Abstract
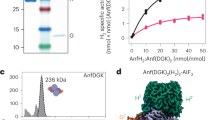
The flavoenzyme ferredoxin–NADP+ reductase (FNR) catalyzes the production of NADPH during photosynthesis. Whereas the structures of FNRs from spinach leaf and a cyanobacterium as well as many of their homologs have been solved, none of these studies has yielded a productive geometry of the flavin–nicotinamide interaction. Here, we show that this failure occurs because nicotinamide binding to wild type FNR involves the energetically unfavorable displacement of the C-terminal Tyr side chain. We used mutants of this residue (Tyr 308) of pea FNR to obtain the structures of productive NADP+ and NADPH complexes. These structures reveal a unique NADP+ binding mode in which the nicotinamide ring is not parallel to the flavin isoalloxazine ring, but lies against it at an angle of ~30°, with the C4 atom 3 Å from the flavin N5 atom.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakaki, A.K., Ceccarelli, E.A. & Carrillo, N. FASEB J. 11, 133– 140 (1997).
Karplus, P.A., Daniels, M.J. & Herriott, J.R. Science 251, 60– 66 (1991).
Bruns, C.M. & Karplus, P.A. J. Mol. Biol. 247, 125–145 (1995).
Serre, L. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 263, 20– 39 (1996).
Correll, C.C., Ludwig, M.L., Bruns, C.M. & Karplus, P.A. Protein Sci. 2, 2112–2133 (1993).
Ingelman, M., Bianchi, V. & Eklund, H. J. Mol. Biol. 268, 147– 157 (1997).
Nishida, H. et al. Biochemistry 34, 2763– 2767 (1995).
Lu, G., Campbell, W.H., Schneider, G. & Lindqvist, Y. Structure (London) 2, 809–821 (1994).
Correll, C.C., Batie, C.J., Ballou, D.P. & Ludwig, M.L. Science 258, 1604–1610 ( 1992).
Wang, M. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 8411– 8416 (1997).
Pai, E., Karplus, P.A. & Schulz, G.E. Biochemistry 27, 4465– 4474 (1988).
Karplus, P.A. & Schulz, G.E. J. Mol. Biol. 210, 163–180 (1989).
Stehle, T., Claiborne, A. & Schulz, G.E. Eur. J. Biochem. 211, 221– 226 (1993).
Li, R., Bianchet, M.A., Talalay, P. & Amzel, L.M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8846– 8850 (1995).
Orellano, E.G., Calcaterra, N.B., Carrillo, N. & Ceccarelli, E.A. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 19267–19273 (1993).
Calcaterra,N.B. et al. Biochemistry 34, 12842– 12848 (1995).
Aliverti, A., Gadda, G., Ronchi, S., and Zanetti, G. Eur. J. Biochem 198, 21–24 ( 1991).
Aliverti, A., Lubberstedt, T., Zanetti, G., Herrmann, R.G., and Curti, B. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 17760–17763 (1991).
Aliverti, A. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 34008– 34016 (1998).
Saenger, W. Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure, Springer-Verlag, New York (1983).
Ammeraal, R.N., Krakow, G. & Vennesland, B. J. Biol. Chem. 240, 1820– 1823 (1965).
Young, L. & Post, C.B. Biochemistry 35, 15129–15133 (1996).
Batie, C.J. & Kamin, H. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 11214–11223 (1986).
Strickland, S., Palmer, G. & Massey, V. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 4048– 4052 (1975).
Batie, C.J. & Kamin, H. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 8832–8839 (1984).
Aliverti, A. et al. Biochemistry 34, 8371– 8379 (1995).
Aliverti, A. et al. Biochemistry 32, 6374– 6380 (1993).
Medina, M., Martinez-Julvez, M. Hurley, J.K., Tollin, G. & Gomez-Moreno, C. Biochemistry 37 , 2715–2728 (1998).
Karplus, P.A. & Bruns, C.M. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 26, 89–99 (1994).
Krauth-Siegel, R.L., Arscott, L.D., Schönleben-Janas, A., Schirmer, R.H. & Williams, C.H., Jr. Biochemistry 37, 13968–13977 (1998).
Serra, E.C., Carrillo, N., Krapp, A.R. & Ceccarelli, E.A. Protein Express. Purif. 4, 539–546 (1993).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 ( 1997).
Leslie, A.G.W. CCP4 and ESF-EACMB Newsletters on Protein Crystallography 26 (1992).
Collaborative Computational Project Number 4, Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760–763 (1994).
Navaza, J. Acta Crystallogr. A50, 157–163 (1994).
Brünger, A.T. X-PLOR, a system for crystallography and NMR, Version 3.1, Yale Univ. Press, New Haven, CT (1992).
Sack, J.S. J. Molec. Graphics 6, 224–225 (1988).
Kraulis, P. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
McRee, D.E. J. Molec. Graphics 10, 44–46 (1992).
Merrit, E.A. & Murphy, M.E.P. Acta Crystallogr. D50, 869–873 (1994).
Diederichs, K. & Karplus, P.A. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 269–275 ( 1997).
Brünger, A.T. Nature 355, 472– 475 (1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Piubelli for performing some of the spectroscopic experiments, S.E. Ealick for the use of his area detector facility, and T.P. Begley and V. Massey for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the NSF to P.A.K., from CONICET and FONCYT (Argentina) to E.A.C., and from MURST to G.Z. N.C. was a recipient of a John Simon Guggenheim Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Z., Aliverti, A., Zanetti, G. et al. A productive NADP+ binding mode of ferredoxin–NADP+ reductase revealed by protein engineering and crystallographic studies. Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 847–853 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/12307
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/12307
This article is cited by
-
Structure of human phagocyte NADPH oxidase in the activated state
Nature (2024)
-
Molecular and functional characterization of ferredoxin NADP(H) oxidoreductase from Gracilaria chilensis and its complex with ferredoxin
Biological Research (2017)
-
Engineering of versatile redox partner fusions that support monooxygenase activity of functionally diverse cytochrome P450s
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Interaction and electron transfer between ferredoxin–NADP+ oxidoreductase and its partners: structural, functional, and physiological implications
Photosynthesis Research (2017)
-
Design and improvement of artificial redox modules by molecular fusion of flavodoxin and flavodoxin reductase from Escherichia coli
Scientific Reports (2015)