Abstract
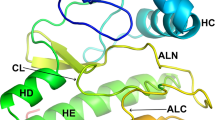
Intracellular protein phosphorylation by protein kinase C (PKC) plays a major role in the translation of extracellular signals into cellular events. Speculations on the structural basis for PKC activation are based on sequence homology between their cysteine-rich domains (CRD) and the DNA-binding ‘zinc-fingers’. We produced a fragment comprising the second CRD (CRD2) of rat PKC-α and determined its three-dimensional structure in solution by NMR spectroscopy. This revealed that CRD2 adopts a globular fold allowing two non-consecutive sets of zinc-binding residues to form two separate metal-binding sites. The fold is different to those previously proposed and allows insight into the molecular topology of a family of homologous proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hug, H. & Sarre, T.F. Protein kinase C isoenzymes: divergence in signal transaction? Biochem. J. 291, 329–343 (1993).
Nishizuka, Y. The molcular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Science 258, 607–614 (1992).
Stabel, S. & Parker, P.J. Protein kinase C. Pharmac. Ther. 51, 71–95 (1991).
Berg, J.M. Zinc fingers and other metal-binding domains. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 6513–6516 (1990).
Bell, R.M. & Burns, D.J. Lipid activation of protein kinase C. J. biol. Chem. 266, 4661–4664 (1991).
Campbell, I.D. & Baron, M. The structure and function of protein modules. Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. Lond. B 332, 165–170 (1991).
Burns, D.J. & Bell, R.M. Protein kinase C contains two phorbol ester binding domains. J. biol. Chem 266, 18330–18338 (1991).
Quest, A.F.G., Bardes, E.S.G. & Bell, R.M. A phorbol ester binding domain of protein kinase C. J. biol. Chem. 269, 2961–2970 (1994).
Wüthrich, K. Protein structure determination in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Science 243, 45–50 (1989).
Clore, G.M. & Gronenborn, A.M. Determination of three-dimensional structures of proteins and nucleic acids in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Crit. Rev. Biochem. molec. Biol. 24, 479–564 (1989).
Hubbard, S.R., Bishop, W.R., Kirschmeier, P., George, S.J., Cramer, S.P. & Hendrickson, W.A. Identification and characterization of zinc binding sites in protein kinase C. Science 254, 1776–1779 (1991).
Nilges, M. X-PLOR Manual V3.0 Brunger, A.T. (Yale University, New Haven, CT, 1992).
Kraulis, P.J., Raine, A.R.C., Gadhavi, P.L. & Laue, E.D. Structure of the DNA-binding domain of zinc GAL4. Nature 356, 448–450 (1992).
Härd, T. et al. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science 249, 157–160 (1990).
Schwabe, J.W.R., Neuhaus, D. & Rhodes, D. Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor. Nature 348, 458–461 (1990).
Lee, M.S., Gippert, G.P., Soman, K.V., Case, D.A. & Wright, P.E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science 245, 635–637 (1989).
Ahmed, S., Kozma, R., Lee, J., Monfries, C., Harden, N. & Lim, L. The cysteine-rich domain of human proteins, neuronal chimaerin, protein kinase C and diacylglycerol kinase binds zinc. Biochem. J. 280, 233–241 (1991).
Ono, Y. et al. Phorbol ester binding to protein kinase C requires a cysteine-rich zinc-finger-like sequence. Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 4868–4871 (1989).
Marion, D. & Wüthrich, K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 113, 967–974 (1983).
Plateau, P. & Guéron, M. Exchangeable proton N.M.R. without baseline distortion, using new strong-pulse sequences. J. Am. chem. Soc. 104, 7310–7311 (1982).
Bax, A., Sklenar, V., Clore, G.M. & Groneborn, A.M. Water suppression in two-dimensional spin-locked nuclear magnetic resonance experiments using a novel phase-cycling procedure. J. Am. chem. Soc. 109, 6511–6513 (1987).
Macura, S., Huang, Y., Suter, D., & Ernst, R.R. (1981). Two-dimensional chemical exchange and cross-relaxation spectroscopy of coupled nuclear spins. J. magn. Reson. 43, 259–281 (1981).
Davis, D.G. & Bax, A. Assignment of complex 1H n.m.r. spectra via two-dimensional homonuclear Hartmann-Hahn spectroscopy. J. Am. chem. Soc. 107, 2820–2821 (1985).
Kay, L.E. & Bax, A. (1990) New methods for the measurement of NH-CαH coupling constants in 15N-labelled proteins. J. magn. Reson. 86, 110–126 (1990).
Griesinger, C., Sorensen, O.W. & Ernst, R.R. Practical aspects of the E.COSY technique. Measurement of scalar spin-spin coupling constants in peptides. J. magn. Reson. 75, 474–492 (1987).
Messerle, B.A., Wider, G., Otting, G., Weber, C. & Wüthrich, K. Solvent suppression using a spin lock in 2D and 3D NMR spectroscopy with H2O solutions. J. magn. Reson. 85, 608–613 (1989).
Marion, D., Ikura, M. & Bax, A. Involved solvent suppression in one-and two-dimensional n.m.r. spectra by convolution of time-domain data. J. magn. Reson. 84, 425–430 (1989).
Nilges, M., Clore, G.M. & Gronenborn, A.M. 1H-N.M.R. stereospecific assignments by conformational data-base searches. Biopolymers 29, 813–822 (1990).
Sakana, F., Yamada, K., Kanoh, H., Yokoyama, C. & Tanabe, T. Porcine diacylglycerol kinase sequence has zinc finger and E-F hand motifs. Nature 344, 345–348 (1990).
Levin, D., Field, O., Kunisawa, R., Bishop, J.M. & Thorner, J. A candidate protein kinase C gene, PKC1 is requiered for the S. cerevisiae cell cycle. Cell 62, 213–224 (1990).
Rosenthal, A., Rhee, L., Yadegari, R., Paro, R., Ullrich, A. & Goeddel, D.V. Structure and nucleotide sequence of a Drosophila melanogaster protein kinase C gene. EMBO J. 6, 433–441 (1987).
Mayurama, I.N. & Brenner, S. A phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding protein encoded by the unc-13 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans . Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 5729–5733 (1991).
Beck, T.W., Huleihel, M., Gunnell, M., Bonner, T.I. & Rapp, U.R. The complete coding sequence of the human A-raf-1 oncogene and transforming activity of a human A-raf carrying retrovirus. Nucleic Acid Res. 15, 595–609 (1987).
Katzav, S., Martin-Zanca, D. & Barbacid, M. vav, a novel human oncogene derived from a locus ubiquitously expressed in hematopoietic cells. EMBO J. 8, 2283–2290 (1989).
Hall, C. et al. Novel human brain cDNA encoding a 34,000 Mrprotein n-chimaerin, related to both the regulatory domain of protein kinase C and BCR, the product of the Breakpoint cluster region gene. J. molec. Biol. 221, 11–16 (1990).
Kikkawa, U. et al. The common structure and activities of four subspecies of rat brain protein kinase C family. FEBS Lett. 223, 212–216 (1987).
Kraulis, P.J.J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hommel, U., Zurini, M. & Luyten, M. Solution structure of a cysteine rich domain of rat protein kinase C. Nat Struct Mol Biol 1, 383–387 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0694-383
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0694-383
This article is cited by
-
Phorbol esters and neurotransmitter release: more than just protein kinase C?
British Journal of Pharmacology (2003)