Abstract
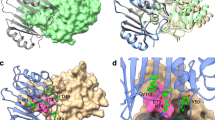
The structure of TEM-1 β-lactamase complexed with the inhibitor BLIP has been determined at 1.7 Å resolution. The two tandemly repeated domains of BLIP form a polar, concave surface that docks onto a predominantly polar, convex protrusion on the enzyme. The ability of BLIP to adapt to a variety of class A β-lactamases is most likely due to an observed flexibility between the two domains of the inhibitor and to an extensive layer of water molecules entrapped between the enzyme and inhibitor. A β-hairpin loop from domain 1 of BLIP is inserted into the active site of the β-lactamase. The carboxylate of Asp 49 forms hydrogen bonds to four conserved, catalytic residues in the β-lactamase, thereby mimicking the position of the penicillin G carboxylate observed in the acyl–enzyme complex of TEM-1 with substrate. This β-hairpin may serve as a template with which to create a new family of peptide-analogue β-lactamase inhibitors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knowles, J.R. RTEM β-Lactamase. Acct. Chem. Res. 18, 97–104 (1985).
Christensen, H., Martin, M.T. & Waley, S.G. β-lactamases as fully efficient enzymes. Determination of all the rate constants in the acyl-enzyme mechanism. Biochem J. 266, 853–861 (1990).
Neu, H.C. The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science 257, 1064–1073 (1992).
Reading, C. & Cole, M. Clavulanic acid: a β-lactamase-inhibiting β-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antibmicrob. Agents Chemother. 11, 852–857 (1977).
Blazquez, J., Baquero, M.F., Canton, R., Alos, R. & Bagnew, F. Characterization of a new TEM-type β-lactamase resistant to clavulanate, sulbactam, and tazobactam in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 37, 2059–2063 (1993).
Strynadka, N.C.J. et al. Molecular structure of the acyl-enzyjne intermediate in β-lactam hydrolysis at 1.7 Å resolution. Nature 359, 700–705 (1992).
Strynadka, N.C.J. et al. Structural and kinetic characterization of a β-lactamase-inhibitor protein. Nature 368, 657–660 (1994).
Adachi, H., Ohta, T. & Martsuzana, H. Site-directed mutants, at position 166, of RTEM-1 β-lactamase that form a stable acyl-enzyme intermediate with penicillin. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 3186–3191 (1991).
Escobar, W.A., Tan, A.K. & Fink, A.L. Site-directed mutagenesis of β-lactamase leading to accumulation of a catalytic intermediate. Biochemistry 30, 10783–10787 (1991).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins 11, 281–296 (1991).
Bode, W. & Huber, R. Proteinase-protein inhibitor interaction. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 50, 437–446, (1991).
Janin, J. Elusive affinities. Proteins 21, 30–39 (1995)
Kim, J.C., Nikolov, D.B. & Burley, S. Co-crystal structure of TBP recognizing the minor groove of a TATA element. Nature 365, 520–527 (1993).
Kim, Y., Geiger, J.H., Hahn, S. & Sigler, P.B. Crystal structure of a TBP/TATA-box complex. Nature 365, 512–520 (1993).
Endrizzi, J.A., Cronk, J.D., Wang, W., Crabtree, J.R. & Alber, T. Crystal structure of DCoH, a bifunctional protein-binding transcriptional coactivator. Science 268, 556–558 (1995).
Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. The CCP4 Suite: Programs for Protein Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760–763 (1991).
Janin, J. & Chothia, C. The structure of protein-protein recognition sites. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 16027–16030 (1990).
De Vos, A.M., Ultsch, M. & Kossiakoff, A.A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science 255, 306–312 (1992).
Kobe, B. & Diesenhofer, H. A structural basis of the interactions between leucine-rich repeats and protein ligands. Nature 374, 183–186 (1995).
Ambler, R.P. et al. A standard numbering scheme for the class A β-lactamases. Biochem. J. 276, 269–272 (1991).
Guillet, V., Lapthorn, A., Hartley, R.W. & Maugeuen, Y. Three-dimensional structure of a barnase-3-GMP complex at 2.2 Å resolution. Structure 3, 165–176 (1993).
Buckle, A.M., Schreiber, G. & Fersht, A.R. Protein-protein recognition: crystal structure analysis of a barstar-barnase complex at 2.0 Å resolution. Biochemistry 33, 8878–8889 (1994).
McGrath, M.E., Erpel, T., Bystroff, C. & Fletterick, R.J. Macromolecular chelation as an improved mechanism of protease inhibition:structure of the ecotin-trypsin complex. EMBO J 13, 1502–1507 (1994)
Herzberg, O.J. Refined crystal structure of the β-lactamase from Staphylococcus aureus PC1. J. Mol. Biol. 217, 701–719 (1991).
Leatherbarrow, R.J. & Salacinski, H.J. Design of a small peptide-based proteinase inhibitor by modelling the active site region of barley chymotrypsin inhibitor 2. Biochemistry 30, 10717–10721 (1991).
Viera, J. & Messing, J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Meth. Enzym. 153, 3–11 (1987).
Doran, J.C., Leskiw, B.K., Aippersbach, S. & Jensen, S.E. Isolation and characterization of a β-lactamase inhibitory protein from Streptomyces clavuligerus and cloning and analysis of the corresponding gene. J. Bact. 172, 4904–4918 (1990).
Leslie, A.G.W., Brick, P. & Wonnacott, A.J. MOSFILM. CCP4 Newsletter 18, 33–39 (1986).
Navaza, J. On the fast rotation function. Acta Crystallogr. A43, 645–660 (1993).
Brünger, A.T. X-PLOR Manual version 3.1 (Yale University, New Haven, CT, 1987).
Otwinowski, Z. et al. Crystal structure of trp represser/operator complex at atomic resolution. Nature 335, 321–329 (1988).
Tronrud, D.E. Conjugate-direction minimization: an improved method for the refinement of macromolecules. Acta Crystallogr. A48, 912–916 (1992).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein molecules in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A47, 110–119 (1991).
Bernstein, F.C. et al. The Protein Data Bank: A computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Biol. 112, 535–592.
Kraulis, P.J. Molscript: A program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strynadka, N., Jensen, S., Alzari, P. et al. A potent new mode of β-lactamase inhibition revealed by the 1.7 Å X-ray crystallographic structure of the TEM-1–BLIP complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3, 290–297 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0396-290
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0396-290
This article is cited by
-
An active site loop toggles between conformations to control antibiotic hydrolysis and inhibition potency for CTX-M β-lactamase drug-resistance enzymes
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Efficient production of secretory Streptomyces clavuligerus β-lactamase inhibitory protein (BLIP) in Pichia pastoris
AMB Express (2018)
-
Detecting transitions in protein dynamics using a recurrence quantification analysis based bootstrap method
BMC Bioinformatics (2017)
-
Weighted protein residue networks based on joint recurrences between residues
BMC Bioinformatics (2015)
-
Ankyrin-mediated self-protection during cell invasion by the bacterial predator Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus
Nature Communications (2015)