyer, C. & Sacchettini, J.C. Crystal structure of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase. Biochem. 33, 1287–1294 (1994).
Czworkowski, J., Wang, J., Steitz, T.A. & Moore, P.B. The crystal structure of elongation factor G complexed with GDP, at 2.7Å resolution. EMBO J. 13, 3661–3668 (1994).
Richardson, J.S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv. Prot. Chem. 34, 167–339 (1981).
Connoly, M.L. Solvent accessible surfaces of proteins and nucleic acids. Science 221, 709–713 (1983).
Nata, K. et al. The structure of the Aplysia kurodai gene encoding ADP-ribosyl cyclase, a second–messenger enzyme. Gene 158, 213–218 (1995).
Leahy, D.J., Axel, R. & Hendrickson, W.A. Crystal structure of a soluble form of the human T cell coreceptor CDS at 2.6 Å resolution. Cell 68, 1145–1162 (1992).
Yeh, J.I., Biemann, H.-P., Pandit, J., Koshland, D.E. & Kim, S.-H. The three-dimensional structure of the ligand-binding domain of a wild-type bacterial chemotaxis receptor: structural comparison to the cross-linked mutant forms and conformational changes upon ligand binding. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 9787–9792 (1993).
Fryxell, K.B., O'Donoghue, K., Graeff, R.M., Lee, H.C. & Branton, W.D. Functional expression of soluble forms of human CD38 in Escherichia coli and Pichia pastoris. Protein Expres. Purif. 6, 329–336 (1995).
Tohgo, A. et al. Essential cysteine residues for cyclic ADP-ribose synthesis and hydrolysis by CD38. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 28555–28557 (1994).
Kim, S.-H. “Frozen” dynamic dimer model for transmembrane signaling in bacterial chemotaxis receptors. Protein Sci. 3, 159–165 (1994).
Flier, J.S. & Underbill, L.H. The tumor necrosis factor ligand and receptorfamilies. New England J. Med. 334, 1717–1725 (1996).
Silvennoinen, O. et al. CD38 signal transduction in human B cell precursors. J. Immunol. 156, 100–107 (1996).
Guida, L., Franco, L., Zocchi, E. & De Flora, A. Structural role of disulfide bridges in the cyclic ADP-ribose related bifunctional ectoenzyme CD38. FEBS Lett. 368, 481–484 (1995).
Grimaldi, J.C. et al. CD38-mediated ribosylation of proteins. J. Immunol. 155, 811–817 (1995).
Armstrong, S.R., Cook, W.J., Short, S.A. & Ealick, S.E. Crystal structures of nucleoside 2-deoxyribosyltransferase in native and ligand-bound forms reveal architecture of the active site. Structure 4, 97–107 (1996).
Bell, C.E. & Eisenberg, D. Crystal structure of diphtheria toxin bound to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Biochemistry 35, 1137–1149 (1996).
Li, M., Dyda, F., Benhar, I., Pastan, I. & Davies, D.R. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of Pseudomonas exotoxin A complexed with a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide analog: Implications for the activation process and for ADP ribosylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 6902–6906 (1996).
Weiss, M.S., Blanke, S.R., Collier, R.J. & Eisenberg, D. Structure of the isolated catalytic domain of diphtheria toxin. Biochemistry 34, 773–781 (1995).
Li, M., Dyda, F., Benhar, I., Pastan, I. & Davies, D.R. The crystal structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin domain III with nicotinamide and AMP: Conformational differences with intact exotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9308–9312 (1995).
Prasad, G.S., Levitt, D.G., Lee, H.C. & Stout, C.D. Crystallization of ADP-ribosyl cyclase from Aplysia californica. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 24, 138–140 (1996).
Howard, A.J., Nielsen, C. & Xuong, Ng.H. Software for diffractometer with multiwire area detector. Meths. Enzymol. 114A, 452–472 (1985).
Leslie, A.G.W. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760–763 (1994).
McRee, D.E. A visual protein crystallographic software system for XII/Xview. J. Molec. Graphics 10, 44–47 (1992).
Cowtan, K. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760–763 (1994).
Levitt, D.G. & Banaszak, L.J. A new routine for thinning, editing and fitting MIR maps using real-space molecular dynamics. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 736–745 (1993).
Kleyweyt, G.L. & Jones, T.A. in From First Map to Final Model (eds S. Bailey, R. Hubbard, D. Waller) 59 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, 1994).
Read, R.J. Improved Fourier coefficients for maps using phases from partial structures with errors. Acta Crystallogr. A42, 140–149 (1986).
Brünger, A.T., Karplus, M. & Petsko, G.A. Crystallographic refinement by simulated annealing: application to crambin. Acta Crystallogr. A45, 50–61 (1989).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A47, 110–119 (1991).
Laskowski, R.A., MacArthur, M.W., Moss, D.S. & Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 283–291 (1993).
Kraulis, P.J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Furuya, Y. et al. Cloning of a cDNA encoding rat bone marrow stromal cell antigen 1 (BST-1) from the islets of Langerhans. Gene 165, 329–330 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, G., McRee, D., Stura, E. et al. Crystal structure of Aplysia ADP ribosyl cyclase, a homologue of the bifunctional ectozyme CD38. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3, 957–964 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1196-957
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1196-957
This article is cited by
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B is a mediator of cyclic ADP ribose-induced Ca2+ signaling in ventricular myocytes
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2017)
-
NQO1-induced activation of AMPK contributes to cancer cell death by oxygen-glucose deprivation
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Cyclic ADP-ribose and NAADP: fraternal twin messengers for calcium signaling
Science China Life Sciences (2011)
-
N-linked glycosylation of CD38 is required for its structure stabilization but not for membrane localization
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2007)
-
The CD38/CD157 mammalian gene family: An evolutionary paradigm for other leukocyte surface enzymes
Purinergic Signalling (2006)