Abstract
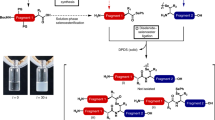
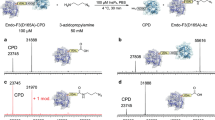
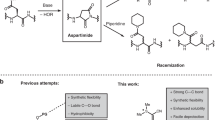
Technologies that allow the efficient chemical modification of proteins under mild conditions are widely sought after. Sortase-mediated peptide ligation provides a strategy for modifying the N or C terminus of proteins. This protocol describes the use of depsipeptide substrates (containing an ester linkage) with sortase A (SrtA) to completely modify proteins carrying a single N-terminal glycine residue under mild conditions in 4–6 h. The SrtA-mediated ligation reaction is reversible, so most labeling protocols that use this enzyme require a large excess of both substrate and sortase to produce high yields of ligation product. In contrast, switching to depsipeptide substrates effectively renders the reaction irreversible, allowing complete labeling of proteins with a small excess of substrate and catalytic quantities of sortase. Herein we describe the synthesis of depsipeptide substrates that contain an ester linkage between a threonine and glycolic acid residue and an N-terminal FITC fluorophore appended via a thiourea linkage. The synthesis of the depsipeptide substrate typically takes 2–3 d.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rostovtsev, V.V., Green, L.G., Fokin, V.V. & Sharpless, K.B. A stepwise Huisgen cycloaddition process: copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective 'ligation' of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 41, 2596–2599 (2002).
Agard, N.J., Prescher, J.A. & Bertozzi, C.R. A strain-promoted [3 + 2] azidealkyne cycloaddition for covalent modification of biomolecules in living systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 15046–15047 (2004).
Nilsson, B.L., Kiessling, L.L. & Raines, R.T. Staudinger ligation: a peptide from a thioester and azide. Org. Lett. 2, 1939–1941 (2000).
Saxon, E. & Bertozzi, C.R. Cell surface engineering by a modified Staudinger reaction. Science 287, 2007–2010 (2000).
Link, A.J., Mock, M.L. & Tirrell, D.A. Non-canonical amino acids in protein engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 14, 603–609 (2003).
Baker, D.P. et al. N-Terminally PEGylated human interferon-β-1a with improved pharmacokinetic properties and in vivo efficacy in a melanoma angiogenesis model. Bioconjugate Chem. 17, 179–188 (2005).
Mazmanian, S.K., Liu, G., Ton-That, H. & Schneewind, O. Staphylococcus aureus sortase, an enzyme that anchors surface proteins to the cell wall. Science 285, 760–763 (1999).
Mazmanian, S.K., Ton-That, H. & Schneewind, O. Sortase-catalysed anchoring of surface proteins to the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 40, 1049–1057 (2001).
Ton-That, H., Liu, G., Mazmanian, S.K., Faull, K.F. & Schneewind, O. Purification and characterization of sortase, the transpeptidase that cleaves surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus at the LPXTG motif. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 12424–12429 (1999).
Ton-That, H., Mazmanian, S.K., Faull, K.F. & Schneewind, O. Anchoring of surface proteins to the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: sortase catalyzed in vitro transpeptidation reaction using LPXTG peptide and NH2-Gly3substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 9876–9881 (2000).
Popp, M.W.-L. & Ploegh, H.L. Making and breaking peptide bonds: protein engineering using sortase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 5024–5032 (2011).
Tsukiji, S. & Nagamune, T. Sortase-mediated ligation: a gift from Gram-positive bacteria to protein engineering. Chembiochem 10, 787–798 (2009).
Popp, M.W., Antos, J.M., Grotenbreg, G.M., Spooner, E. & Ploegh, H.L. Sortagging: a versatile method for protein labeling. Nat. Chem. Biol. 3, 707–708 (2007).
Guo, X., Wang, Q., Swarts, B.M. & Guo, Z. Sortase-catalyzed peptideglycosylphosphatidylinositol analogue ligation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 9878–9879 (2009).
Parthasarathy, R., Subramanian, S. & Boder, E.T. Sortase A as a novel molecular 'stapler' for sequence-specific protein conjugation. Bioconjugate Chem. 18, 469–476 (2007).
Mao, H.Y., Hart, S.A., Schink, A. & Pollok, B.A. Sortase-mediated protein ligation: a new method for protein engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 2670–2671 (2004).
Antos, J.M., Miller, G.M., Grotenbreg, G.M. & Ploegh, H.L. Lipid modification of proteins through sortase-catalyzed transpeptidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 16338–16343 (2008).
Samantaray, S., Marathe, U., Dasgupta, S., Nandicoori, V.K. & Roy, R.P. Peptide-sugar ligation catalyzed by transpeptidase sortase: a facile approach to neoglycoconjugate synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 2132–2133 (2008).
Yamamoto, T. & Nagamune, T. Expansion of the sortase-mediated labeling method for site-specific N-terminal labeling of cell surface proteins on living cells. Chem. Commun. 2009, 1022–1024 (2009).
Antos, J.M. et al. Site-specific N- and C-terminal labeling of a single polypeptide using sortases of different specificity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 10800–10801 (2009).
Williamson, D.J., Fascione, M.A., Webb, M.E. & Turnbull, W.B. Efficient N-terminal labeling of proteins by use of sortase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 9377–9380 (2012).
Theile, C.S. et al. Site-specific N-terminal labeling of proteins using sortase-mediated reactions. Nat. Protoc. 8, 1800–1807 (2013).
Suich, D.J., Ballinger, M.D., Wells, J.A. & DeGrado, W.F. Fmoc-based synthesis of glycolate ester peptides for the assembly of de novo designed multimeric proteins using subtiligase. Tetrahedron Lett. 37, 6653–6656 (1996).
Jobling, M.G., Palmer, L.M., Erbe, J.L. & Holmes, R.K. Construction and characterization of versatile cloning vectors for efficient delivery of native foreign proteins to the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Plasmid 38, 158–173 (1997).
Guimaraes, C.P. et al. Site-specific C-terminal and internal loop labeling of proteins using sortase-mediated reactions. Nat. Protoc. 8, 1787–1799 (2013).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Neylon for providing an expression construct for sortase A and K. Drickamer for providing a plasmid for expressing the gMBP protein. This work was supported by an Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) studentship for D.J.W. and also by EPSRC research grants EP/G043302/1, EP/I013083/1 and Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council research grant BB/G004145/1. W.B.T. thanks the Royal Society for a University Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were involved in the design of the experiments; D.J.W. conducted the experiments; all authors contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williamson, D., Webb, M. & Turnbull, W. Depsipeptide substrates for sortase-mediated N-terminal protein ligation. Nat Protoc 9, 253–262 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2014.003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2014.003
This article is cited by
-
Development of a highly-efficient erythrocyte-drug covalent conjugation platform and its use in treating thrombotic disorders
Cell Research (2023)
-
Nature-inspired protein ligation and its applications
Nature Reviews Chemistry (2023)
-
A Modular Vaccine Development Platform Based on Sortase-Mediated Site-Specific Tagging of Antigens onto Virus-Like Particles
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Efficient segmental isotope labeling of multi-domain proteins using Sortase A
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.