Abstract
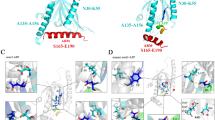
The PDZ domain of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) functions as a scaffold for organizing the signal transduction complex of the enzyme. The NMR structure of a complex composed of the nNOS PDZ domain and an associated peptide suggests that a two-stranded β-sheet C-terminal to the canonical PDZ domain may mediate its interaction with the PDZ domains of postsynaptic density-95 and α-syntrophin. The structure also provides the molecular basis of recognition of Asp–X–Val–COOH peptides by the nNOS PDZ domain. The role of the C-terminal extension in Asp-X-Val-COOH peptide binding is investigated. Additionally, NMR studies further show that the Asp-X-Val-COOH peptide and a C-terminal peptide from a novel cytosolic protein named CAPON bind to the same pocket of the nNOS PDZ domain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Ponting, C.P., Phillips, C., Davies, K.E. & Blakes, D.J. BioEssays 19, 469–479 ( 1997).
Sheng, M. Neuron 17, 575–578 ( 1996).
Craven, S.E. & Bredt, D.E. Cell 93, 495–498 (1998).
Harrision, S.C. Cell 86, 341–343 ( 1996).
Tsunoda, S. et al. Nature 388, 243– 249 (1997).
Kaech, S.M., Whitfield, C.W. & Kim, S.K. Cell 94, 761– 771 (1998).
Doyle, D.A. et al. Cell 85, 1067–1076 (1996).
Songyang, Z. et al. Science 275, 73–77 (1997).
Brenman, J.E. et al. Cell 84, 757–767 (1996).
Schepens, J., Cuppen, E., Wiernga, B. & Hendriks, W. FEBS Lett. 409, 53–56 (1997).
Stricker, N.L. et al. Nature Biotech. 15, 336– 342 (1997).
Shieh, B.H. & Zhu, M.Y. Neuron 16, 991–998 (1996).
Cuppen, E., Gerrits, H., Pepers, B., Wieringa, B. & Hendriks, W. Mol. Biol. Cell 9, 671– 683 (1998).
Cabral, J.H.M. et al. Nature 382, 649– 652 (1996).
Schultz, L. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 5, 19– 24 (1998).
Daniels, D.L., Cohen, A.R., Anderson, J.M. & Brüger, A.T. Nature Struct. Biol. 5, 317–325 (1998).
Stuehr, D.J. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37, 339– 359 (1997).
Jaffrey, S.R. & Snyder S.H. Science 274, 774–777 (1996).
Fan, J.–S. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33472– 33481 (1998).
Jaffrey, S.R., Snowman, A.M., Eliasson, M.J., Cohen, N.A. & Snyder S.H. Neuron 20, 115–124 (1998).
Vesely, D.L. Mol. Cell Biochem. 35, 55–58 (1981).
Vuister, G.W. et al. J. Magn. Reson. B101, 210– 213 (1993).
Gee, S.H. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 21980– 21987 (1998).
Farmer, B.T. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 3, 995– 997 (1996).
Tochio, H., Ohki, S., Zhang. Q., Li, M. & Zhang, M. Nature Struct. Biol. 5, 965–969 (1998).
Bax, A. & Grzesiek, S. Acc. Chem. Res. 26, 131–138 (1993).
Neri, D., Szyperski, T., Otting, G., Senn, H., & Wuthrich, K. Biochemistry 28, 7510–7516 (1989).
Kay, L.E. & Bax, A. J. Magn. Res. 86, 110–126 (1990).
Zwahlen, C. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 6711– 6721 (1997).
Nilges, M., Clore, G.M. & Gronenborn, A.M. FEBS Lett. 239, 129– 136 (1988).
Brüger, A.T. X–PLOR. A system for X–ray crystallography and NMR (Yale University Press, New Haven, Conneticut; 1992).
Koradi, R., Billeter, M. & Wuthrich, K. J. Mol. Graph. 14, 51– 55 (1996).
Kraulis, P.J. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merritt, E. & Murphy, M. Acta Cryst. D50, 869–873 (1994).
Nicholls, A. GRASP: graphical representation and analysis of surface properties (Columbia University, New York, 1992).
Laskwoski, R.A., MacArthur, M.W., Moss, D.S. and Thornton, J.M. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 283–291 (1993).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. E. Kay for providing NMR pulse sequences, R. Muhandiram for help with the NMR experiments, D. Bredt for communicating unpublished experimental results, and D. Miller-Martini for critical reading and comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by the RGC grants from the Research Grant Council of Hong Kong. The NMR spectrometer used in this work was purchased by the Biotechnology Research Institute of HKUST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tochio, H., Zhang, Q., Mandal, P. et al. Solution structure of the extended neuronal nitric oxide synthase PDZ domain complexed with an associated peptide. Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 417–421 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/8216
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/8216
This article is cited by
-
nNOS and Neurological, Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A 20-Year Story
Neuroscience Bulletin (2023)
-
Molecular basis of the interaction of the human tyrosine phosphatase PTPN3 with the hepatitis B virus core protein
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The gentle art of saying NO: how nitric oxide gets things done in the hypothalamus
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2017)
-
CAPON-nNOS coupling can serve as a target for developing new anxiolytics
Nature Medicine (2014)
-
Probing backbone hydrogen bonding in PDZ/ligand interactions by protein amide-to-ester mutations
Nature Communications (2014)