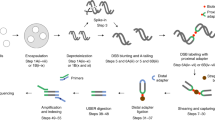
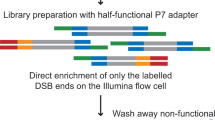
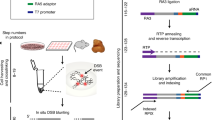
Abstract
Recent advances in our understanding of the management and repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) rely on the study of targeted DSBs that have been induced in living cells by the controlled activity of site-specific endonucleases, usually recombinant restriction enzymes. Here we describe a protocol for quantifying these endonuclease-induced DSBs; this quantification is essential to an interpretation of how DSBs are managed and repaired. A biotinylated double-stranded oligonucleotide is ligated to enzyme-cleaved genomic DNA, allowing the purification of the cleaved DNA on streptavidin beads. The extent of cleavage is then quantified either by quantitative PCR (qPCR) at a given site or at multiple sites by genome-wide techniques (e.g., microarrays or high-throughput sequencing). This technique, named ligation-mediated purification, can be performed in 2 d. It is more accurate and sensitive than existing alternative methods, and it is compatible with genome-wide analysis. It allows the amount of endonuclease-mediated breaks to be precisely compared between two conditions or across the genome, thereby giving insight into the influence of a given factor or of various chromatin contexts on local repair parameters.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helleday, T., Petermann, E., Lundin, C., Hodgson, B. & Sharma, R.A. DNA repair pathways as targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 193–204 (2008).
Curtin, N.J. DNA repair dysregulation from cancer driver to therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 801–817 (2012).
Olive, P.L. & Banath, J.P. The comet assay: a method to measure DNA damage in individual cells. Nat. Protoc. 1, 23–29 (2006).
Bellaiche, Y., Mogila, V. & Perrimon, N. I-SceI endonuclease, a new tool for studying DNA double-strand break repair mechanisms in Drosophila. Genetics 152, 1037–1044 (1999).
Rong, Y.S. & Golic, K.G. Gene targeting by homologous recombination in Drosophila. Science 288, 2013–2018 (2000).
Liang, F., Han, M., Romanienko, P.J. & Jasin, M. Homology-directed repair is a major double-strand break repair pathway in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 5172–5177 (1998).
Berkovich, E., Monnat, R.J. Jr. & Kastan, M.B. Roles of ATM and NBS1 in chromatin structure modulation and DNA double-strand break repair. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 683–690 (2007).
Berkovich, E., Monnat, R.J. Jr. & Kastan, M.B. Assessment of protein dynamics and DNA repair following generation of DNA double-strand breaks at defined genomic sites. Nat. Protoc. 3, 915–922 (2008).
Miller, K.M. et al. Human HDAC1 and HDAC2 function in the DNA-damage response to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 1144–1151 (2010).
Murr, R. et al. Histone acetylation by Trrap-Tip60 modulates loading of repair proteins and repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 91–99 (2006).
Roques, C. et al. MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 is a critical regulator of FANCD2 stability and function during DNA double-strand break repair. EMBO J. 28, 2400–2413 (2009).
Caron, P. et al. Cohesin protects genes against γH2AX induced by DNA double-strand breaks. PLoS Genet. 8, e1002460 (2012).
Iacovoni, J.S. et al. High-resolution profiling of γH2AX around DNA double-strand breaks in the mammalian genome. EMBO J. 29, 1446–1457 (2010).
Massip, L., Caron, P., Iacovoni, J.S., Trouche, D. & Legube, G. Deciphering the chromatin landscape induced around DNA double-strand breaks. Cell Cycle 9, 2963–2972 (2010).
Soutoglou, E. et al. Positional stability of single double-strand breaks in mammalian cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 675–682 (2007).
Bennardo, N., Cheng, A., Huang, N. & Stark, J.M. Alternative-NHEJ is a mechanistically distinct pathway of mammalian chromosome break repair. PLoS Genet. 4, e1000110 (2008).
Guirouilh-Barbat, J. et al. Impact of the KU80 pathway on NHEJ-induced genome rearrangements in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell 14, 611–623 (2004).
Reid, L.J. et al. E3 ligase activity of BRCA1 is not essential for mammalian cell viability or homology-directed repair of double-strand DNA breaks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 20876–20881 (2008).
Xie, A., Kwok, A. & Scully, R. Role of mammalian Mre11 in classical and alternative nonhomologous end joining. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 814–818 (2009).
Boboila, C. et al. Robust chromosomal DNA repair via alternative end-joining in the absence of X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 (XRCC1). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 2473–2478 (2012).
Fnu, S. et al. Methylation of histone H3 lysine 36 enhances DNA repair by nonhomologous end-joining. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 540–545 (2011).
Niida, H. et al. Essential role of Tip60-dependent recruitment of ribonucleotide reductase at DNA damage sites in DNA repair during G1 phase. Genes Dev. 24, 333–338 (2010).
Shakya, R. et al. BRCA1 tumor suppression depends on BRCT phosphoprotein binding, but not its E3 ligase activity. Science 334, 525–528 (2011).
Siaud, N. et al. Plasticity of BRCA2 function in homologous recombination: genetic interactions of the PALB2 and DNA binding domains. PLoS Genet. 7, e1002409 (2011).
Xu, Y. et al. The p400 ATPase regulates nucleosome stability and chromatin ubiquitination during DNA repair. J. Cell Biol. 191, 31–43 (2010).
Courilleau, C. et al. The chromatin remodeler p400 ATPase facilitates Rad51-mediated repair of DNA double-strand breaks. J. Cell Biol. 199, 1067–1081 (2012).
Sartori, A.A. et al. Human CtIP promotes DNA end resection. Nature 450, 509–514 (2007).
You, Z. et al. CtIP links DNA double-strand break sensing to resection. Mol. Cell 36, 954–969 (2009).
Catalan, N. et al. The block in immunoglobulin class switch recombination caused by activation-induced cytidine deaminase deficiency occurs prior to the generation of DNA double strand breaks in switch μregion. J. Immunol. 171, 2504–2509 (2003).
Shahar, O.D. et al. Live imaging of induced and controlled DNA double-strand break formation reveals extremely low repair by homologous recombination in human cells. Oncogene 31, 3495–3504 (2012).
Fenina, M. et al. I-SceI–mediated double-strand break does not increase the frequency of homologous recombination at the Dct locus in mouse embryonic stem cells. PLoS ONE 7, e39895 (2012).
Villalobos, M.J., Betti, C.J. & Vaughan, A.T. Detection of DNA double-strand breaks and chromosome translocations using ligation-mediated PCR and inverse PCR. Methods Mol. Biol. 314, 109–121 (2006).
Besaratinia, A. & Pfeifer, G.P. Measuring the formation and repair of UV damage at the DNA sequence level by ligation-mediated PCR. Methods Mol. Biol. 920, 189–202 (2012).
Leduc, F. et al. Genome-wide mapping of DNA strand breaks. PLoS ONE 6, e17353 (2011).
Crosetto, N. et al. Nucleotide-resolution DNA double-strand break mapping by next-generation sequencing. Nat. Methods 10, 361–365 (2013).
Carroll, D., Morton, J.J., Beumer, K.J. & Segal, D.J. Design, construction and in vitro testing of zinc finger nucleases. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1329–1341 (2006).
Bibikova, M., Golic, M., Golic, K.G. & Carroll, D. Targeted chromosomal cleavage and mutagenesis in Drosophila using zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 161, 1169–1175 (2002).
Li, T. et al. TAL nucleases (TALNs): hybrid proteins composed of TAL effectors and FokI DNA-cleavage domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 359–372 (2011).
Piganeau, M. et al. Cancer translocations in human cells induced by zinc-finger and TALE nucleases. Genome Res. 23, 1182–1193 (2013).
Rass, E. et al. Role of Mre11 in chromosomal nonhomologous end joining in mammalian cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 819–824 (2009).
Citri, A., Pang, Z.P., Sudhof, T.C., Wernig, M. & Malenka, R.C. Comprehensive qPCR profiling of gene expression in single neuronal cells. Nat. Protoc. 7, 118–127 (2012).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants to D.T. from the Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer as an 'équipe labellisée', from the Association pour la Recherche contre le Cancer as a 'programme ARC' and from the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (project 2011 blanc SVSE8 PinGs), and to G.L. from the Association Contre le Cancer (ARC), Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR-09-JCJC-0138), Cancéropôle Grand Sud-Ouest and La Fondation Recherche Innovation Thérapeutiqe Cancérologie (Fondation RITC). F.A., P.C. and C. Courilleau were supported by grants from the French Ministry of Research. We thank M. Vandromme for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C. Chailleux has contributed to the development of the assay and performed experiments for this manuscript. F.A., P.C., V.D., C. Courilleau and Y.C. have contributed to the development of the procedure. G.L. conceived the procedure and has contributed to its development. D.T. conceived the procedure and wrote the manuscript. All authors commented on and edited the manuscript and figures.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Integrated supplementary information
Supplementary Figure 1 Controlling the levels of enzyme-mediated DSBs for a correct interpretation of ChIP data.
U2OS ER-AsiSI cells were treated for 4 hours with OH-Tam to induce AsiSI-mediated cleavage, in the presence of ATM or DNA-PK inhibitors (20μM Ku55933 and 2μM Nu 7441 respectively, added an hour previous OH-tam treatment, as indicated. a) Chromatin was prepared and analysed by chromatin immunoprecipitation using γH2AX antibodies. ChIP efficiency (as percent of input) was measured by qPCR at the vicinity of two AsiSI sites. Note the strong increase in the ChIP signal in the presence of DNA-PK inhibitor, which could be wrongly interpreted as increased DNA damage signalling upon DNA-PK inhibition. b) Genomic DNA was prepared and the amounts of AsiSI-cohesive breaks at these two sites were analysed by Ligation-Mediated Purification. Note the strong increase in the amount of breaks upon DNAPK inhibitor treatment, which indicates that results shown in a) cannot be interpreted.
Supplementary Figure 2 Effects of DNA resection.
a) U2OS ER-AsiSI cells were transfected with a siRNA against CtIP. 52 hours following transfection, total RNA was prepared, retrotranscribed using random primers and levels of CtIP cDNA relative to ribosomal phosphoprotein P0 were assessed by qPCR. b) Same as in a), except that 4OHT was added 48h following transfection to induce AsiSI digestion as described in ref 13. 4 and 24 hours later, as indicated, genomic DNA was prepared and the amounts of AsiSI-cohesive breaks were quantified at two AsiSI sites by Ligation-Mediated Purification. Note that DNA resection leads to the underestimation of the presence of breaks 24 hours, but not 4 hours, following break induction.
Supplementary Figure 3 Comparison with other methods.
a) Left panel: Results obtained by Ligation-Mediated Purification (this experiment is also shown in Figure 3b). Right panel: Extent of cleavage in the same samples measured by qPCR with primers on each side of the break (5'-CACTATAGGGAGACCCAAGCTG and 5'-CTGGTCGGCGATTAGCGACT). Errors bars represent standard deviation of the qPCR measurements. The % of cleavage is given by the decrease in PCR efficiency (represented by the arrow). Note that the variations between two identical samples (the +I-SceI sample and the no-ligase sample which should give the same signal since they are produced from the same genomic DNA) are higher than variations between different genomic DNA. Thus, the decrease observed in the +I-SceI sample is not significant, and cleavage efficiency in this experiment is below the detection level of this method. b) Left panel: Results obtained by Ligation-Mediated Purification as shown in Figure 3c, but with a log scale. Right panel: a similar standard curve of I-SceI-digested versus uncleaved genomic DNA was analysed by LM-PCR as described in 30, 31 except that genomic DNA was treated by T4 DNA polymerase following I-SceI-mediated digestion to obtain blunt ends. Quantification of ligation products was performed by qPCR using the following primers: 5'-GGGAGATCTGAATTCCCCTA and 5'-GTCGGCGATTAGCGACTTCT. Note that the sensitivity of ligation-mediated purification is about 10-fold higher than that of LMPCR.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figure 1
Controlling the levels of enzyme-mediated DSBs for a correct interpretation of ChIP data. (PDF 100 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
Effects of DNA resection. (PDF 92 kb)
Supplementary Figure 3
Comparison with other methods. (PDF 94 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chailleux, C., Aymard, F., Caron, P. et al. Quantifying DNA double-strand breaks induced by site-specific endonucleases in living cells by ligation-mediated purification. Nat Protoc 9, 517–528 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2014.031
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2014.031
This article is cited by
-
RNA transcripts stimulate homologous recombination by forming DR-loops
Nature (2021)
-
qDSB-Seq is a general method for genome-wide quantification of DNA double-strand breaks using sequencing
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Drosha drives the formation of DNA:RNA hybrids around DNA break sites to facilitate DNA repair
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Tissue-selective effects of nucleolar stress and rDNA damage in developmental disorders
Nature (2018)
-
Senataxin resolves RNA:DNA hybrids forming at DNA double-strand breaks to prevent translocations
Nature Communications (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.