Abstract
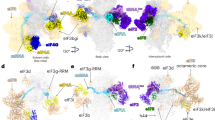
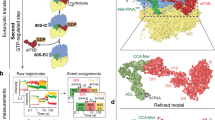
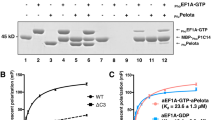
elF4E, the mRNA cap binding protein, is a master switch that controls eukaryotic translation. To be active, it must bind elF4G and form the elF4F complex, which also contains elF4A. Translation is downregulated by association of elF4E with 4E-BP, which occupies the elF4G binding site. Signalling events acting on 4E-BP cause it to dissociate from elF4E, and elF4E is then free to bind elF4G to form the active elF4F complex. We have solved the structure of the yeast elF4E/m7Gpp complex in a CHAPS micelle. We determined the position of the second nucleotide in a complex with m7GpppA, and identified the 4E-BP binding site. elF4E has a curved eight-stranded antiparallel β-sheet, decorated with three helices on the convex face and three smaller helices inserted in connecting loops. The m7G of the cap is intercalated into a stack of tryptophans in the concave face. The 4E-BP binding site is located in a region encompassing one edge of the β-sheet, the adjacent helix a2 and several regions of non-regular secondary structure. It is adjacent to, but does not overlap the cap-binding site.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Merrick, W.C. & Hershey, J.W.B. The pathway and mechanism of eukaryotic protein synthesis. In Translational control (eds Hershey, J.W.B., Mathews, M.B., & Sonenberg, N.) 31–69 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, New York; 1996).
Lamphear, B.J., Kirchweger, R., Skern, T. & Rhoads, R.E. Mapping of functional domains in eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor4G (elF4G) with picornaviral proteases. Implications for cap-dependent and cap-independent translational initiation. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 21975–21983 (1995).
Tarun, S.Z. & Sachs, A.B. Association of the yeast poly(A) tail binding protein with translation initiation factor elF-4G. EMBO J. 15, 7168–7177 (1992).
Haghighat, A., Mader, S., Pause, A. & Sonenberg, N. Repression of cap-dependent translation by 4E-binding protein 1: competition with p220 for binding to eukaryotic initiation factor-4E. EMBO J. 14, 5701–5709 (1995).
Pause, A. et al. Insulin-dependent stimulation of protein synthesis by phosphorylation of a regulator of 5′-cap function. Nature 371, 762–767 (1994).
Sonenberg, N. mRNA 5′cap protein elF4E and control of cell growth. In Translational Control (eds Hershey, J.W.B., Mathews, M.B., & Sonenberg, N.) 245–269 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, New York; 1996).
Lazaris-Karatzas, A., Montine, K.S. & Sonenberg, N. Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5′ cap. Nature 345, 544–547 (1990).
Altmann, M., Mueller, P.P., Pelletier, J., Sonenberg, N. & Trachsel, H. A mammalian translation initiation factor can substitute for its yeast homologue in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 12145–12147 (1989).
Morino, S. et al. Analysis of the mRNA cap-binding ability of human eukaryotic initiation factor-4E by use of recombinant wild-type and mutant forms. Eur. J. Biochem. 239, 597–601 (1996).
Altmann, M., Edery, I., Trachsel, H. & Sonenberg, N. Site-directed mutagenesis of the tryptophan residues in yeast eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Effects on cap binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 17229–17232 (1988).
Vasilescu, S., Ptushkina, M., Linz, B., Muller, P.P. & McCarthy, J.E. Mutants of eukaryotic initiation factor elF4E with altered mRNA cap binding specificity reprogram mRNA selection by ribosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 7030–7037 (1996).
Goyer, C. et al. TIF4631 and TIF4632: Two yeast genes encoding the high-molecular-weight subunits of the cap-binding protein complex (eukaryotic initiation factor 4F) contain an RNA recognition motif-like sequence and carry out an essential function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 4860–4874 (1993).
Altmann, M., Schmitz, N., Berset, C. & Trachsel, H. A novel inhibitor of cap-dependent translation initiation in yeast: p20 competes with elF4G for binding to elF4E. EMBO J. 16, 1114–1121 (1997).
Chattopadhyay, A. & Harikumar, K.G. Dependence of critical micelle concentration of a zwitterionic detergent on ionic strength: implications in receptor solubilization. FEBS Lett. 391, 199–202 (1996)
Walters, K., Matsuo, H. & Wagner, G. Use of deuteration to distinguish intermonomer NOEs in homodimeric proteins with C2 symmetry. J. Am. Chem Soc 119, 5958–5959 (1997).
Rhoads, R.E., Hellmann, G.M., Remy, P. & Ebel, J.-P. Translational recognition of messenger ribonucleic acid caps as a function of pH. Biochemistry 22, 6084–6088 (1983).
Ueda, H. et al. Expression of a synthetic gene for human cap binding protein (Human IF-4E) in Escherichia coli and fluorescence studies on interaction with mRNA cap structure analogues. J. Biochem. 109, 882–889 (1991).
Ishida, T. et al., Specific ring stacking interaction on the tryptophan-7methylguanine system: Comparativecrystallographic studies of indolederivatives-7-methylguanine base, nucleoside, and nucleotide complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 10, 2286–2294 (1988).
Carberry, S.E. et al., A spectroscopic study o the binding of N-7-substituted cap analogues to human protein synthesis initiation factor 4E. Biochemistry, 29, 3337–3341 (1990).
Nagai, K. RNA-protein complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 6, 53–61 (1996).
Hodel, A.E., Gershon, P.O., Shi, X., Wang, S.-M. & Quiocho, F.A. Specific protein recognition of an mRNA cap through its alkylated base. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 350–354 (1997).
Labahn, J. et al. Structural basis for the excision repair of alkylation-damaged DNA. Cell, 86, 321–329 (1996).
Marcotrigiano, J., Gingras, A.-C., Sonenberg, N., Burley, S.K. Cocrystal structure of the messenger RNA 5′ cap-binding protein (elF4E) bound to 7-methyl-GDP. Cell, 89 951–961 (1997).
Edery, I., Altmann, M. & Sonenberg, N. High-level synthesis in Escherichia coli of functional cap-binding eukaryotic initiation factor elF4E and affinity purification using a simplified cap-analog resin. Gene 74, 517–525 (1988).
Whalen, S.G. et al. Phosphorylation of elF4E on serine 209 by protein kinase C is inhibited by the translational repressers, 4E-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem 271, 11831–11837 (1996).
NMR of Proteins (eds Clore, G.M. & Gronenborn, A.M.) (CRC Press, Ann Arbor Michigan;1993).
Bartels, C., Xia, T., Billeter, M. Guntert & Wuthrich, K. The program XEASY for computer-supported NMR specral analysis of biological macromolecules. J. Biomol. NMR, 5, 1–10 (1995).
Dunbrack, R. & Karplus, M. Backbone-dependent rotamer library for proteins. Application to side-chain prediction. J. Mol. Biol. 230, 543–574 (1993).
Nilges, M., Clore, G.M. & Gronenborn, A.M. Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins from interproton distance data by dynamical simulated annealing from a random array of atoms. FEBS Lett., 239, 129–136 (1988).
Brünger, A.T. XPLOR Version 3.1 (Yale University Press, New Haven, Connecticut; 1993).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins, 11, 281–296 (1991).
Laskowski, R.A., MacArthur, M.W., Moss, D.S. & Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J.Appl Crystallogr. 26, 283–291 (1993).
Kraulis, P.J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuo, H., Li, H., McGuire, A. et al. Structure of translation factor elF4E bound to m7GDP and interaction with 4E-binding protein. Nat Struct Mol Biol 4, 717–724 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0997-717
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0997-717
This article is cited by
-
Cap-dependent translation initiation monitored in living cells
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Multiple aromatic amino acids are involved in potyvirus movement by forming π-stackings to maintain coat protein accumulation
Phytopathology Research (2021)
-
Control of the eIF4E activity: structural insights and pharmacological implications
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Non-cooperative 4E-BP2 folding with exchange between eIF4E-binding and binding-incompatible states tunes cap-dependent translation inhibition
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Autophagy inhibition by biotin elicits endoplasmic reticulum stress to differentially regulate adipocyte lipid and protein synthesis
Cell Stress and Chaperones (2019)