Abstract
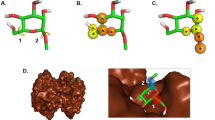
We describe here the use of a rapid computational method to predict the relative binding strengths of a series of small-molecule ligands for the serine proteinase trypsin. Flexible molecular models of the ligands were docked to the proteinase using an all-atom potential set, without cutoff limits for the non-bonded and electrostatic energies. The binding-strength calculation is done directly in terms of a molecular mechanics potential. The binding of eighteen different compounds, including non-binding controls, has been successfully predicted. The measured Ki is correlated with the predicted energy. The correctness of the theoretical calculations is demonstrated with both kinetics measurements and X-ray structure determination of six enzyme-inhibitor complexes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Troll, W. & Kennedy, A.R. Proteinase inhibitors as cancer chemopreventive agents. (Plenum Press, NY, 1993)
Bode, W. & Huber, R. Natural protein proteinase inhibitors and their interaction with proteinases. Eur.J.Biochem 204, 433–452 (1992).
Gettins, P. & Patson, P.A. Structure and mechanism of action of serpins. Hemat. Oncol. Clinics N.America 6, 1393–1408 (1992).
Straatsma, T.P. & McCammon, J.A. Theoretical Calculations of Relative Affinities of Binding. Meth. Enzymol 202, 497–511 (1991).
Kuntz, I.D. Structure-based strategies for drug design and discovery. Science 257, 1078–1082 (1992). Shoichet, B.K. & Kuntz, I.D. Matching chemistry and shape in molecular docking. 6, 723–732 (1993).
Goodford, P.J. A computational procedure for determining energetically favorable binding sites on biologically important macromolecules. J.med.Chem., 28, 849–857 (1985).
Martin, Y. 3D Database searching in drug design J. med. Chem. 35, 2145–2155 (1992).
Harrison, R.W. Stiffness and energy conservation in molecular dynamics. J.comp.Chem., 14, 1112–1122 (1993).
Schreiber, H. & Steinhauser, O. Cutoff Size Does Strongly Influence Molecular Dynamics Results Solvated Polypeptides. Biochemistry 31, 5856–5860 (1992).
Harrison, R.W., Kurinov, I.V. & Andrews, L.C. The Fourier-Green's function and the rapid evaluation of molecular potentials. Prot. Engng., 7, 359–369 (1994).
Bernstein, F.C. et al. The protein data bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J. molec. Biol., 112 535–542 (1977).
Marquart, M., Walter, J., Deisenhofer, J., Bode, W. & Huber, R. The geometry of the reactive site and the peptide groups in trypsin, trypsinogen and its complexes with inhibitors. Acta crystallogr. B39 480 (1983).
Rappe, A.K., Casewit, C.J., Colwell, K.S., Goddard, W.A. III Skiff, W.M. UFF, a full periodic table force field for molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. chem. Soc., 114, 10024–10046 (1992).
Rappe, A.K. & Goddard, W.A., III Charge equilibrium for molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem., 95, 3358–3363 (1991).
Brunger, A.T. X-PLOR (version 3.0) Manual (1992).
Weiner, S.J., Kollman, P.A., Nguyen, D.T. & Case, D.A. (1986) An All Atom Force Field for Simulations of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. J. Comp Chem. 7, 230–252.
Hermans, J., Berendsen, H.J.C., Van Gunsteren, W.F. & Postma, J.P.M. A Consistent Empirical Potential for Water-Protein Interactions. Biopolymers 23, 1513–1518 (1984).
Nose, S. A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J. chem.Phys. 84: 511–519 (1984).
Chambers, J.L. & Stroud, R.M. The accuracy of refined protein structures, comparison of two independently refined models of bovine trypsin. Acta crystallogr. B35 1861– (1979) .
Jones, T.A. A Graphics Model Building and Refinement System for Macromolecules J. Appl. Crystallogr. 11: 268–272 (1978).
Mikes, O., Holeysovsky, V., Tomasek, V. & Sorm, F. Biochem, Biophys Res. Commun. 24 346–352 (1986).
Feynman, R.P. Statistical Mechanics Addison Wesley Frontiers in Physics p66–71 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurinov, I., Harrison, R. Prediction of new serine proteinase inhibitors. Nat Struct Mol Biol 1, 735–743 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1094-735
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1094-735
This article is cited by
-
Sunsetting Binding MOAD with its last data update and the addition of 3D-ligand polypharmacology tools
Scientific Reports (2023)