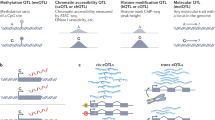
Abstract
Functional genomics is rapidly progressing towards the elucidation of elements that are crucial for the cis-regulatory control of gene expression, and population-based studies of disease and gene expression traits are yielding widespread evidence of the influence of non-coding variants on trait variance. Recently, genome-wide allele-specific approaches that harness high-throughput sequencing technology have started to allow direct evaluation of how these cis-regulatory polymorphisms control gene expression and affect chromatin states. The emerging data is providing exciting opportunities for comprehensive characterization of the allele-specific events that govern human gene regulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cookson, W., Liang, L., Abecasis, G., Moffatt, M. & Lathrop, M. Mapping complex disease traits with global gene expression. Nature Rev. Genet. 10, 184–194 (2009).
Yan, H., Yuan, W., Velculescu, V. E., Vogelstein, B. & Kinzler, K. W. Allelic variation in human gene expression. Science 297, 1143 (2002).
Knight, J. C., Keating, B. J., Rockett, K. A. & Kwiatkowski, D. P. In vivo characterization of regulatory polymorphisms by allele-specific quantification of RNA polymerase loading. Nature Genet. 33, 469–475 (2003).
Ge, B. et al. Global patterns of cis variation in human cells revealed by high-density allelic expression analysis. Nature Genet. 41, 1216–1222 (2009).
Hindorff, L. A. et al. Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 9362–9367 (2009).
Gimelbrant, A., Hutchinson, J. N., Thompson, B. R. & Chess, A. Widespread monoallelic expression on human autosomes. Science 318, 1136–1140 (2007).
Milani, L. et al. Allele-specific gene expression patterns in primary leukemic cells reveal regulation of gene expression by CpG site methylation. Genome Res. 19, 1–11 (2009).
Maynard, N. D., Chen, J., Stuart, R. K., Fan, J. B. & Ren, B. Genome-wide mapping of allele-specific protein–DNA interactions in human cells. Nature Methods 5, 307–309 (2008).
Kerkel, K. et al. Genomic surveys by methylation-sensitive SNP analysis identify sequence-dependent allele-specific DNA methylation. Nature Genet. 40, 904–908 (2008).
Gunderson, K. L. Whole-genome genotyping on bead arrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 529, 197–213 (2009).
Lee, J. H. et al. A robust approach to identifying tissue-specific gene expression regulatory variants using personalized human induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS Genet. 5, e1000718 (2009).
Zhang, K. et al. Digital RNA allelotyping reveals tissue-specific and allele-specific gene expression in human. Nature Methods 6, 613–618 (2009).
Verlaan, D. J. et al. Targeted screening of cis-regulatory variation in human haplotypes. Genome Res. 19, 118–127 (2009).
Shoemaker, R., Deng, J., Wang, W. & Zhang, K. Allele-specific methylation is prevalent and is contributed by CpG-SNPs in the human genome. Genome Res. 23 Apr 2010 (doi:10.1101/gr.104695.109).
Heap, G. A. et al. Genome-wide analysis of allelic expression imbalance in human primary cells by high-throughput transcriptome resequencing. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, 122–134 (2010).
Montgomery, S. B. et al. Transcriptome genetics using second generation sequencing in a Caucasian population. Nature 464, 773–777 (2010).
Pickrell, J. K. et al. Understanding mechanisms underlying human gene expression variation with RNA sequencing. Nature 464, 768–772 (2010).
Wittkopp, P. J., Haerum, B. K. & Clark, A. G. Evolutionary changes in cis and trans gene regulation. Nature 430, 85–88 (2004).
Ameur, A., Rada-Iglesias, A., Komorowski, J. & Wadelius, C. Identification of candidate regulatory SNPs by combination of transcription-factor-binding site prediction, SNP genotyping and haploChIP. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, e85 (2009).
McDaniell, R. et al. Heritable individual-specific and allele-specific chromatin signatures in humans. Science 328, 235–239 (2010).
Degner, J. F. et al. Effect of read-mapping biases on detecting allele-specific expression from RNA-sequencing data. Bioinformatics 25, 3207–3212 (2009).
Fontanillas, P. et al. Key considerations for measuring allelic expression on a genomic scale using high-throughput sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 9 (Suppl. 1), 212–227 (2010).
Cheung, V. G. et al. Monozygotic twins reveal germline contribution to allelic expression differences. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 1357–1360 (2008).
Plagnol, V. et al. Extreme clonality in lymphoblastoid cell lines with implications for allele specific expression analyses. PLoS ONE 3, e2966 (2008).
Dimas, A. S. et al. Common regulatory variation impacts gene expression in a cell type-dependent manner. Science 325, 1246–1250 (2009).
Emilsson, V. et al. Genetics of gene expression and its effect on disease. Nature 452, 423–428 (2008).
Kasowski, M. et al. Variation in transcription factor binding among humans. Science 328, 232–235 (2010).
Verlaan, D. J. et al. Allele-specific chromatin remodeling in the ZPBP2/GSDMB/ORMDL3 locus associated with the risk of asthma and autoimmune disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 85, 377–393 (2009).
Fogarty, M. P., Xiao, R., Prokunina-Olsson, L., Scott, L. J. & Mohlke, K. L. Allelic expression imbalance at high-density lipoprotein cholesterol locus MMAB–MVK. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, 1921–1929 (2010).
McCarroll, S. A. et al. Deletion polymorphism upstream of IRGM associated with altered IRGM expression and Crohn's disease. Nature Genet. 40, 1107–1112 (2008).
Gaulton, K. J. et al. A map of open chromatin in human pancreatic islets. Nature Genet. 42, 255–259 (2010).
Pastinen, T. et al. Mapping common regulatory variants to human haplotypes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 3963–3971 (2005).
Hom, G. et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13–BLK and ITGAM–ITGAX. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 900–909 (2008).
Acknowledgements
I thank T. Kwan for critical reading of the manuscript. T.P. holds a Canada Research Chair and is supported by grants from Genome Canada, Genome Quebec and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Glossary
- Clonal read
-
NGS produces, in principle, independent reads from each molecule in the input sample. However, in some cases, the amplification of molecules yields copies of the same short read, which can potentially bias allelic read counts.
- DNase I hypersensitivity
-
The susceptibility of a genomic region to digestion by DNase I. Promoter, enhancer and other active regulatory DNA sequences are more easily digested than inactive non-coding sequences.
- Expression quantitative trait locus
-
A locus at which gene expression variance in a population —typically measured by microarrays or by RNA-seq — correlates significantly with genotype. This locus can be near the measured gene (cis) or elsewhere in the genome (trans).
- Histone modification
-
Regulatory elements in actively transcribed versus repressed loci have differences in post-translational modifications (for example, methylation or acetylation of lysines) of histones that can be identified by ChIP using modification-specific antibodies.
- Padlock probe
-
An oligonucleotide with 5′ and 3′ sequences that are specific for target regions of the genome and are separated by generic sequence. After binding to its target, the probe can be circularized by ligase, and the generic sequence portion is used to amplify or capture the probes.
- Standing genetic variation
-
Allelic variation that is currently segregating within a population; as opposed to alleles that appear by new mutation events.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pastinen, T. Genome-wide allele-specific analysis: insights into regulatory variation. Nat Rev Genet 11, 533–538 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2815
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2815
This article is cited by
-
Direct haplotype-resolved 5-base HiFi sequencing for genome-wide profiling of hypermethylation outliers in a rare disease cohort
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Allele-specific expression reveals genes with recurrent cis-regulatory alterations in high-risk neuroblastoma
Genome Biology (2022)
-
DeCAF: a novel method to identify cell-type specific regulatory variants and their role in cancer risk
Genome Biology (2022)
-
Human–chimpanzee fused cells reveal cis-regulatory divergence underlying skeletal evolution
Nature Genetics (2021)
-
Allele-specific expression of Parkinson’s disease susceptibility genes in human brain
Scientific Reports (2021)