Abstract
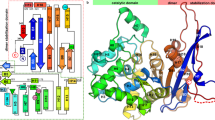
Glutamate racemase (MurI) is responsible for the synthesis of D-glutamate, an essential building block of the peptidoglycan layer in bacterial cell walls. The crystal structure of glutamate racemase from Aquifex pyrophilus, determined at 2.3 Å resolution, reveals that the enzyme forms a dimer and each monomer consists of two α/β fold domains, a unique structure that has not been observed in other racemases or members of an enolase superfamily. A substrate analog, D-glutamine, binds to the deep pocket formed by conserved residues from two monomers. The structural and mutational analyses allow us to propose a mechanism of metal cofactor-independent glutamate racemase in which two cysteine residues are involved in catalysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bugg, T.D. & Walsh, C.T. Nat. Prod. Rep. 9, 199–215 (1992).
Walsh, C.T. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 2393–2396 (1989).
Kim, S.–S. et al. Extremophiles in the press, ( 1999).
Shaw, J.P., Petsko, G.A. & Ringe, D. Biochemistry 36, 1329– 1342 (1997).
Yorifugi, T., Misono, H. & Soda, K. J. Biol. Chem. 246, 5093– 5101 (1971).
Gallo, K.A. & Knowles, J.R. Biochemistry 32, 3981–3990 (1993).
Yagasaki, M. et al. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 59, 610 –614 (1995).
Gallo, K.A., Tanner, M.E. & Knowles, J.R. Biochemistry 32, 3991– 3997 (1993).
Tanner, M.E., Gallo, K.A. & Knowles, J.R. Biochemistry 32, 3998– 4006 (1993).
Doublet, P., van Heijenoort, J. & MengeN-Lecreulx, D. Microb. Drug Resist. 2, 43–49 (1996).
Choi, S.Y., Esaki, N., Yoshimura, T. & Soda, K. J. Biochem. 112, 139–142 (1992).
Yamauchi, T. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 18361– 18364 (1992).
Stamper, C.G., Morollo, A.A. & Ringe, D. Biochemistry 37, 10438– 10445 (1998).
Glavas, S. & Tanner, M.E. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 7, 2265–2270 (1997).
Tanner, M.E. & Miao, S. Tetrahedron Lett. 35, 4073–4076 (1994).
Sander, C. & Schneider, R. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 9, 56–68 (1991 ).
Friedman, A.M., Fischmann, T.O. & Steitz, T.A. Science 268, 1721– 1727 (1995).
Wolodko, W.T., Fraser, M.E., James, M.N.G. & Bridger, W.A. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 10883–10890 (1994).
van Montfort, R.L. et al. Structure 5, 217–225 (1997).
Cole, S.T. et al. Nature 393, 537–544 (1998).
Fleischmann, R.D. et al. Science 269, 496–512 (1995).
Tomb, J.F. et al. Nature 388, 539–547 (1997).
Neidhart, D.J., et al. Biochemistry 30, 9264– 9273 (1991).
Tanner, M.E. & Kenyon, G.L. Comprehensive biological catalysis II, 7–41 (Academic Press, San Diego, CA; 1998).
Gerlt, J.A. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 9667– 9669 (1991).
Gerlt, J.A. & Gassman, P.G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114, 5928–5934 (1992).
Kallarakal, A.T. et al. Biochemistry 34, 2788– 2797 (1995).
Hasson, M.S. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 10396 –10401 (1998).
Babbitt P.C., et al. Biochemistry 35, 16489– 16501 (1996).
Hwang, K. Y. et al Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 927– 928 (1999).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 ( 1997).
Collaborative Computational Project Number 4. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Sack, J.S. J. Mol. Graphics 6, 224–225 (1988).
Brünger, A.T. X–PLOR, a system for crystallography and NMR, Version 3.1 (Yale Univ. Press, New Haven, CT; 1992).
Kabsch, W. & Sander, C. Biopolymers 22, 2577–2637 (1983).
Acknowledgements
We thank S.-H. Kim, T. Earnest and L.-W. Huang for help during data collection on the ALS (LBNL; Berkeley), and M. Tanner (UBC, Vancouver, BC) and J.-H. Yu (KIST) for helpful comments and critical reading of the manuscript. The Macromolecular Crystallography facility at beamline 5.0.2 in the ALS is principally funded by the Office of Biological and Environmental Research (US Department of Energy), with contributions from LBNL, Amgen, Roche Biosciences, the University of California (Berkeley), and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. This work was supported by the KIST (KIST 2000 program), MOST (Biotech 2000 program) and KAST (young scientist award to Y.C.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, K., Cho, CS., Kim, S. et al. Structure and mechanism of glutamate racemase from Aquifex pyrophilus . Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 422–426 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/8223
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/8223
This article is cited by
-
Discovering functionally important sites in proteins
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Structure of lasso peptide epimerase MslH reveals metal-dependent acid/base catalytic mechanism
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Screening of natural compounds that targets glutamate racemase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis reveals the anti-tubercular potential of flavonoids
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Ethambutol targets the glutamate racemase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis—an enzyme involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2019)
-
Exploiting racemases
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2016)