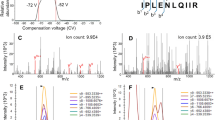
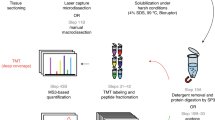
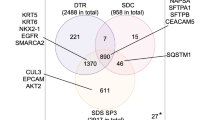
Abstract
Archived formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue collections represent a valuable informational resource for proteomic studies. Multiple FFPE core biopsies can be assembled in a single block to form tissue microarrays (TMAs). We describe a protocol for analyzing protein in FFPE-TMAs using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) imaging mass spectrometry (IMS). The workflow incorporates an antigen retrieval step following deparaffinization, in situ trypsin digestion, matrix application and then mass spectrometry signal acquisition. The direct analysis of FFPE-TMA tissue using IMS allows direct analysis of multiple tissue samples in a single experiment without extraction and purification of proteins. The advantages of high speed and throughput, easy sample handling and excellent reproducibility make this technology a favorable approach for the proteomic analysis of clinical research cohorts with large sample numbers. For example, TMA analysis of 300 FFPE cores would typically require 6 h of total time through data acquisition, not including data analysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Metz, B. et al. Identification of formaldehyde-induced modifications in proteins: Reactions with insulin. Bioconjugate Chem. 17, 815–822 (2006).
Rahimi, F., Shepherd, C.E., Halliday, G.M., Geczy, C.L. & Raftery, M.J. Antigen-epitope retrieval to facilitate proteomic analysis of formalin-fixed archival brain tissue. Anal. Chem. 78, 7216–7221 (2006).
Werner, M., Chott, A., Fabiano, A. & Battifora, H. Effect of formalin tissue fixation and processing on immunohistochemistry. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 24, 1016–1019 (2000).
Shi, S.R., Key, M.E. & Kalra, K.L. Antigen retrieval in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues: an enhancement method for immunohistochemical staining based on microwave oven heating of tissue sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39, 741–748 (1991).
Groseclose, M.R., Massion, P.P., Chaurand, P. & Caprioli, R.M. High-throughput proteomic analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue microarrays using MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Proteomics 8, 3715–3724 (2008).
Groseclose, M.R., Andersson, M., Hardesty, W.M. & Caprioli, R.M. Identification of proteins directly from tissue: in situ tryptic digestions coupled with imaging mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 42, 254–262 (2007).
Schwartz, S.A., Reyzer, M.L. & Caprioli, R.M. Direct tissue analysis using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: practical aspects of sample preparation. J. Mass Spectrom. 38, 699–708 (2003).
Chaurand, P., Norris, J.L., Cornett, D.S., Mobley, J.A. & Caprioli, R.M. New developments in profiling and imaging of proteins from tissue sections by MALDI mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 5, 2889–2900 (2006).
Lemaire, R. et al. Direct analysis and MALDI imaging of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections. J. Proteome Res. 6, 1295–1305 (2007).
Uhlen, M. & Ponten, F. Antibody-based proteomics for human tissue profiling. Mol. Cell Proteomics 4, 384–393 (2005).
Wessels, J.T. et al. In vivo imaging in experimental preclinical tumor research-a review. Cytometry A 71, 542–549 (2007).
Ntziachristos, V. Going deeper than microscopy: the optical imaging frontier in biology. Nat. Methods 7, 603–614 (2010).
Pepperkok, R. & Ellenberg, J. High-throughput fluorescence microscopy for systems biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 690–696 (2006).
Becker, K.F. & Taylor, C.R. 'Liquid morphology': immunochemical analysis of proteins extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues: combining proteomics with immunohistochemistry. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 19, 1–9 (2011).
Teruya-Feldstein, J. The immunohistochemistry laboratory: looking at molecules and preparing for tomorrow. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 134, 1659–1665 (2010).
Leong, T.Y., Cooper, K. & Leong, A.S. Immunohistology-past, present, and future. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 17, 404–418 (2010).
Grey, A.C., Chaurand, P., Caprioli, R.M. & Schey, K.L. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry of integral membrane proteins from ocular lens and retinal tissue. J. Proteome Res. 8, 3278–3283 (2009).
Yang, Y.L. et al. Connecting chemotypes and phenotypes of cultured marine microbial assemblages by imaging mass spectrometry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 50, 5839–5842 (2011).
Iijima, M. Visualization of lateral water transport pathways in soybean by a time of flight-secondary ion mass spectrometry cryo-system. J. Exp. Bot. 62, 2179–2188 (2011).
Reyzer, M.L. & Caprioli, R.M. MALDI-MS-based imaging of small molecules and proteins in tissues. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 11, 29–35 (2007).
Cornett, D.S., Frappier, S.L. & Caprioli, R.M. MALDI-FTICR imaging mass spectrometry of drugs and metabolites in tissue. Anal. Chem. 80, 5648–5653 (2008).
Djidja, M.C. et al. Novel molecular tumour classification using MALDI-mass spectrometry imaging of tissue micro-array. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 397, 587–601 (2010).
Caprioli, R.M. Deciphering protein molecular signatures in cancer tissues to aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Cancer Res. 65, 10642–10645 (2005).
Shi, S.-R., Shi, Y. & Taylor, C.R. Antigen retrieval immunohistochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 59, 13–32 (2011).
Seeley, E.H. & Caprioli, R.M. Molecular imaging of proteins in tissues by mass spectrometry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 18126–18131 (2008).
Westermark, P. & Nilsson, G.T. Demonstration of amyloid protein Aa in old museum specimens. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 108, 217–219 (1984).
Schwamborn, K. & Caprioli, R.M. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry—painting molecular pictures. Mol. Oncol. 4, 529–538 (2010).
Kononen, J. et al. Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat. Med. 4, 844–847 (1998).
Chaurand, P. et al. Integrating histology and imaging mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 76, 1145–1155 (2004).
Schwamborn, K. et al. Identifying prostate carcinoma by MALDI-Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Med. 20, 155–159 (2007).
Evers, P., Uylings, H.B.M. & Suurmeijer, A.J.H. Antigen retrieval in formaldehyde-fixed human brain tissue. Methods 15, 133–140 (1998).
Shi, S.R., Liu, C., Balgley, B.M., Lee, C. & Taylor, C.R. Protein extraction from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections: quality evaluation by mass spectrometry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 54, 739–743 (2006).
Sato, T.A., Aoki, Y., Toyama, A. & Shimada, T. A novel method for analyzing formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue sections by mass spectrometry imaging. Neurosci. Res. 61, S19 (2008).
Shi, S.R., Cote, R.J. & Taylor, C.R. Antigen retrieval techniques: current perspectives. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 49, 931–937 (2001).
Taylor, C.R. et al. Comparative study of antigen retrieval heating methods: microwave, microwave and pressure cooker, autoclave, and steamer. Biotech. Histochem. 71, 263–270 (1996).
Yamashita, S. Heat-induced antigen retrieval: Mechanisms and application to histochemistry. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 41, 141–200 (2007).
Hoetelmans, R.W.M., van Slooten, H.J., Keijzer, R., van de Velde, C.J.H. & van Dierendonck, J.H. Comparison of the effects of microwave heating and high pressure cooking for antigen retrieval of human and rat Bcl-2 protein in formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections. Biotech. Histochem. 77, 137–144 (2002).
Aerni, H.R., Cornett, D.S. & Caprioli, R.M. High-throughput profiling of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue using parallel electrophoresis and matrix assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 81, 7490–7495 (2009).
Nirmalan, N.J., Harnden, P., Selby, P.J. & Banks, R.E. Mining the archival formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue proteome: opportunities and challenges. Mol. Biosyst. 4, 712–720 (2008).
Reyzer, M.L., Chaurand, P., Angel, P.M. & Caprioli, R.M. Direct molecular analysis of whole-body animal tissue sections by MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 656, 285–301 (2010).
Schuerenberg, M., Luebbert, C., Deininger, S.O., Ketterlinus, R. & Suckau, D. MALDI tissue imaging: mass spectrometric localization of biomarkers in tissue slices. Nat. Methods 4, iii–iv (2007).
Nilsson, A. et al. Fine mapping the spatial distribution and concentration of unlabeled drugs within tissue micro-compartments using imaging mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 5, e11411 (2010).
Baluya, D.L., Garrett, T.J. & Yost, R.A. Automated MALDI matrix deposition method with inkjet printing for imaging mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 79, 6862–6867 (2007).
Wisztorski, M., Franck, J., Salzet, M. & Fournier, I. MALDI direct analysis and imaging of frozen versus FFPE tissues: what strategy for which sample? Methods Mol. Biol. 656, 303–322 (2010).
Aerni, H.R., Cornett, D.S. & Caprioli, R.M. Automated acoustic matrix deposition for MALDI sample preparation. Anal. Chem. 78, 827–834 (2006).
Hardesty, W.M. Proteomic Analysis and Classification of Metastatic Melanoma by MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Ph.D. Dissertation, Vanderbilt University http://etd.library.vanderbilt.edu/available/etd-08252010-081820/unrestricted/Hardesty.pdf (2010).
Norris, J.L. et al. Processing MALDI mass spectra to improve mass spectral direct tissue analysis. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 260, 212–221 (2007).
Mann, M., Hendrickson, R.C. & Pandey, A. Analysis of proteins and proteomes by mass spectrometry. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 437–473 (2001).
Tabb, D.L., Friedman, D.B. & Ham, A.J.L. Verification of automated peptide identifications from proteomic tandem mass spectra. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2213–2222 (2006).
Holle, A., Haase, A., Kayser, M. & Hohndorf, J. Optimizing UV laser focus profiles for improved MALDI performance. J. Mass Spectrom. 41, 705–716 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank P.M. Angel, M.L. Reyzer and E.H. Seeley for helpful discussions and critical reviewing of the manuscript. We also thank J.L. Allen, E.H. Seeley and K. Schwamborn for development and optimization of the deparaffinization and antigen retrieval methods, and M. Reid Groseclose for providing some TMA images and the figures in the Anticipated Results section. This work was supported by the US National Institutes of Health/National Institute of General Medical Sciences grants 5RO1GM058008-11 and DOD W81XWH-05-1-0179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to the development of the protocol and the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casadonte, R., Caprioli, R. Proteomic analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue by MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. Nat Protoc 6, 1695–1709 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.388
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.388
This article is cited by
-
Mapping the single cell spatial immune landscapes of the melanoma microenvironment
Clinical & Experimental Metastasis (2024)
-
Cardiac transthyretin/leukocyte chemotactic factor (LECT) 2 double amyloidosis in a patient suffering from heart failure
Clinical Research in Cardiology (2023)
-
High-throughput analysis of tissue microarrays using automated desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
RapidET: a MEMS-based platform for label-free and rapid demarcation of tumors from normal breast biopsy tissues
Microsystems & Nanoengineering (2022)
-
Label-free cell assays to determine compound uptake or drug action using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
Nature Protocols (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.