Abstract
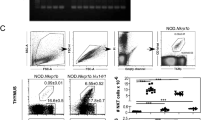
Recent data from three laboratories have identified the TEC kinases, ITK and RLK, as crucial regulators of CD8+ T-cell development into the conventional lymphocyte lineage. In the absence of ITK and RLK, CD4+CD8+ thymocytes upregulate the T-box transcription factor eomesodermin, and develop into mature CD8+ T cells that resemble memory cells, exhibit immediate effector cytokine production and depend on IL-15. Furthermore, the selection of these non-conventional 'innate' T cells results from interactions with haematopoietic cells in the thymus. These findings lead to the hypothesis that altered TCR signalling, together with distinct co-stimulatory signals, is the basis for the development of non-conventional T-cell lineages.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fowlkes, B. J., Edison, L., Mathieson, B. J. & Chused, T. M. Early T lymphocytes. Differentiation in vivo of adult intrathymic precursor cells. J. Exp. Med. 162, 802–822 (1985).
Jameson, S. C., Hogquist, K. A. & Bevan, M. J. Positive selection of thymocytes. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 13, 93–126 (1995).
Fontenot, J. D. & Rudensky, A. Y. A well adapted regulatory contrivance: regulatory T cell development and the forkhead family transcription factor Foxp3. Nature Immunol. 6, 331–337 (2005).
Cabarrocas, J. et al. Foxp3+ CD25+ regulatory T cells specific for a neo-self-antigen develop at the double-positive thymic stage. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 8453–8458 (2006).
Gapin, L., Matsuda, J. L., Surh, C. D. & Kronenberg, M. NKT cells derive from double-positive thymocytes that are positively selected by CD1d. Nature Immunol. 2, 971–978 (2001).
Chiu, N. M. et al. The selection of M3-restricted T cells is dependent on M3 expression and presentation of N-formylated peptides in the thymus. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1869–1878 (1999).
Urdahl, K. B., Sun, J. C. & Bevan, M. J. Positive selection of MHC class Ib-restricted CD8+ T cells on hematopoietic cells. Nature Immunol. 3, 772–779 (2002).
Sullivan, B. A., Kraj, P., Weber, D. A., Ignatowicz, L. & Jensen, P. E. Positive selection of a Qa-1-restricted T cell receptor with specificity for insulin. Immunity 17, 95–105 (2002).
Tilloy, F. et al. An invariant T cell receptor α chain defines a novel TAP-independent major histocompatibility complex class Ib-restricted α/β T cell subpopulation in mammals. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1907–1921 (1999).
Treiner, E. et al. Selection of evolutionarily conserved mucosal-associated invariant T cells by MR1. Nature 422, 164–169 (2003).
Atherly, L. O. et al. The Tec family tyrosine kinases Itk and Rlk regulate the development of conventional CD8+ T cells. Immunity 25, 79–91 (2006).
Broussard, C. et al. Altered development of CD8+ T cell lineages in mice deficient for the Tec kinases Itk and Rlk. Immunity 25, 93–104 (2006).
Dubois, S., Waldmann, T. A. & Muller, J. R. ITK and IL-15 support two distinct subsets of CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12075–12080 (2006).
Lodoen, M. B. & Lanier, L. L. Natural killer cells as an initial defense against pathogens. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 18, 391–398 (2006).
Dutton, R. W., Bradley, L. M. & Swain, S. L. T cell memory. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16, 201–223 (1998).
Bendelac, A., Killeen, N., Littman, D. R. & Schwartz, R. H. A subset of CD4+ thymocytes selected by MHC class I molecules. Science 263, 1774–1778 (1994).
Kurepa, Z., Su, J. & Forman, J. Memory phenotype of CD8+ T cells in MHC class Ia-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 170, 5414–5420 (2003).
Kawachi, I., Maldonado, J., Strader, C. & Gilfillan, S. MR1-restricted Vα19i mucosal-associated invariant T cells are innate T cells in the gut lamina propria that provide a rapid and diverse cytokine response. J. Immunol. 176, 1618–1627 (2006).
Das, G., Sheridan, S. & Janeway, C. A. Jr. The source of early IFN-γ that plays a role in Th1 priming. J. Immunol. 167, 2004–2010 (2001).
Bendelac, A., Rivera, M. N., Park, S. H. & Roark, J. H. Mouse CD1-specific NK1 T cells: development, specificity, and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 535–562 (1997).
Townsend, M. J. et al. T-bet regulates the terminal maturation and homeostasis of NK and Vα14i NKT cells. Immunity 20, 477–494 (2004).
Ohteki, T. Critical role for IL-15 in innate immunity. Curr. Mol. Med. 2, 371–380 (2002).
Bix, M., Coles, M. & Raulet, D. Positive selection of Vβ8+ CD4-8- thymocytes by class I molecules expressed by hematopoietic cells. J. Exp. Med. 178, 901–908 (1993).
Ohteki, T. & MacDonald, H. R. Major histocompatibility complex class I related molecules control the development of CD4+8− and CD4−8− subsets of natural killer 1.1+ T cell receptor-α/β+ cells in the liver of mice. J. Exp. Med. 180, 699–704 (1994).
Bendelac, A. Positive selection of mouse NK1+ T cells by CD1-expressing cortical thymocytes. J. Exp. Med. 182, 2091–2096 (1995).
Anderson, G., Moore, N. C., Owen, J. J. & Jenkinson, E. J. Cellular interactions in thymocyte development. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 73–99 (1996).
Teitell, M. et al. Structure and function of H-2 T (Tla) region class I MHC molecules. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 14, 1–27 (1994).
Balk, S. P., Bleicher, P. A. & Terhorst, C. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA and gene coding for a fourth CD1 molecule. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 252–256 (1989).
Jiang, H. & Chess, L. The specific regulation of immune responses by CD8+ T cells restricted by the MHC class Ib molecule, Qa-1. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 185–216 (2000).
Behar, S. M., Dascher, C. C., Grusby, M. J., Wang, C. R. & Brenner, M. B. Susceptibility of mice deficient in CD1D or TAP1 to infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1973–1980 (1999).
Xu, H., Chun, T., Choi, H. J., Wang, B. & Wang, C. R. Impaired response to Listeria in H2-M3-deficient mice reveals a nonredundant role of MHC class Ib-specific T cells in host defense. J. Exp. Med. 203, 449–459 (2006).
Bouwer, H. G., Seaman, M. S., Forman, J. & Hinrichs, D. J. MHC class Ib-restricted cells contribute to antilisterial immunity: evidence for Qa-1b as a key restricting element for Listeria-specific CTLs. J. Immunol. 159, 2795–2801 (1997).
Seaman, M. S., Perarnau, B., Lindahl, K. F., Lemonnier, F. A. & Forman, J. Response to Listeria monocytogenes in mice lacking MHC class Ia molecules. J. Immunol. 162, 5429–5436 (1999).
Chun, T. et al. Induction of M3-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses by N-formylated peptides derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Exp. Med. 193, 1213–1220 (2001).
Lo, W. F. et al. Molecular mimicry mediated by MHC class Ib molecules after infection with Gram-negative pathogens. Nature Med. 6, 215–218 (2000).
Kerksiek, K. M., Busch, D. H., Pilip, I. M., Allen, S. E. & Pamer, E. G. H2-M3-restricted T cells in bacterial infection: rapid primary but diminished memory responses. J. Exp. Med. 190, 195–204 (1999).
Maher, J. K. & Kronenberg, M. The role of CD1 molecules in immune responses to infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 9, 456–461 (1997).
Chow, M. T., Dhanji, S., Cross, J., Johnson, P. & Teh, H. S. H2-M3-restricted T cells participate in the priming of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 177, 5098–5104 (2006).
Michie, A. M. & Zuniga-Pflucker, J. C. Regulation of thymocyte differentiation: pre-TCR signals and β-selection. Semin. Immunol. 14, 311–323 (2002).
Gadue, P., Morton, N. & Stein, P. L. The Src family tyrosine kinase Fyn regulates natural killer T cell development. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1189–1196 (1999).
Pasquier, B. et al. Defective NKT cell development in mice and humans lacking the adapter SAP, the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome gene product. J. Exp. Med. 201, 695–701 (2005).
Nichols, K. E. et al. Regulation of NKT cell development by SAP, the protein defective in XLP. Nature Med. 11, 340–345 (2005).
Schmidt-Supprian, M. et al. Differential dependence of CD4+CD25+ regulatory and natural killer-like T cells on signals leading to NF-κB activation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 4566–4571 (2004).
Stanic, A. K. et al. Cutting edge: the ontogeny and function of Va14Ja18 natural T lymphocytes require signal processing by protein kinase Cτ and NF-κB. J. Immunol. 172, 4667–4671 (2004).
Chan, G., Hanke, T. & Fischer, K. D. Vav-1 regulates NK T cell development and NK cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Immunol. 31, 2403–2410 (2001).
Stanic, A. K. et al. NF-κB controls cell fate specification, survival, and molecular differentiation of immunoregulatory natural T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 172, 2265–2273 (2004).
Sivakumar, V., Hammond, K. J., Howells, N., Pfeffer, K. & Weih, F. Differential requirement for Rel/nuclear factor κB family members in natural killer T cell development. J. Exp. Med. 197, 1613–1621 (2003).
Ohteki, T. et al. The transcription factor interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) is important during the maturation of natural killer 1.1+ T cell receptor-α/β+ (NK1+ T) cells, natural killer cells, and intestinal intraepithelial T cells. J. Exp. Med. 187, 967–972 (1998).
Walunas, T. L., Wang, B., Wang, C. R. & Leiden, J. M. Cutting edge: the Ets1 transcription factor is required for the development of NK T cells in mice. J. Immunol. 164, 2857–2860 (2000).
Lacorazza, H. D. et al. The ETS protein MEF plays a critical role in perforin gene expression and the development of natural killer and NK-T cells. Immunity 17, 437–449 (2002).
Egawa, T. et al. Genetic evidence supporting selection of the Vα14i NKT cell lineage from double-positive thymocyte precursors. Immunity 22, 705–716 (2005).
Murphy, K. M. & Reiner, S. L. The lineage decisions of helper T cells. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2, 933–944 (2002).
Intlekofer, A. M. et al. Effector and memory CD8+ T cell fate coupled by T-bet and eomesodermin. Nature Immunol. 6, 1236–1244 (2005).
Ranson, T. et al. IL-15 availability conditions homeostasis of peripheral natural killer T cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 2663–2668 (2003).
Kennedy, M. K. et al. Reversible defects in natural killer and memory CD8 T cell lineages in interleukin 15-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 191, 771–780 (2000).
Lucas, P. C., McAllister-Lucas, L. M. & Nunez, G. NF-κB signaling in lymphocytes: a new cast of characters. J. Cell Sci. 117, 31–39 (2004).
Wang, N. et al. CD150 is a member of a family of genes that encode glycoproteins on the surface of hematopoietic cells. Immunogenetics 53, 382–394 (2001).
Yamagata, T., Mathis, D. & Benoist, C. Self-reactivity in thymic double-positive cells commits cells to a CD8αα lineage with characteristics of innate immune cells. Nature Immunol. 5, 597–605 (2004).
Yamagata, T., Benoist, C. & Mathis, D. A shared gene-expression signature in innate-like lymphocytes. Immunol. Rev. 210, 52–66 (2006).
Berg, L. J., Finkelstein, L. D., Lucas, J. A. & Schwartzberg, P. L. Tec family kinases in T lymphocyte development and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23, 549–600 (2005).
Bendelac, A., Savage, P. B. & Teyton, L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 297–336 (2007).
Vugmeyster, Y. et al. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I KbDb−/− deficient mice possess functional CD8+ T cells and natural killer cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 12492–12497 (1998).
Ilangumaran, S., Ramanathan, S., La Rose, J., Poussier, P. & Rottapel, R. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 regulates IL-15 receptor signaling in CD8+CD44high memory T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 171, 2435–2445 (2003).
Ilangumaran, S. et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 attenuates IL-15 receptor signaling in CD8+ thymocytes. Blood 102, 4115–4122 (2003).
Miley, M. J. et al. Biochemical features of the MHC-related protein 1 consistent with an immunological function. J. Immunol. 170, 6090–6098 (2003).
Borowski, C. & Bendelac, A. Signaling for NKT cell development: the SAP–FynT connection. J. Exp. Med. 201, 833–836 (2005).
Li, W. et al. An alternate pathway for CD4 T cell development: thymocyte-expressed MHC class II selects a distinct T cell population. Immunity 23, 375–386 (2005).
Choi, E. Y. et al. Thymocyte-thymocyte interaction for efficient positive selection and maturation of CD4 T cells. Immunity 23, 387–396 (2005).
Kane, L. P., Lin, J. & Weiss, A. It's all Rel-ative: NF-κB and CD28 costimulation of T-cell activation. Trends Immunol. 23, 413–420 (2002).
Sun, G. et al. The zinc finger protein cKrox directs CD4 lineage differentiation during intrathymic T cell positive selection. Nature Immunol. 6, 373–381 (2005).
He, X. et al. The zinc finger transcription factor Th-POK regulates CD4 versus CD8 T-cell lineage commitment. Nature 433, 826–833 (2005).
Pai, S. Y. et al. Critical roles for transcription factor GATA-3 in thymocyte development. Immunity 19, 863–875 (2003).
Lin, W. et al. Regulatory T cell development in the absence of functional Foxp3. Nature Immunol. 8, 359–368 (2007).
Williams, L. M. & Rudensky, A. Y. Maintenance of the Foxp3-dependent developmental program in mature regulatory T cells requires continued expression of Foxp3. Nature Immunol. 8, 277–284 (2007).
Zheng, Y. et al. Genome-wide analysis of Foxp3 target genes in developing and mature regulatory T cells. Nature 445, 936–940 (2007).
Leishman, A. J. et al. Precursors of functional MHC class I- or class II-restricted CD8αα+ T cells are positively selected in the thymus by agonist self-peptides. Immunity 16, 355–364 (2002).
Colmone, A. & Wang, C. R. H2-M3-restricted T cell response to infection. Microbes Infect. 8, 2277–2283 (2006).
Acknowledgements
I thank J. Kang, P. Schwartzberg, M. Felices, and A. Prince for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants from the NIH (AI37584) and the Center for Disease Control (CI000101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Related links
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berg, L. Signalling through TEC kinases regulates conventional versus innate CD8+ T-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol 7, 479–485 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2091
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2091
This article is cited by
-
IL-4/IL-4 Ab complex enhances the accumulation of both antigen-specific and bystander CD8 T cells in mouse lungs infected with influenza A virus
Laboratory Animal Research (2023)
-
MicroRNA-181a regulates IFN-γ expression in effector CD8+ T cell differentiation
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
Antigen-inexperienced memory CD8+ T cells: where they come from and why we need them
Nature Reviews Immunology (2017)
-
T-Bet independent development of IFNγ secreting natural T helper 1 cell population in the absence of Itk
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
The tyrosine kinase Itk suppresses CD8+ memory T cell development in response to bacterial infection
Scientific Reports (2015)