Abstract
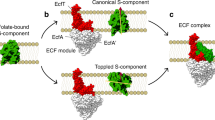
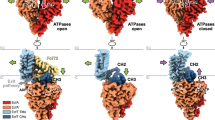
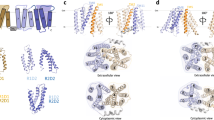
Energy-coupling factor (ECF) transporters belong to the ATP-binding cassette (ABC)-transporter family and mediate the uptake of essential micronutrients in many prokaryotic species. Two crystal structures of bacterial ECF transporters have recently been obtained and suggest that transport involves an unprecedented re-orientation of a membrane protein in the lipid bilayer during catalysis. In this Progress article, I present the new structural insights, discuss a testable model for the transport mechanism and consider the more general implications of these findings for our understanding of membrane transporters.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henderson, G. B. & Zevely, E. M. Binding and transport of thiamine by Lactobacillus casei. J. Bacteriol. 133, 1190–1196 (1978).
Henderson, G. B., Zevely, E. M. & Huennekens, F. M. Coupling of energy to folate transport in Lactobacillus casei. J. Bacteriol. 139, 552–559 (1979).
Henderson, G. B., Zevely, E. M. & Huennekens, F. M. Purification and properties of a membrane-associated, folate-binding protein from Lactobacillus casei. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 3760–3765 (1977).
Henderson, G. B., Zevely, E. M., Kadner, R. J. & Huennekens, F. M. The folate and thiamine transport proteins of Lactobacillus casei. J. Supramol. Struct. 6, 239–247 (1977).
Henderson, G. B., Zevely, E. M. & Huennekens, F. M. Mechanism of folate transport in Lactobacillus casei: evidence for a component shared with the thiamine and biotin transport systems. J. Bacteriol. 137, 1308–1314 (1979).
Rodionov, D. A. et al. A novel class of modular transporters for vitamins in prokaryotes. J. Bacteriol. 191, 42–51 (2009).
Rodionov, D. A., Hebbeln, P., Gelfand, M. S. & Eitinger, T. Comparative and functional genomic analysis of prokaryotic nickel and cobalt uptake transporters: evidence for a novel group of ATP-binding cassette transporters. J. Bacteriol. 188, 317–327 (2006).
Hebbeln, P., Rodionov, D. A., Alfandega, A. & Eitinger, T. Biotin uptake in prokaryotes by solute transporters with an optional ATP-binding cassette-containing module. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 2909–2914 (2007).
Duurkens, R. H., Tol, M. B., Geertsma, E. R., Permentier, H. P. & Slotboom, D. J. Flavin binding to the high affinity riboflavin transporter RibU. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 10380–10386 (2007).
Burgess, C. M. et al. The riboflavin transporter RibU in Lactococcus lactis: molecular characterization of gene expression and the transport mechanism. J. Bacteriol. 188, 2752–2760 (2006).
Eudes, A. et al. Identification of genes encoding the folate- and thiamine-binding membrane proteins in Firmicutes. J. Bacteriol. 190, 7591–7594 (2008).
Yakhnin, H., Zhang, H., Yakhnin, A. V. & Babitzke, P. The trp RNA-binding attenuation protein of Bacillus subtilis regulates translation of the tryptophan transport gene trpP (yhaG) by blocking ribosome binding. J. Bacteriol. 186, 278–286 (2004).
Rodionov, D. A., Vitreschak, A. G., Mironov, A. A. & Gelfand, M. S. Comparative genomics of thiamin biosynthesis in procaryotes. New genes and regulatory mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 48949–48959 (2002).
Vogl, C. et al. Characterization of riboflavin (vitamin B2) transport proteins from Bacillus subtilis and Corynebacterium glutamicum. J. Bacteriol. 189, 7367–7375 (2007).
Schauer, K., Stolz, J., Scherer, S. & Fuchs, T. M. Both thiamine uptake and biosynthesis of thiamine precursors are required for intracellular replication of Listeria monocytogenes. J. Bacteriol. 191, 2218–2227 (2009).
Glass, J. I. et al. Essential genes of a minimal bacterium. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 425–430 (2006).
Ji, Y. et al. Identification of critical staphylococcal genes using conditional phenotypes generated by antisense RNA. Science 293, 2266–2269 (2001).
Forsyth, R. A. et al. A genome-wide strategy for the identification of essential genes in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 43, 1387–1400 (2002).
Thanassi, J. A., Hartman-Neumann, S. L., Dougherty, T. J., Dougherty, B. A. & Pucci, M. J. Identification of 113 conserved essential genes using a high-throughput gene disruption system in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 3152–3162 (2002).
Song, J.-H. & Ko, K. S. Detection of essential genes in Streptococcus pneumoniae using bioinformatics and allelic replacement mutagenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 416, 401–408 (2008).
Xu, K. et al. Crystal structure of a folate energy-coupling factor transporter from Lactobacillus brevis. Nature 497, 268–271 (2013).
Wang, T. et al. Structure of a bacterial energy-coupling factor transporter. Nature 497, 272–276 (2013).
Zhang, P., Wang, J. & Shi, Y. Structure and mechanism of the S component of a bacterial ECF transporter. Nature 468, 717–720 (2010).
Berntsson, R. P.-A. et al. Structural divergence of paralogous S components from ECF-type ABC transporters. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 13990–13995 (2012).
Erkens, G. B. et al. The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 755–760 (2011).
Erkens, G. B. & Slotboom, D. J. Biochemical characterization of ThiT from Lactococcus lactis: a thiamin transporter with picomolar substrate binding affinity. Biochemistry 49, 3203–3212 (2010).
Eitinger, T., Rodionov, D. A., Grote, M. & Schneider, E. Canonical and ECF-type ATP-binding cassette importers in prokaryotes: diversity in modular organization and cellular functions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 35, 3–67 (2011).
Rees, D. C., Johnson, E. & Lewinson, O. ABC transporters: the power to change. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 218–227 (2009).
ter Beek, J., Duurkens, R. H., Erkens, G. B. & Slotboom, D. J. Quaternary structure and functional unit of energy coupling factor (ECF)-type transporters. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 5471–5475 (2011).
Serganov, A. & Nudler, E. A decade of riboswitches. Cell 152, 17–24 (2013).
Finkenwirth, F., Kirsch, F. & Eitinger, T. Solitary BioY proteins mediate biotin transport into recombinant Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 195, 4105–4111 (2013).
Fisher, D. J., Fernández, R. E., Adams, N. E. & Maurelli, A. T. Uptake of biotin by Chlamydia spp. through the use of a bacterial transporter (BioY) and a host-cell transporter (SMVT). PLoS ONE 7, e46052 (2012).
Karpowich, N. K. & Wang, D.-N. Assembly and mechanism of a group II ECF transporter. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 2534–2539 (2013).
Neubauer, O., Reiffler, C., Behrendt, L. & Eitinger, T. Interactions among the A and T units of an ECF-type biotin transporter analyzed by site-specific crosslinking. PLoS ONE 6, e29087 (2011).
Finkenwirth, F. et al. Subunit composition of an energy-coupling-factor-type biotin transporter analysed in living bacteria. Biochem. J. 431, 373–380 (2010).
Kirsch, F. et al. Essential amino acid residues of BioY reveal that dimers are the functional S unit of the Rhodobacter capsulatus biotin transporter. J. Bacteriol. 194, 4505–4512 (2012).
von Heijne, G. Membrane-protein topology. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 909–918 (2006).
von Heijne, G. Control of topology and mode of assembly of a polytopic membrane protein by positively charged residues. Nature 341, 456–458 (1989).
Majsnerowska, M. et al. Substrate-induced conformational changes in the S component ThiT from an energy coupling factor transporter. Structure 21, 861–867 (2013).
Jardetzky, O. Simple allosteric model for membrane pumps. Nature 211, 969–970 (1966).
Tanford, C. Simple model for the chemical potential change of a transported ion in active transport. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2882–2884 (1982).
Boudker, O. & Verdon, G. Structural perspectives on secondary active transporters. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 31, 418–426 (2010).
Forrest, L. R. & Rudnick, G. The rocking bundle: a mechanism for ion-coupled solute flux by symmetrical transporters. Physiol. (Bethesda) 24, 377–386 (2009).
Mitchell, P. Osmochemistry of solute translocation. Res. Microbiol. 141, 286–289 (1990).
Widdas, W. F. Inability of diffusion to account for placental glucose transfer in the sheep and consideration of the kinetics of a possible carrier transfer. J. Physiol. 118, 23–39 (1952).
Lee, C. et al. A two-domain elevator mechanism for sodium/proton antiport. Nature 501, 573–577 (2013).
Bowie, J. U. Structural biology. Membrane protein twists and turns. Science 339, 398–399 (2013).
Choi-Rhee, E. & Cronan, J. E. Biotin synthase is catalytic in vivo, but catalysis engenders destruction of the protein. Chem. Biol. 12, 461–468 (2005).
Bennett, B. D. et al. Absolute metabolite concentrations and implied enzyme active site occupancy in Escherichia coli. Nature Chem. Biol. 5, 593–599 (2009).
Slotboom, D. J., Duurkens, R. H., Olieman, K. & Erkens, G. B. Static light scattering to characterize membrane proteins in detergent solution. Methods 46, 73–82 (2008).
Smith, P. C. et al. ATP binding to the motor domain from an ABC transporter drives formation of a nucleotide sandwich dimer. Mol. Cell 10, 139–149 (2002).
Neubauer, O. et al. Two essential arginine residues in the T components of energy-coupling factor transporters. J. Bacteriol. 191, 6482–6488 (2009).
Hollenstein, K., Dawson, R. J. P. & Locher, K. P. Structure and mechanism of ABC transporter proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 17, 412–418 (2007).
Hänelt, I., Wunnicke, D., Bordignon, E., Steinhoff, H.-J. & Slotboom, D. J. Conformational heterogeneity of the aspartate transporter GltPh . Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 210–214 (2013).
Erkens, G. B., Hänelt, I., Goudsmits, J. M. H., Slotboom, D. J. & van Oijen, A. M. Unsynchronised subunit motion in single trimeric sodium-coupled aspartate transporters. Nature 502, 119–123 (2013).
Robertson, J. L., Kolmakova-Partensky, L. & Miller, C. Design, function and structure of a monomeric ClC transporter. Nature 468, 844–847 (2010).
Chen, S., Oldham, M. L., Davidson, A. L. & Chen, J. Carbon catabolite repression of the maltose transporter revealed by X-ray crystallography. Nature 499, 364–368 (2013).
Oldham, M. L. & Chen, J. Crystal structure of the maltose transporter in a pretranslocation intermediate state. Science 332, 1202–1205 (2011).
Oldham, M. L. & Chen, J. Snapshots of the maltose transporter during ATP hydrolysis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 15152–15156 (2011).
Khare, D., Oldham, M. L., Orelle, C., Davidson, A. L. & Chen, J. Alternating access in maltose transporter mediated by rigid-body rotations. Mol. Cell 33, 528–536 (2009).
Oldham, M. L., Khare, D., Quiocho, F. A., Davidson, A. L. & Chen, J. Crystal structure of a catalytic intermediate of the maltose transporter. Nature 450, 515–521 (2007).
Locher, K. P., Lee, A. T. & Rees, D. C. The E. coli BtuCD structure: a framework for ABC transporter architecture and mechanism. Science 296, 1091–1098 (2002).
Hvorup, R. N. et al. Asymmetry in the structure of the ABC transporter-binding protein complex BtuCD–BtuF. Science 317, 1387–1390 (2007).
Korkhov, V. M., Mireku, S. A. & Locher, K. P. Structure of AMP-PNP-bound vitamin B12 transporter BtuCD–F. Nature 490, 367–372 (2012).
Hinz, A. & Tampé, R. ABC transporters and immunity: mechanism of self-defense. Biochemistry 51, 4981–4989 (2012).
Dawson, R. J. P. & Locher, K. P. Structure of a bacterial multidrug ABC transporter. Nature 443, 180–185 (2006).
Hohl, M., Briand, C., Grütter, M. G. & Seeger, M. A. Crystal structure of a heterodimeric ABC transporter in its inward-facing conformation. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 19, 395–402 (2012).
Berntsson, R. P.-A., Smits, S. H. J., Schmitt, L., Slotboom, D. J. & Poolman, B. A structural classification of substrate-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 584, 2606–2617 (2010).
Zhang, Y., Rodionov, D. A., Gelfand, M. S. & Gladyshev, V. N. Comparative genomic analyses of nickel, cobalt and vitamin B12 utilization. BMC Genomics 10, 78 (2009).
Siche, S., Neubauer, O., Hebbeln, P. & Eitinger, T. A bipartite S unit of an ECF-type cobalt transporter. Res. Microbiol. 161, 824–829 (2010).
Abramson, J. et al. Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science 301, 610–615 (2003).
Reyes, N., Ginter, C. & Boudker, O. Transport mechanism of a bacterial homologue of glutamate transporters. Nature 462, 880–885 (2009).
Acknowledgements
The author would like to acknowledge support from the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) and the European Research Council (ERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Related links
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slotboom, D. Structural and mechanistic insights into prokaryotic energy-coupling factor transporters. Nat Rev Microbiol 12, 79–87 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3175
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3175
This article is cited by
-
Identification of inhibitors targeting the energy-coupling factor (ECF) transporters
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Agricultural by-products and oyster shell as alternative nutrient sources for microbial sealing of early age cracks in mortar
AMB Express (2021)
-
Membrane mediated toppling mechanism of the folate energy coupling factor transporter
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Transcriptional activation by MafR, a global regulator of Enterococcus faecalis
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Whole genome sequencing and function prediction of 133 gut anaerobes isolated from chicken caecum in pure cultures
BMC Genomics (2018)