Abstract
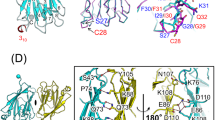
Transcription factor IRF-3 is post-translationally activated by Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling and has critical roles in the regulation of innate immunity. Here we present the X-ray crystal structure of the C-terminal regulatory domain of IRF-3(175–427) (IRF-3 175C) at a resolution of 2.3 Å. IRF-3 175C is structurally similar to the Mad homology domain 2 of the Smad family. Structural and functional analyses reveal phosphorylation-induced IRF-3 dimerization, which generates an extensive acidic pocket responsible for binding with p300/CBP. Although TLR and Smad signaling are evolutionarily independent, our results suggest that IRF-3 originates from Smad and acquires its function downstream of TLR.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Kawai, T. et al. Lipopolysaccharide stimulates the MyD88-independent pathway and results in activation of IFN-regulatory factor 3 and the expression of a subset of lipopolysaccharide-inducible genes. J. Immunol. 167, 5887–5894 (2001).
Doyle, S. et al. IRF3 mediates a TLR3/TLR4-specific antiviral gene program. Immunity 17, 251–263 (2002).
Kaisho, T. & Akira, S. Dendritic-cell function in Toll-like receptor- and MyD88-knockout mice. Trends Immunol. 22, 78–83 (2001).
Mamane, Y. et al. Interferon regulatory factors: the next generation. Gene 237, 1–14 (1999).
Taniguchi, T., Ogasawara, K., Takaoka, A. & Tanaka, N. IRF family of transcription factors as regulators of host defense. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 19, 623–655 (2001).
Alexopoulou, L., Holt, A.C., Medzhitov, R. & Flavell, R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413, 732–738 (2001).
Yoneyama, M., Suhara, W. & Fujita, T. Control of IRF-3 activation by phosphorylation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 22, 73–76 (2002).
Sato, M. et al. Distinct and essential roles of transcription factors IRF-3 and IRF-7 in response to viruses for IFN-α/β gene induction. Immunity 13, 539–548 (2000).
Yoneyama, M. et al. Direct triggering of the type I interferon system by virus infection: activation of a transcription factor complex containing IRF-3 and CBP/p300. EMBO J. 17, 1087–1095 (1998).
Iwamura, T. et al. Induction of IRF-3/-7 kinase and NF-κB in response to double-stranded RNA and virus infection: common and unique pathways. Genes Cells 6, 375–388 (2001).
Marie, I., Durbin, J.E. & Levy, D.E. Differential viral induction of distinct interferon-α genes by positive feedback through interferon regulatory factor-7. EMBO J. 17, 6660–6669 (1998).
Lin, R., Mamane, Y. & Hiscott, J. Structural and functional analysis of interferon regulatory factor 3: localization of the transactivation and autoinhibitory domains. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 2465–2474 (1999).
Holm, L. & Sander, C. Protein structure comparison by alignment of distance matrices. J. Mol. Biol. 233, 123–138 (1993).
Wu, J. et al. Crystal structure of a phosphorylated Smad2. Recognition of phosphoserine by the MH2 domain and insights on Smad function in TGF-β signaling. Mol. Cell 8, 1277–1289 (2001).
Shi, Y., Hata, A., Lo, R.S. & Massague, J. & Pavletich, N.P. A structural basis for mutational inactivation of the tumour suppressor Smad4. Nature 388, 87–93 (1997).
Qin, B., Lam, S.S. & Lin, K. Crystal structure of a transcriptionally active Smad4 fragment. Structure Fold. Des. 7, 1493–1503 (1999).
Suhara, W. et al. Analyses of virus-induced homomeric and heteromeric protein associations between IRF-3 and coactivator CBP/p300. J. Biochem. 128, 301–307 (2000).
Onishi, M. et al. Identification and characterization of a constitutively active STAT5 mutant that promotes cell proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 3871–3879 (1998).
Yang, H. et al. Transcriptional activity of interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-3 depends on multiple protein-protein interactions. Eur. J. Biochem. 269, 6142–6151 (2002).
Sharma, S. et al. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 300, 1148–1151 (2003).
Fitzgerald, K.A. et al. IKKε and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 4, 491–496 (2003).
Lin, C.H. et al. A small domain of CBP/p300 binds diverse proteins: solution structure and functional studies. Mol. Cell 8, 581–590 (2001).
Demarest, S.J. et al. Mutual synergistic folding in recruitment of CBP/p300 by p160 nuclear receptor coactivators. Nature 415, 549–553 (2002).
Qin, B. et al. Crystal structure of IRF-3 transactivation domain: autoinhibition and virus-induced phospho-activation. Nat. Struct. Biol. advance online publication, 12 October 2003 (doi: 10.1038/nsb1002).
Eroshkin, A. & Mushegian, A. Conserved transactivation domain shared by interferon regulatory factors and Smad morphogens. J. Mol. Med. 77, 403–405 (1999).
Durocher, D. et al. The molecular basis of FHA domain:phosphopeptide binding specificity and implications for phospho-dependent signaling mechanisms. Mol. Cell 6, 1169–1182 (2000)
Yasukawa, T. et al. Increase of solubility of foreign proteins in Escherichia coli by coproduction of the bacterial thioredoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 25328–25331 (1995).
Leslie, A.G.W. Mosflm User Guide, Mosflm Version 6.0 (MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK, 1999).
Collaborative Computing Project Number 4. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Brnnger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1991).
Roussel, A. & Cambillau, C. TURBO-FRODO Manual (AFMB-CNRS, Marseille, France, 1996).
Kraulis, P.J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merritt, E.A. & Bacon, J.A. Raster3D: photorealistic molecular graphics. Methods Enzymol. 277, 505–524 (1997).
Jones, T.A., Zhou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins 11, 281–296 (1991).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant-in-aids for CREST of Japan Science and Technology, Scientific Research on Priority Areas and National Project on Protein Structural and Functional Analyses from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan to F.I.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahasi, K., Suzuki, N., Horiuchi, M. et al. X-ray crystal structure of IRF-3 and its functional implications. Nat Struct Mol Biol 10, 922–927 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1001
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb1001
This article is cited by
-
Deactylation by SIRT1 enables liquid–liquid phase separation of IRF3/IRF7 in innate antiviral immunity
Nature Immunology (2022)
-
TOB1 attenuates IRF3-directed antiviral responses by recruiting HDAC8 to specifically suppress IFN-β expression
Communications Biology (2022)
-
Modulation of innate immune response to viruses including SARS-CoV-2 by progesterone
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
IRF3 prevents colorectal tumorigenesis via inhibiting the nuclear translocation of β-catenin
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Vibrio vulnificus quorum-sensing molecule cyclo(Phe-Pro) inhibits RIG-I-mediated antiviral innate immunity
Nature Communications (2018)