Abstract
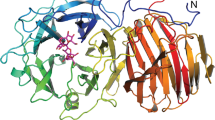
The crystal structure of UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine reductase in the presence of its substrate, enolpyruvyl-UDP-N-acetylglucosamine, has been solved to 2.7 Å resolution. This enzyme is responsible for the synthesis of UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis and consequently provides an attractive target for the design of antibacterial agents. The structure reveals a novel flavin binding motif, shows a striking alignment of the flavin with the substrate, and suggests a catalytic mechanism for the reduction of this unusual enol ether.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bugg, T.D.H. & Walsh, C.T. Intracellular steps of bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan biosynthesis: Enzymology, antibiotics and antibiotic resistance. Nat. prod. Rep. 199–215 (1993).
Brown, E.D., Vivas, E.I., Walsh, C.T. & Kolter, R. MurA (MurZ), the enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in peptidoglycan biosynthesis, is essential in Esherichia coli. J. Bact. in the press, (1995).
Marquardt, J.L., Siegele, D.S., Kolter, R. & Walsh, C.T. Cloning and sequencing of E. coli murZ and purification of its product UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase to homogeneity. J. Bact. 174, 5748–5752 (1992).
Kahan, F.M., Kahan, J.S., Cassidy, P.J. & Kropp, H. Mechanism of action of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin). Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 235, 364–386 (1974).
Benson, T.E., Marquardt, J.L., Marquardt, A.C., Etzkorn, F.A. & Walsh, C.T., Overexpression, purification, and mechanistic study of UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine reductase. Biochemistry 32, 2024–2030 (1993).
Pucci, M.J., Discotto, L.F. & Dougherty, T.J. Cloning and identification of the Escherichia coli murB DNA sequence, which encodes UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase. J. Bact. 174, 1690–1693 (1992).
Dhalla, A.M., Yanchunas, J., Ho, H.T., Falk, P.J., Villafranca, J.J. & Robertson, J.G. Steady-state kinetic mechanism of Eschericia coli UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine reductase. Biochemistry 34, 5390–5402 (1995).
Benson,T.E., Walsh, C.T. & Hogle, J.M. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvylglucosamine reductase. Protein Sci. 3, 1125–1127 (1994).
Baumann, U., Wu, S., Flaherty, K.M. & McKay, D.B. Three-dimensional structure of the alkaline protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a two-domain protein with a calcium binding parallel beta roll motif. EMBO J. 12, 3357–3364 (1993).
Yoder, M.D., Lietzke, S.E. & Jurnak, F. Unusual structural features in the parallel β-helix in pectate lyases. Structure 1, 241–251 (1993).
Orengo, C.A. & Thorton, J.M. Alpha plus beta folds revisited: some favoured motifs. Structure 1, 105–120 (1993).
Anwar, R.A. & Vlaovic, M. Purification of UDP-N-acetylenolpyruvoylglucosamine reductase from Escherichia coli by affinity chromatography, its subunit structure and the absence of flavin as the prosthetic group. Can. J. Biochem. 57, 188–196 (1979).
Bauer, A.J., Rayment, I., Frey, P.A. & Holden, H.M. The molecular structure of UDP-galactose-4-epimerase from Escherichia coli determined at 2.5 Å resolution. Proteins 12, 372–381 (1992).
Vrielink, A., Rüger, W., Driessen, H.P.C. & Freemont, P.S. Crystal structure of the DNA modifying enzyme β-glucosyltransferase in the presence and absence of the substrate uridine diphosphoglucose. EMBO J. 13, 3413–3422 (1994).
Dombrosky, P.M., Schmid, M.B. & Young, K.D. Sequence divergence of the murB and rrfB genes from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Arch. Microbiol. 161, 501–507 (1994).
Lindqvist, Y. & Branden, C. The active site of spinach glycolate oxidase. J. biol. Chem. 264, 3624–3628 (1989).
Lindqvist, Y., Branden, C.-I., Matthews, F.S. & Lederer, F. Spinach glycolate oxidase and yeast flavocytochrome b2 are structurally homologous and evolutionary related enzymes with distinctly different function and flavin mononucleotide binding. J. biol. Chem. 266, 3198–3207 (1991).
Rossmann, M.G., Moras, D. & Olsen, K.W. Chemical and biological evolution of nucleotide-binding protein. Nature 250, 194–199 (1974).
Wierenga, R.K., Maeyer, M.C.H. & Hoi, W.G.J. Interaction of pyrophosphate moieties with α-helices in dinucleotide binding proteins. Biochemistry 24, 1346–1357 (1985).
Karplus, P.A., Daniels, M.J. & Herriott, J.R. Atomic structure of ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase: Prototype for a structurally novel flavoenzyme family. Science 251, 60–66 (1991).
Correll, C.C., Batie, C.J., Ballou, D.P. & Ludwig, M.L. Pthalate dioxygenase reductase: A modular structure for electron transfer from pyridine nucleotides to [2Fe-2S]. Science 258, 1604–1610 (1992).
Manstein, D.J., Pai, E.F., Schopfer, L.M. & Massey, V. Absolute stereochemistry of flavins in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Biochemistry 25, 6807–6816 (1986).
Ghisla, S. & Massey, V. Mechansims of flavoprotein-catalyzed reactions. Eur. J. Biochem. 181, 1–17 (1989).
Schreuder, H.A., Hoi, W.G.J. & Drenth, J. Analysis of the active site of the flavoprotein p-hydroxybenzoate hydrolyase and some ideas with respect to its reaction mechanism. Biochemistry 29, 3101–3108 (1990).
Pai, E.F. & Schulz, G.E. The catalytic mechanism of glutathione reductase as derived from X-ray diffraction analyses of reaction intermediates. J. biol. Chem. 258, 1752–1757 (1983).
Schiering, N., Kabsch, W., Moore, M.J., Distefano, M.D., Walsh, C.T. & Pai, E.F. Structure of the detoxification catalyst mercuric ion reductase from Bacillus sp. strain RC607. Nature 352, 168–171 (1991).
Stehle, T., Claiborne, A. & Schulz, G.E. NADH binding site and catalysis of NADH peroxidase. Eur. J. Biochem. 221, 221–226 (1993).
Mattevi, A., Schierbeek, A.J. & Hoi, W.G.J. Refined crystal structure of lipoamide dehydrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii at 2.2 Å resolution. J. molec. Biol. 220, 975–994 (1991).
Gerlt, J.A. & Gassman, P.G. Understanding enzyme-catalyzed proton abstraction from carbon acids: Details of stepwise mechanisms for β-elimination reactions. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 114, 5928–5934 (1992).
Gerlt, J.A. & Gassman, P.G. Understanding the rates of certain enzyme-catalyzed reactions: Proton abstraction from carbon acids, acyl-transfer reactions, and displacement reactions of phophodiesters. Biochemistry 32, 11943–11952 (1993).
Veyriées, A. & Jeanloz, R.W. Absolute configuration of the carboxyethyl(lactyl)side chain of muramic acid [2-amino-3-O-(d-1-carbonxyethyl)-2-deoxy-d-glucose]. Biochemistry 9, 4153–4159 (1970).
Van Duyne, G.D., Standaert, R.F., Karplus, P.A., Schreiber, S.L. & Clardy, J. Atomic structures of the human immunophilin FKBP-12 complexes with FK506 and rapamycin. J. molec. Biol. 229, 105–124 (1993).
Gruner, S.M. X-ray detectors for macromolecular crystallography. Curr. Opin. struct. Biol. 4, 765–769 (1994).
Otwinowski, Z. In Data Collection and Processing (eds. Sawyer, L., Isaacs, N. & Bailey, S.) 56–62 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington; 1993).
Collaborative Computational Project No. 4. The CCP4 suite: Programs for protein crystallography. Acta crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Otwinowski, Z. in Isomorphous replacement and anomalous scattering, Proceedings of the CCP4 study weekend (eds. Wolf, W., Evans, P.R. & Leslie, A.G.W.) 80–86 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, 1991).
Ramakrishnan, V., Finch, J.T., Graziano, V., Lee, P.L. & Sweet, R.M. Crystal structure of gobular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature 362, 219–223 (1993).
Tesmer, J.J.G., Stemmler, T.L., Penner-Hahn, J.E., Davisson, V.J. & Smith, J.L., X-ray analysis of Escherichia coli GMP synthetase: Determination of anomalous scattering factors for a cysteinyl mercury derivative. Proteins 18, 394–403 (1994).
Wang, B.C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 115, 90–112 (1985).
Zhang, K.Y.J. & Main, P. Histogram matching as a new density modification technique for phase refinement and extension of protein molecules. Acta crystallogr. A46, 41–46 (1990).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.-Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods of building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta crystallogr. A47, 110–119 (1991).
Brünger, A.T. X-PLOR version 3.1: A System for X-ray Crystallography and NMR (Yale Univ. Press, New Haven; 1992).
Read, R.J. Improved fourier coefficients for maps using phases from partial structures with errors. Acta crystallogr. A42, 140–149 (1986).
Brünger, A.T. Free R value: a novel statistical quantity for assessing the accuracy of crystal structures. Nature 355, 472–475 (1992).
Lüthy, R., Bowie, J.U. & Eisenberg, D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 356, 83–85 (1992).
Laskowski, R.A., MacAurthur, M.W., Moss, D.S. & Thorton, J.M. PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. appl. Crystallogr. 26, 283–291 (1993).
Kraulis, P.J. Molscript: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benson, T., Filman, D., Walsh, C. et al. An enzyme–substrate complex involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2, 644–653 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0895-644
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0895-644
This article is cited by
-
Prospects for new antibiotics: a molecule-centered perspective
The Journal of Antibiotics (2014)
-
Identification of hotspot regions of MurB oxidoreductase enzyme using homology modeling, molecular dynamics and molecular docking techniques
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2011)
-
QSAR analysis of Mur B inhibitors with antibacterial properties discussing role of physico-chemical parameters
Medicinal Chemistry Research (2011)
-
Localizing the NADP+ binding site on the MurB enzyme by NMR
Nature Structural Biology (1996)
-
Cure for a crisis?
Nature Structural Biology (1996)