Abstract
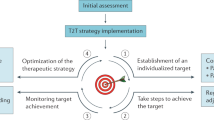
In the current therapeutic climate, mortality rates from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) remain unacceptably high. Although new therapies are on the horizon, pending their emergence and availability, optimization of the currently available therapies is potentially achievable. A 'treat-to-target' approach is now considered routine for many diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, for which it has substantially improved patient outcomes. The heterogeneity of SLE, as well as lack of universal agreement over methods to measure disease activity and treatment responses, has impeded the development of such an approach for this disease. In this article, the potential benefits of a treatment-target definition are explored, obstacles to the development of a treatment target in SLE are identified, and possible strategies to achieve this goal are discussed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uramoto, K. M. et al. Trends in the incidence and mortality of systemic lupus erythematosus, 1950–1992. Arthritis Rheum. 42, 46–50 (1999).
Mak, A., Cheung, M. W., Chiew, H. J., Liu, Y. & Ho, R. C. Global trend of survival and damage of systemic lupus erythematosus: meta-analysis and meta-regression of observational studies from the 1950s to 2000s. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 41, 830–839 (2012).
Cook, C. D., Wedgewood, R. J., Craig, J. M., Hartmann, J. R. & Janeway, C. A. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Description of 37 cases in children and a discussion of endocrine therapy in 32 of the cases. Pediatrics 26, 570–585 (1960).
van Vollenhoven, R. F. et al. Treat-to-target in systemic lupus erythematosus: recommendations from an international task force. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 958–967 (2014).
Verdecchia, P. et al. Usual versus tight control of systolic blood pressure in non-diabetic patients with hypertension (Cardio-Sis): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet 374, 525–533 (2009).
Grigor, C. et al. Effect of a treatment strategy of tight control for rheumatoid arthritis (the TICORA study): a single-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 364, 263–269 (2004).
Verstappen, S. M. et al. Intensive treatment with methotrexate in early rheumatoid arthritis: aiming for remission. Computer Assisted Management in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis (CAMERA, an open-label strategy trial). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 66, 1443–1449 (2007).
Bernatsky, S. et al. Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 2550–2557 (2006).
Mok, C. C., To, C. H., Ho, L. Y. & Yu, K. L. Incidence and mortality of systemic lupus erythematosus in a southern Chinese population, 2000–2006. J. Rheumatol. 35, 1978–1982 (2008).
Urowitz, M. B., Gladman, D. D., Tom, B. D., Ibañez, D. & Farewell, V. T. Changing patterns in mortality and disease outcomes for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 35, 2152–2158 (2008).
Manzi, S. et al. Age-specific incidence rates of myocardial infarction and angina in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: comparison with the Framingham Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 145, 408–415 (1997).
Nived, O., Jönsen, A., Bengtsson, A. A., Bengtsson, C. & Sturfelt, G. High predictive value of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for survival in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 29, 1398–1400 (2002).
Nossent, J. et al. Disease activity and damage accrual during the early disease course in a multinational inception cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 19, 949–956 (2010).
Uribe, A. G., McGwin, G., Jr, Reveille, J. D. & Alarcón, G. S. What have we learned from a 10-year experience with the LUMINA (Lupus in Minorities; Nature vs. nurture) cohort? Where are we heading? Autoimmun. Rev. 3, 321–329 (2004).
Alarcón, G. S. et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. XX. Damage as a predictor of further damage. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43, 202–205 (2004).
Da Silva, J. A. Safety of low dose glucocorticoid treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: published evidence and prospective trial data. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 65, 285–293 (2006).
Ibañez, D., Gladman, D. D. & Urowitz, M. B. Adjusted mean Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index-2K is a predictor of outcome in SLE. J. Rheumatol. 32, 824–827 (2005).
Nikpour, M., Urowitz, M. B., Ibañez, D., Harvey, P. J. & Gladman, D. D. Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective proofofconcept cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 13, R156 (2011).
Golder, V., Connelly, K., Staples, M., Morand, E. & Hoi, A. Association of Asian ethnicity with disease activity in SLE: an observational study from the Monash Lupus Clinic. Lupus 22, 1425–1430 (2013).
Turchetti, G., Yazdany, J., Palla, I., Yelin, E. & Mosca, M. Systemic lupus erythematosus and the economic perspective: a systematic literature review and points to consider. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 30 (4 Suppl. 73) S116–S122 (2012).
Sutcliffe, N., Clarke, A. E., Taylor, R., Frost, C. & Isenberg, D. A. Total costs and predictors of costs in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 40, 37–47 (2001).
Gladman, D. et al. The development and initial validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology damage index for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 39, 363–369 (1996).
Bombardier, C., Gladman, D. D., Urowitz, M. B., Caron, D. & Chang, C. H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The committee on prognosis studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 35, 630–640 (1992).
Strand, V. Clinical trial design in systemic lupus erythematosus: lessons learned and future directions. Lupus 13, 406–411 (2004).
Yee, C.S. et al. Revised British Isles Lupus Assessment Group 2004 index: a reliable tool for assessment of systemic lupus erythematosus activity. Arthritis Rheum. 54, 3300–3305 (2006).
Neville, C. et al. Learning from discordance in patient and physician global assessments of systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity. J. Rheumatol. 27, 675–679 (2000).
Yen, J. C. et al. Determinants of discordance between patients and physicians in their assessment of lupus disease activity. J. Rheumatol. 30, 1967–1976 (2003).
Wallace, D. J. et al. A phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 61, 1168–1178 (2009).
Wallace, D. J. et al. Efficacy and safety of epratuzumab in patients with moderate/severe active systemic lupus erythematosus: results from EMBLEM, a phase IIb, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 73, 183–190 (2013).
Urowitz, M. B., Feletar, M., Bruce, I. N., Ibañez, D. & Gladman, D. D. Prolonged remission in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 32, 1467–1472 (2005).
Steiman, A. J., Gladman, D. D., Ibañez, D. & Urowitz, M. B. Prolonged serologically active clinically quiescent systemic lupus erythematosus: frequency and outcome. J. Rheumatol. 37, 1822–1827 (2010).
Steiman, A. J., Gladman, D. D., Ibañez, D. & Urowitz, M. B. Outcomes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with and without a prolonged serologically active clinically quiescent period. Arthritis Care Res. 64, 511–518 (2012).
Khanna, D. et al. Evaluation of the preliminary definitions of minimal disease activity and remission in an early seropositive rheumatoid arthritis cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 57, 440–447 (2007).
Rullo, O. J. & Tsao, B. P. Recent insights into the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 72 (Suppl. 2), ii56–ii61 (2013).
Alarcón, G. S. et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. VII [correction of VIII]. Predictors of early mortality in the LUMINA cohort. LUMINA Study Group. Arthritis Rheum. 45, 191–202 (2001).
Walsh, S. J. & DeChello, L. M. Geographical variation in mortality from systemic lupus erythematosus in the United States. Lupus 10, 637–646 (2001).
Bossingham, D. Systemic lupus erythematosus in the far north of Queensland. Lupus 12, 327–331 (2003).
Gladman, D. D., Ibañez, D. & Urowitz, M. B. Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J. Rheumatol. 29, 288–291 (2002).
van der Heijde, D. M., van 't Hof, M., van Riel, P. L. & van de Putte, L. B. Development of a disease activity score based on judgment in clinical practice by rheumatologists. J. Rheumatol. 20, 579–581 (1993).
Felson, D. T. et al. American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism provisional definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis for clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 63, 573–586 (2011).
Acknowledgements
E.F.M. receives funding support from Arthritis Victoria and the National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia. M.N. receives funding support from the National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia. K.F. receives funding support from Arthritis Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.F. researched the data for the article and wrote the manuscript. A.H, M.N. and E.F.M provided a substantial contribution to discussions of the content, and to review and/or editing of the manuscript before submission. M.N. and E.F.M. contributed equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
E.F.M. declares that he has received an unrestricted educational grant from GSK. The other authors declare no competing interests.
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franklyn, K., Hoi, A., Nikpour, M. et al. The need to define treatment goals for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10, 567–571 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2014.118
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2014.118
This article is cited by
-
Treat-to-target in systemic lupus erythematosus: advancing towards its implementation
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2022)
-
Determinants and protective associations of the lupus low disease activity state in a prospective Chinese cohort
Clinical Rheumatology (2022)
-
‘Not at target’: prevalence and consequences of inadequate disease control in systemic lupus erythematosus—a multinational observational cohort study
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2022)
-
Increased MLKL mRNA level in the PBMCs is correlated with autoantibody production, renal involvement, and SLE disease activity
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2020)
-
Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of PF-06650833, a selective interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) inhibitor, in single and multiple ascending dose randomized phase 1 studies in healthy subjects
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019)