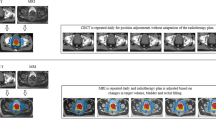
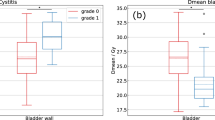
Abstract
Organ preservation protocols that incorporate chemoradiotherapy have shown good efficacy in bladder cancer. Owing to changes in rectal filling, urinary inflow and subsequent bladder volume with bladder wall deformations, irradiation must take into account interfractional and intrafractional internal target motion. Growing evidence suggests that image guidance during irradiation is essential in order to appropriately treat bladder cancer in this way. We performed a literature search on the imaging techniques and margins used for radiation therapy planning in the context of whole-bladder and partial-bladder irradiation. The most common image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) method was based on cone-beam CT using anisotropic margins. The role of cine-MRI for the prediction of intraindividual bladder changes, in association with cone-beam CT or ultrasonography, is promising. Drinking protocols, diet and laxatives were used in most cases to minimize large variations in bladder size and shape. IGRT is crucial for avoiding tumor undercoverage and undue toxicity during radiation therapy for bladder cancer. IGRT-based adaptive radiation therapy can be performed using cone-beam CT or ultrasonography: modeling of bladder changes with cine-MRI or other imaging techniques might also be useful for facilitating adaptive radiation therapy with personalized margins.
Key Points
-
Significant bladder volume and asymmetrical shape changes occur during the course of radiation therapy for bladder cancer
-
The use of isotropic margins is not appropriate in up to 65% of patients owing to asymmetrical bladder expansion, with limited variations at the level of the trigone and larger changes at the apex
-
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), based on cine-MRI, cone-beam CT and/or ultrasonography for the prediction of intraindividual bladder changes, can be used to adapt the radiation therapy plan to individual interfractional and intrafractional changes
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shipley, W. U. Full-dose irradiation for invasive bladder cancer: prognostic factors and techniques. Urology 23 (4 Suppl.), 95–100 (1984).
Housset, M. et al. Combined radiation and chemotherapy for invasive transitional-cell carcinoma of the bladder: a prospective study. J. Clin. Oncol. 11, 2150–2157 (1993).
Rodel, C., Weiss, C. & Sauer, R. Trimodality treatment and selective organ preservation for bladder cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 5536–5544 (2006).
Housset, M., Durdux, C., Thariat, J. & Dufour, B. Chemoradiation in bladder cancer [French]. Bull. Cancer 97 (Suppl. Cancer de la vessie), 19–25 (2010).
Thariat, J. et al. State of the art and advances in radiotherapy for bladder cancer [French]. Prog. Urol. 19, 85–93 (2009).
Pos, F. J., Hart, G., Schneider, C. & Sminia, P. Radical radiotherapy for invasive bladder cancer: what dose and fractionation schedule to choose? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 64, 1168–1173 (2006).
Pos, F. J., Koedooder, K., Hulshof, M. C., van Tienhoven, G. & González González, D. Influence of bladder and rectal volume on spatial variability of a bladder tumor during radical radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 55, 835–841 (2003).
Pos, F. & Remeijer, P. Adaptive management of bladder cancer radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 20, 116–120 (2010).
Majewski, W. et al. Clinical radiobiology of stage T2–T3 bladder cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 60, 60–70 (2004).
Efstathiou, J. A. et al. Late pelvic toxicity after bladder-sparing therapy in patients with invasive bladder cancer: RTOG 89-03, 95-06, 97-06, 99-06. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 4055–4061 (2009).
Viswanathan, A. N., Yorke, E. D., Marks, L. B., Eifel, P. J. & Shipley, W. U. Radiation dose–volume effects of the urinary bladder. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 76, S116–S122 (2010).
Miyanaga, N. et al. A bladder preservation regimen using intra-arterial chemotherapy and radiotherapy for invasive bladder cancer: a prospective study. Int. J. Urol. 7, 41–48 (2000).
Lagrange, J. L. et al. Quality of life assessment after concurrent chemoradiation for invasive bladder cancer: results of a multicenter prospective study (GETUG 97–015). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 79, 172–178 (2010).
Kim, H. L. & Steinberg, G. D. The current status of bladder preservation in the treatment of muscle invasive bladder cancer. J. Urol. 164, 627–632 (2000).
Sternberg, C. N. Current perspectives in muscle invasive bladder cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 38, 460–467 (2002).
Rodel, C. et al. Organ preservation in patients with invasive bladder cancer: initial results of an intensified protocol of transurethral surgery and radiation therapy plus concurrent cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 52, 1303–1309 (2002).
Weiss, C. et al. Radiochemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil after transurethral surgery in patients with bladder cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 68, 1072–1080 (2007).
Pos, F. J., van Tienhoven, G., Hulshof, M. C., Koedooder, K. & Gonzalez Gonzalez, D. Concomitant boost radiotherapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 68, 75–80 (2003).
Pos, F. J. et al. Adaptive radiotherapy for invasive bladder cancer: a feasibility study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 64, 862–868 (2006).
Jenkins, P., Anjarwalla, S., Gilbert, H. & Kinder, R. Defining the clinical target volume for bladder cancer radiotherapy treatment planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 75, 1379–1384 (2009).
Beer, A. et al. MR cystography for bladder tumor detection. Eur. Radiol. 14, 2311–2319 (2004).
Cowan, R. A. et al. Radiotherapy for muscle-invasive carcinoma of the bladder: results of a randomized trial comparing conventional whole bladder with dose-escalated partial bladder radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 59, 197–207 (2004).
Turner, S. L. et al. Bladder movement during radiation therapy for bladder cancer: implications for treatment planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 39, 355–360 (1997).
Pan, Q., Thariat, J., Bogalhas, F. & Lagrange, J. Assessment of movements of the different anatomic portions of the bladder—implications for image guided radiation therapy. Cancer Radiotherapie (in press).
Burridge, N. et al. Online adaptive radiotherapy of the bladder: small bowel irradiated-volume reduction. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 66, 892–897 (2006).
Muren, L. P., Redpath, A. T., Lord, H. & McLaren, D. Image-guided radiotherapy of bladder cancer: bladder volume variation and its relation to margins. Radiother. Oncol. 84, 307–313 (2007).
McBain, C. A. et al. Assessment of bladder motion for clinical radiotherapy practice using cine-magnetic resonance imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 75, 664–671 (2009).
Stam, M. R., van Lin, E. N., van der Vight, L. P., Kaanders, J. H. & Visser, A. G. Bladder filling variation during radiation treatment of prostate cancer: can the use of a bladder ultrasound scanner and biofeedback optimize bladder filling? Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 65, 371–377 (2006).
Ahmad, R. et al. Inter-fraction bladder filling variations and time trends for cervical cancer patients assessed with a portable 3-dimensional ultrasound bladder scanner. Radiother. Oncol. 89, 172–179 (2008).
Aluwini, S. et al. CyberKnife stereotactic radiotherapy as monotherapy for low- to intermediate-stage prostate cancer: early experience, feasibility, and tolerance. J. Endourol. 24, 865–869 (2010).
Lotz, H. T. et al. Reproducibility of the bladder shape and bladder shape changes during filling. Med. Phys. 32, 2590–2597 (2005).
Mangar, S. A. et al. Assessing intra-fractional bladder motion using cine-MRI as initial methodology for Predictive Organ Localization (POLO) in radiotherapy for bladder cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 85, 207–214 (2007).
Lotz, H. T. et al. Tumor motion and deformation during external radiotherapy of bladder cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 64, 1551–1558 (2006).
Krywonos, J. et al. MRI image-based FE modelling of the pelvis system and bladder filling. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 13, 669–676 (2010).
Thariat, J. et al. Innovative image-guided CyberKnife stereotactic radiotherapy for bladder cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 83, e118–e121 (2010).
Hulshof, M. C., van Andel, G., Bel, A., Gangel, P. & van de Kamer, J. B. Intravesical markers for delineation of target volume during external focal irradiation of bladder carcinomas. Radiother. Oncol. 84, 49–51 (2007).
Chai, X. et al. Behavior of lipiodol markers during image guided radiotherapy of bladder cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 77, 309–314 (2010).
Letourneau, D. et al. Cone-beam-CT guided radiation therapy: technical implementation. Radiother. Oncol. 75, 279–286 (2005).
Lu, C. et al. An integrated approach to segmentation and nonrigid registration for application in image-guided pelvic radiotherapy. Med. Image Anal. 15, 772–785 (2011).
Tolan, S. et al. Patient-specific PTV margins in radiotherapy for bladder cancer—a feasibility study using cone beam CT. Radiother. Oncol. 99, 131–136 (2011).
Pinkawa, M. et al. Bladder extension variability during pelvic external beam radiotherapy with a full or empty bladder. Radiother. Oncol. 83, 163–167 (2007).
Pinkawa, M. et al. Prostate position variability and dose-volume histograms in radiotherapy for prostate cancer with full and empty bladder. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 64, 856–861 (2006).
Chen, J. et al. Dose-guided radiation therapy with megavoltage cone-beam CT. Br. J. Radiol. 79 (Spec. No. 1), S87–S98 (2006).
Murthy, V. et al. 'Plan of the day' adaptive radiotherapy for bladder cancer using helical tomotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 99, 55–60 (2011).
Tuomikoski, L. et al. Adaptive radiotherapy in muscle invasive urinary bladder cancer—an effective method to reduce the irradiated bowel volume. Radiother. Oncol. 99, 61–66 (2011).
Lalondrelle, S. et al. Adaptive-predictive organ localization using cone-beam computed tomography for improved accuracy in external beam radiotherapy for bladder cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 79, 705–712 (2011).
Vestergaard, A., Søndergaard, J., Petersen, J. B., Høyer, M. & Muren, L. P. A comparison of three different adaptive strategies in image-guided radiotherapy of bladder cancer. Acta Oncol. 49, 1069–1076 (2010).
Wright, P., Muren, L. P., Hoyer, M. & Malinen, E. Evaluation of adaptive radiotherapy of bladder cancer by image-based tumour control probability modelling. Acta Oncol. 49, 1045–1051 (2010).
Søndergaard, J. et al. The normal tissue sparing obtained with simultaneous treatment of pelvic lymph nodes and bladder using intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 48, 238–244 (2009).
Redpath, A. T. & Muren, L. P. CT-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for bladder cancer: isocentre shifts, margins and their impact on target dose. Radiother. Oncol. 81, 276–283 (2006).
Muren, L. P., Ekerold, R., Kvinnsland, Y., Karlsdottir, A. & Dahl, O. On the use of margins for geometrical uncertainties around the rectum in radiotherapy planning. Radiother. Oncol. 70, 11–19 (2004).
Meijer, G. J., Rasch, C., Remeijer, P. & Lebesque, J. V. Three-dimensional analysis of delineation errors, setup errors, and organ motion during radiotherapy of bladder cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 55, 1277–1287 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J. Thariat and Q. Pan researched data for the article. J. Thariat, Q. Pan, M. Housset and J.-L. Lagrange made substantial contributions to discussing the content. J. Thariat and S. Alumini wrote the article. All authors participated in review/editing of the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thariat, J., Aluwini, S., Pan, Q. et al. Image-guided radiation therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol 9, 23–29 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2011.173
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2011.173
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of inter- and intra fractional partial bladder wall movement using implanted fiducial markers
Radiation Oncology (2017)
-
Evaluation of inter-observer variability of bladder boundary delineation on cone-beam CT
Radiation Oncology (2013)
-
Past, present, and future of radiotherapy for the benefit of patients
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2013)