Abstract
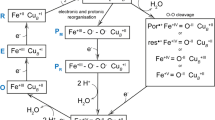
Various enzymes use semi-stable ferryl intermediates and free radicals during their catalytic cycle, amongst them haem catalases. Structures for two transient intermediates (compounds I and II) of the NADPH-dependent catalase from Proteus mirabilis (PMC) have been determined by time-resolved X-ray crystallography and single crystal microspectrophotometry. The results show the formation and transformation of the ferryl group in the haem, and the unexpected binding of an anion during this reaction at a site distant from the haem.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirkman, H.N. & Gaetani, G.F. Catalase: A tetrameric enzyme with four tightly bound molecules of NADPH. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 81, 4343–4347 (1984).
Kirkman, H.N., Galiano, S. & Gaetani, G.F. The function of catalase-bound NADPH. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 660–666 (1987).
Hillar, A. & Nicholls, P. A mechanism for NADPH inhibition of catalase compound II formation. FEBS 314, 179–182 (1992).
Hentze, M.W. Enzymes as RNA-binding proteins: A role for (di)nucleotide-binding domains. Trends Bioch. Sci. 19, 101–103 (1994).
Clerch, L.B. A 3′ untranslated region of catalase mRNA composed of a stem-loop and dinucleotide repeat elements binds a 69-kDa redox-sensitive protein. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 317, 267–274 (1995).
Halliwell, B. & Gutteridge, J.M.C. Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. J. Biochem. 219, 1–14 (1984).
Vuillaume, M. Reduced oxygen species, mutation, induction and cancer initiation. Mut. Res. 186, 43–72 (1987).
Mallery, S.R. et al. Cultured AIDS-related kaposis-sarcoma (AIDS-KS) cells demonstrate impaired bioenergetic adaptation to oxidant challenge. Implication for oxidant stress in AIDS-KS pathogenesis. J. Cell. Bioc. 59, 317–328 (1995).
Deisseroth, A. & Dounce, A.L. Catalase: physical and chemical properties, mechanism of catalysis, and physiological role. Physiol. Rev. 50, 319–375 (1970).
Retey, J. Enzymatic-reaction selectivity by negative catalysis or how do enzymes deal with highly reactive intermediates. Angewandte Chemie 29, 355–361 (1990).
Edwards, S.L., Xuong, N.H., Hamlin, R.C. & Kraut, J. Crystal structure of cytochrome c peroxidase compound I. Biochemistry 26, 1503–1511 (1987).
Fülöp, V. et al. Laue diffraction study on the structure of cytochrome c peroxidase compound I. Structure 2, 201–208 (1994).
Gouet, P., Jouve, H.M. & Dideberg, O. Crystal structure of Proteus mirabilis PR catalase with and without bound NADPH. J. Mol. Biol. 249, 933–954 (1995).
Fita, I., Silva, A.M., Murthy, M.R.N. & Rossmann, M.G. The Refined Structure of Beef Liver Catalase at 2.5 Å Resolution. Acta Cryst. B42, 497–515 (1986).
Hajdu, J. & Andersson, I. Fast X-ray crystallography and time-resolved structures. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomolec. Struct. 22, 467–498 (1993).
Farber, G.K. Laue crystallography - it's show down time. Curr. Biol. 5, 1088–1090 (1995).
Mozzarelli, A. & Rossi, G.L. Proteing Function in the crystal. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 25, 343–365 (1996).
Jones, P. & Middlemiss, D.N. Formation of compound I by the reaction of catalase with peroxoacetic acid. J. Biochem. 130, 411–415 (1972).
Hadfield, A.T. & Hajdu, J. A fast and portable micro-spectrophotometer for time-resolved X-ray diffraction experiments. J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 839–842 (1993).
Jouve, H.M., Gaillard, J. & Pelmont, J. Characterization and spectral properties of Proteus mirabilis PR catalase. Can. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 62, 935–944 (1984).
Sakabe, N. A focusing Weissenberg camera with multi-layer-line screens for macromolecular crystallography. J. App. Cryst. 16, 542–547 (1983).
Sakabe, N. X-ray data collection system for modern protein crystallography with a Weissenberg camera and an imaging plate using synchrotron radiation. Nucl. Instrument. Meths Phys. Res. 448–463 (1991).
Andersson, I., Clifton, I.J., Fülöp, V. & Hajdu, J. High speed high resolution data collection on spinach Rubisco using a Weissenberg camera at the Photon Factory. In Crystallographic Computing 5: From Chemistry to Biology (Eds. D. Moras, A.D. Podjarny & J.C. Thierry) 20–28 (Oxford University Press; 1991).
Hajdu, J. & Andersson, I. Fast Weissenberg data collection as an alternative to the Laue method in kinetic crystallography. In Synchrotron Radiation in Biosciences (ed. B. Chance et al.) 110–116 (Oxford University Press; 1994).
Vainshtein, B.K. et al. Three-dimensional structure of catalase from Penicillium vitale at 2.0 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 188, 49–61 (1986).
Murshudov, G.N. et al. Three-dimensional structure of catalase from Micrococcus lysodeikticus at 1.5 Å resolution. FEBS. 312, 127–131 (1992).
Bravo, J. et al. Crystal structure of catalase HPII from Escherichia coli. Structure 3, 491–502 (1995).
Lardinois, O.M. Reactions of bovine liver catalase with superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxyde. Free Rad. Res. 22, 251–274 (1995).
Sevinc, M.S., Ens, W. & Loewen, P.C. The cysteines of catalase HPII of Escherichia coli, including Cys438 which is blocked, do not have a catalytic role. Eur. J. Biochem. 230, 127–132 (1995).
Murshudov, G.N. et al. Structure of the heme d of Penicillium vitale and Escherichia coli catalases. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 8863–8868 (1996).
Otwinowski, Z. Osciftation data reduction program. In Data collection and processing (eds. Sawyer, L., Isaac, N. & Bailey, S.) 56–62 (SERC, Daresbury Laboratory, UK; 1993).
Brünger, A.T., Kuriyan, J. & Karplus, M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science 235, 458–460 (1987).
Roussel, A. & Cambillau, C. TURBO-FRODO. In Silicon Graphics Geometry Partner Directory (ed. Silicon-Graphics) 77–78 (Silicon Graphics, Mountain View, CA, 1989).
Kraulis, P.J. MOLSCRIPT: a Program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein. J. Appl. Cryst. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Buzy, A. et al. Complete amino acid sequence of Proteus mirabilis PR catalase. Occurrence of a methionine sulfone in the close proximity of the active site. J. Prot. Chem. 14, 59–72 (1995).
Chance, M., Powers, L., Poulos, T. & Chance, B. Cytochrome c peroxidase compound ES is identical with horseradish peroxide compound I in iron-ligand distances. Biochemistry 25, 1266–1270 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gouet, P., Jouve, HM., Williams, P. et al. Ferryl intermediates of catalase captured by time-resolved Weissenberg crystallography and UV-VIS spectroscopy. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3, 951–956 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1196-951
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1196-951
This article is cited by
-
Environmentally benign synthesis of substituted pyrazoles as potent antioxidant agents, characterization and docking studies
Journal of the Iranian Chemical Society (2021)
-
The heat released during catalytic turnover enhances the diffusion of an enzyme
Nature (2015)
-
Human catalase: looking for complete identity
Protein & Cell (2010)
-
Spectroscopic description of an unusual protonated ferryl species in the catalase from Proteus mirabilis and density functional theory calculations on related models. Consequences for the ferryl protonation state in catalase, peroxidase and chloroperoxidase
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2007)
-
Caught in a chemical trap
Nature Structural Biology (1996)