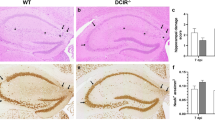
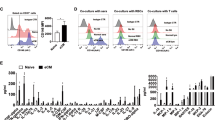
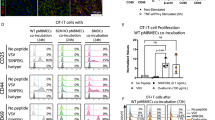
Abstract
We have recently demonstrated that brain endothelial cells cross-present parasite antigen during mouse experimental cerebral malaria (ECM). Here we describe a 2-d protocol to detect cross-presentation by isolating the brain microvessels and incubating them with a reporter cell line that expresses lacZ upon detection of the relevant peptide–major histocompatibility complex. After X-gal staining, a typical positive result consists of hundreds of blue spots, compared with fewer than 20 spots from a naive brain. The assay is generalizable to other disease contexts by using reporter cells that express appropriate specific T cell receptors. Also described is the protocol for culturing endothelial cells from brain microvessels isolated from naive mice. After 7–10 d, an in vitro cross-presentation assay can be performed by adding interferon-γ, antigen (e.g., Plasmodium berghei–infected red blood cells) and reporter cells in sequence over 3 d. This is useful for comparing different antigen forms or for probing the effects of various interventions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mai, J., Virtue, A., Shen, J., Wang, H. & Yang, X.F. An evolving new paradigm: endothelial cells—conditional innate immune cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 6, 61 (2013).
Bagai, R. et al. Mouse endothelial cells cross-present lymphocyte-derived antigen on class I MHC via a TAP1- and proteasome-dependent pathway. J. Immunol. 174, 7711–7715 (2005).
Limmer, A. et al. Efficient presentation of exogenous antigen by liver endothelial cells to CD8+ T cells results in antigen-specific T-cell tolerance. Nat. Med. 6, 1348–1354 (2000).
Savinov, A.Y., Wong, F.S., Stonebraker, A.C. & Chervonsky, A.V. Presentation of antigen by endothelial cells and chemoattraction are required for homing of insulin-specific CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 197, 643–656 (2003).
Galea, I. et al. An antigen-specific pathway for CD8 T cells across the blood-brain barrier. J. Exp. Med. 204, 2023–2030 (2007).
Pryce, G., Male, D. & Sedgwick, J. Antigen presentation in brain: brain endothelial cells are poor stimulators of T-cell proliferation. Immunology 66, 207–212 (1989).
Risau, W., Engelhardt, B. & Wekerle, H. Immune function of the blood-brain barrier: incomplete presentation of protein (auto-)antigens by rat brain microvascular endothelium in vitro. J. Cell Biol. 110, 1757–1766 (1990).
Wang, Y., Calder, V.L., Lightman, S.L. & Greenwood, J. Antigen presentation by rat brain and retinal endothelial cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 61, 231–239 (1995).
Prat, A., Biernacki, K., Becher, B. & Antel, J.P. B7 expression and antigen presentation by human brain endothelial cells: requirement for proinflammatory cytokines. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 59, 129–136 (2000).
Wheway, J., Obeid, S., Couraud, P.O., Combes, V. & Grau, G.E. The brain microvascular endothelium supports T cell proliferation and has potential for alloantigen presentation. PLoS ONE 8, e52586 (2013).
Howland, S.W. et al. Brain microvessel cross-presentation is a hallmark of experimental cerebral malaria. EMBO Mol. Med. 5, 916–931 (2013).
Poh, C.M., Howland, S.W., Grotenbreg, G.M. & Renia, L. Damage to the blood-brain barrier during experimental cerebral malaria results from synergistic effects of CD8+ T cells with different specificities. Infect. Immun. 82, 4854–4864 (2014).
Howland, S.W., Poh, C.M. & Renia, L. Activated brain endothelial cells cross-present malaria antigen. PLoS Pathog. 11, e1004963 (2015).
Belnoue, E. et al. On the pathogenic role of brain-sequestered αβ CD8+ T cells in experimental cerebral malaria. J. Immunol. 169, 6369–6375 (2002).
Nitcheu, J. et al. Perforin-dependent brain-infiltrating cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes mediate experimental cerebral malaria pathogenesis. J. Immunol. 170, 2221–2228 (2003).
Haque, A. et al. Granzyme B expression by CD8+ T cells is required for the development of experimental cerebral malaria. J. Immunol. 186, 6148–6156 (2011).
Song, L. & Pachter, J.S. Culture of murine brain microvascular endothelial cells that maintain expression and cytoskeletal association of tight junction-associated proteins. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 39, 313–320 (2003).
Wu, Z., Hofman, F.M. & Zlokovic, B.V. A simple method for isolation and characterization of mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Neurosci. Methods 130, 53–63 (2003).
Lu, C. et al. Pertussis toxin induces angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 86, 2624–2640 (2008).
Tigges, U., Welser-Alves, J.V., Boroujerdi, A. & Milner, R. A novel and simple method for culturing pericytes from mouse brain. Microvasc. Res. 84, 74–80 (2012).
Howland, S.W., Claser, C., Poh, C.M., Gun, S.Y. & Renia, L. Pathogenic CD8+ T cells in experimental cerebral malaria. Semin. Immunopathol. 37, 221–231 (2015).
Karttunen, J., Sanderson, S. & Shastri, N. Detection of rare antigen-presenting cells by the lacZ T-cell activation assay suggests an expression cloning strategy for T-cell antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 6020–6024 (1992).
Sanderson, S. & Shastri, N. LacZ-inducible, antigen/MHC-specific T cell hybrids. Int. Immunol. 6, 369–376 (1994).
Lachenmaier, S.M., Deli, M.A., Meissner, M. & Liesenfeld, O. Intracellular transport of Toxoplasma gondii through the blood-brain barrier. J. Neuroimmunol. 232, 119–130 (2011).
Blanchard, N. et al. Immunodominant, protective response to the parasite Toxoplasma gondii requires antigen processing in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat. Immunol. 9, 937–944 (2008).
Shwetank Date, O.S., Kim, K.S. & Manjunath, R. Infection of human endothelial cells by Japanese encephalitis virus: increased expression and release of soluble HLA-E. PLoS ONE 8, e79197 (2013).
Verma, S. et al. West Nile virus infection modulates human brain microvascular endothelial cells tight junction proteins and cell adhesion molecules: transmigration across the in vitro blood-brain barrier. Virology 385, 425–433 (2009).
Chapagain, M.L., Verma, S., Mercier, F., Yanagihara, R. & Nerurkar, V.R. Polyomavirus JC infects human brain microvascular endothelial cells independent of serotonin receptor 2A. Virology 364, 55–63 (2007).
Nizet, V. et al. Invasion of brain microvascular endothelial cells by group B streptococci. Infect. Immun. 65, 5074–5081 (1997).
Uchiyama, S. et al. The surface-anchored NanA protein promotes pneumococcal brain endothelial cell invasion. J. Exp. Med. 206, 1845–1852 (2009).
Unkmeir, A. et al. Fibronectin mediates Opc-dependent internalization of Neisseria meningitidis in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Mol. Microbiol. 46, 933–946 (2002).
Prasadarao, N.V. et al. Outer membrane protein A of Escherichia coli contributes to invasion of brain microvascular endothelial cells. Infect. Immun. 64, 146–153 (1996).
Jarry, U. et al. Efficiently stimulated adult microglia cross-prime naive CD8+ T cells injected in the brain. Eur. J. Immunol. 43, 1173–1184 (2013).
Zhao, H. et al. Olfactory plays a key role in spatiotemporal pathogenesis of cerebral malaria. Cell Host Microbe 15, 551–563 (2014).
Lau, L.S. et al. CD8+ T cells from a novel T cell receptor transgenic mouse induce liver-stage immunity that can be boosted by blood-stage infection in rodent malaria. PLoS Pathog. 10, e1004135 (2014).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by an intramural grant from Singapore's Agency for Science, Technology and Research. S.Y.G. and C.M.P. were supported by postgraduate scholarships from the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore. We thank N. Shastri (University of California, Berkeley) for providing the BWZ.36/CD8α cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.W.H. conceived the methods and C.C., S.Y.G. and C.M.P. helped optimize the protocols. L.R. supervised the project. S.W.H. and L.R. wrote and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howland, S., Gun, S., Claser, C. et al. Measuring antigen presentation in mouse brain endothelial cells ex vivo and in vitro. Nat Protoc 10, 2016–2026 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.129
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2015.129
This article is cited by
-
In vitro model of brain endothelial cell barrier reveals alterations induced by Plasmodium blood stage factors
Parasitology Research (2023)
-
Immunomodulation by endothelial cells — partnering up with the immune system?
Nature Reviews Immunology (2022)
-
Tissue-specific immunopathology during malaria infection
Nature Reviews Immunology (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.