Abstract
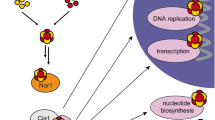
The copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase (CCS) activates the eukaryotic antioxidant enzyme copper, zinc superoxide dismutase (SOD1). The 2.9 Å resolution structure of yeast SOD1 complexed with yeast CCS (yCCS) reveals that SOD1 interacts with its metallochaperone to form a complex comprising one monomer of each protein. The heterodimer interface is remarkably similar to the SOD1 and yCCS homodimer interfaces. Striking conformational rearrangements are observed in both the chaperone and target enzyme upon complex formation, and the functionally essential C-terminal domain of yCCS is well positioned to play a key role in the metal ion transfer mechanism. This domain is linked to SOD1 by an intermolecular disulfide bond that may facilitate or regulate copper delivery.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holm, R.H., Kennepohl, P. & Solomon, E.I. Chem. Rev. 96, 2239–2314 (1996).
Radisky, D. & Kaplan, J. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 4481–4484 (1999).
Rosenzweig, A.C. Acc. Chem. Res. 34, 119–128 (2001).
Rae, T.D., Schmidt, P.J., Pufahl, R.A., Culotta, V.C. & O'Halloran, T.V. Science 284, 805–808 (1999).
McCord, J.M. & Fridovich, I. J. Biol. Chem. 244, 6049–6055 (1969).
Gaudette, M., Hirano, M. & Siddique, T. Amyotroph. Lateral Sc. 1, 83–89 (2000).
Culotta, V.C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 23469–23472 (1997).
Pufahl, R.A. et al. Science 278, 853–856 (1997).
Srinivasan, C., Posewitz, M.C., George, G.N. & Winge, D.R. Biochemistry 37, 7572–7577 (1998).
Bertini, I., Mangani, S. & Viezzoli, M.S. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 45, 127–250 (1997).
Lamb, A.L., Wernimont, A.K., Pufahl, R.A., O'Halloran, T.V. & Rosenzweig, A.C. Nature Struct. Biol. 6, 724–729 (1999).
Lamb, A.L., Wernimont, A.K., Pufahl, R.A., O'Halloran, T.V. & Rosenzweig, A.C. Biochemistry 39, 1589–1595 (2000).
Rosenzweig, A.C. et al. Structure 7, 605–617 (1999).
Schmidt, P.J. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23719–23725 (1999).
Zhu, H. et al. Biochemistry 39, 5413–5421 (2000).
Eisses, J.F., Stasser, J.P., Ralle, M., Kaplan, J.H. & Blackburn, N.J. Biochemistry 39, 7337–7342 (2000).
Lamb, A.L., Torres, A.S., O'Halloran, T.V. & Rosenzweig, A.C. Biochemistry 39, 14720–14727 (2000).
Valentine, J.S. & Pantoliano, M.W. In Copper proteins (ed. Spiro, T.G.) 291–358 (Wiley-Interscience, New York; 1981).
Djinovic, K. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 225, 791–809 (1992).
Schmidt, P.J., Kunst, C. & Culotta, V.C. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 33771–33776 (2000).
Poulos, T.L. Nature Struct. Biol. 6, 709–711 (1999).
Falconi, M., Iovino, M. & Desideri, A. Structure 7, 903–908 (1999).
Hall, L.T. et al. Biochemistry 39, 3611–3623 (2000).
Bordo, D., Djinovic, K. & Bolognesi, M. J. Mol. Biol. 238, 366–386 (1994).
Getzoff, E.D. et al. Nature 306, 287–290 (1983).
Fisher, C.L., Cabelli, D.E., Tainer, J.A., Hallewell, R.A. & Getzoff, E.D. Proteins 19, 24–34 (1994).
Altschul, S.F. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402 (1997).
Rae, T.D., Torres, A.S., Pufahl, R.A. & O'Halloran, T.V. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 5166–5176 (2001).
Dancis, A., Haile, D., Yuan, D.S. & Klausner, R.D. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 25660–25667 (1994).
Knight, S.A.B., Labbe, S., Kwon, L.F., Kosman, D.J. & Thiele, D.J. Genes Dev. 10, 1917–1929 (1996).
Maret, W. & Vallee, B.L. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 3478–3482 (1998).
Rothstein, J.D. et al. J. Neurochemistry 72, 422–429 (1999).
Bruijn, L.I. et al. Science 281, 1851–1854 (1998).
Johnston, J.A., Dalton, M.J., Gurney, M.E. & Kopito, R.R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 12571–12576 (2000).
Hausinger, R.P., Colpas, G.J. & Soriano, A. ASM News 67, 78–84 (2001).
Nguyen, H.-H.T., Ge, J., Perlstein, D.L. & Stubbe, J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 12339–12344 (1999).
Agar, J.N. et al. Biochemistry 39, 7856–7862 (2000).
Allen, R.M. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 15869–15874 (1999).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.-Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
McRee, D.E. J. Struct. Biol. 125, 156–165 (1999).
Brünger, A.T. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Laskowski, R.A. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 283–291 (1993).
Kraulis, P.J. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merritt, E.A. & Bacon, D.J. Methods Enzymol. 277, 505–524 (1997).
Esnouf, R.M. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 15, 132–143 (1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an NIH grant to A.C.R., by a grant from the ALS Association to A.C.R. and by an NIH NRSA Fellowship to A.L.L. The DND-CAT Synchrotron Research Center at the Advanced Photon Source is supported by the E.I. DuPont de Nemours & Co., the Dow Chemical Co., the State of Illinois, the U. S. Department of Energy and the NSF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamb, A., Torres, A., O'Halloran, T. et al. Heterodimeric structure of superoxide dismutase in complex with its metallochaperone. Nat Struct Mol Biol 8, 751–755 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0901-751
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0901-751
This article is cited by
-
Role of the interaction between troponin T and AMP deaminase by zinc bridge in modulating muscle contraction and ammonia production
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2023)
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of superoxide dismutases in four oyster species reveals functional differentiation in response to biotic and abiotic stress
BMC Genomics (2022)
-
A lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase-like protein functions in fungal copper import and meningitis
Nature Chemical Biology (2020)
-
Soluble and membrane-bound protein carrier mediate direct copper transport to the ethylene receptor family
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Copper–zinc superoxide dismutase (Sod1) activation terminates interaction between its copper chaperone (Ccs) and the cytosolic metal-binding domain of the copper importer Ctr1
BioMetals (2019)