Abstract
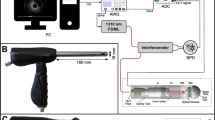
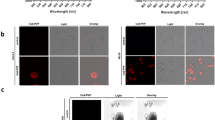
New endoscopic techniques such as narrow-band imaging (NBI) and confocal laser endomicroscopy (CLE) have improved the in vivo diagnosis of human gastrointestinal diseases in the colon. Whereas NBI may facilitate the identification of neoplastic lesions, CLE permits real-time histology of the inflamed or neoplastic colonic mucosa through the use of fluorescent dyes. These techniques have been recently adopted for use during ongoing endoscopy in mice. This protocol, which can be completed in 2 h, provides a detailed description of NBI and CLE in the mouse colon. In contrast to other techniques, this approach does not require laparotomy, and it allows direct CLE analysis of lesions identified by NBI. Mice exposed to models of colitis or colorectal cancer are anesthetized and examined with a miniaturized NBI endoscope, which provides an increased contrast of the vasculature. Upon identification of suspicious areas by NBI and the administration of fluorescent dyes, a confocal laser probe can be directed to the area of interest through the endoscope and confocal images can be obtained. Through the use of various fluorescent dyes, different aspects of the mucosa can be assessed. In addition, fluorescence-labeled antibodies can be used for molecular imaging of mice in vivo. Mouse NBI endoscopy and CLE represent reliable and fast high-quality techniques for the endoscopic characterization and molecular imaging of the mucosa in colitis and colon cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taketo, M.M. Mouse models of gastrointestinal tumors. Cancer Sci. 97, 355–361 (2006).
Taketo, M.M. & Edelmann, W. Mouse models of colon cancer. Gastroenterology 136, 780–798 (2009).
Wirtz, S. & Neurath, M.F. Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59, 1073–1083 (2007).
Becker, C., Fantini, M.C. & Neurath, M.F. High resolution colonoscopy in live mice. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2900–2904 (2006).
Becker, C. et al. In vivo imaging of colitis and colon cancer development in mice using high resolution chromoendoscopy. Gut 54, 950–954 (2005).
Goetz, M. & Neurath, M.F. Imaging techniques in inflammatory bowel disease: recent trends, questions and answers. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 33 (Suppl 3): S174–S182 (2009).
Kiesslich, R., Goetz, M., Vieth, M., Galle, P.R. & Neurath, M.F. Technology insight: confocal laser endoscopy for in vivo diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 4, 480–490 (2007).
Kiesslich, R. Chromoendoscopy: what is its true value for ulcerative colitis surveillance? Dig. Dis. 28, 445–451 (2010).
Wallace, M.B. & Kiesslich, R. Advances in endoscopic imaging of colorectal neoplasia. Gastroenterology 138, 2140–2150 (2010).
Kiesslich, R. & Neurath, M.F. Magnifying chromoendoscopy: effective diagnostic tool for screening colonoscopy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 22, 1700–1701 (2007).
Muto, M., Horimatsu, T., Ezoe, Y., Morita, S. & Miyamoto, S. Improving visualization techniques by narrow band imaging and magnification endoscopy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 24, 1333–1346 (2009).
Neumann, H., Kiesslich, R., Wallace, M.B. & Neurath, M.F. Confocal laser endomicroscopy: technical advances and clinical applications. Gastroenterology 139, 388–392, 392.e381–382 (2010).
Goetz, M. & Kiesslich, R. Advanced imaging of the gastrointestinal tract: research versus clinical tools? Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 25, 412–421 (2009).
Kiesslich, R. et al. Confocal laser endoscopy for diagnosing intraepithelial neoplasias and colorectal cancer in vivo. Gastroenterology 127, 706–713 (2004).
Kiesslich, R. et al. Diagnosing Helicobacter pylori in vivo by confocal laser endoscopy. Gastroenterology 128, 2119–2123 (2005).
Moussata, D. et al. Confocal laser endomicroscopy is a new imaging modality for recognition of intramucosal bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease in vivo. Gut 60, 26–33 (2011).
Waldner, M.J. et al. VEGF receptor signaling links inflammation and tumorigenesis in colitis-associated cancer. J. Exp. Med. 207, 2855–2868 (2010).
Larghi, A., Lecca, P.G. & Costamagna, G. High-resolution narrow band imaging endoscopy. Gut 57, 976–986 (2008).
Foersch, S. et al. Molecular imaging of VEGF in gastrointestinal cancer in vivo using confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gut 59, 1046–1055 (2010).
Goetz, M. et al. In vivo molecular imaging of colorectal cancer with confocal endomicroscopy by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor. Gastroenterology 138, 435–446 (2010).
Neurath, M.F. & Kiesslich, R. Molecular detection of CD44v6 on aberrant crypt foci by confocal laser endoscopy. Endoscopy 42 (Suppl 2): E314–E315 (2010).
Kim, P. et al. In vivo wide-area cellular imaging by side-view endomicroscopy. Nat. Methods 7, 303–305 (2010).
Jain, R.K., Munn, L.L. & Fukumura, D. Dissecting tumour pathophysiology using intravital microscopy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 266–276 (2002).
Scaldaferri, F. et al. VEGF-A links angiogenesis and inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 136, 585–595.e5 (2009).
Massberg, S. et al. Fibrinogen deposition at the postischemic vessel wall promotes platelet adhesion during ischemia-reperfusion in vivo. Blood 94, 3829–3838 (1999).
Neufert, C., Becker, C. & Neurath, M.F. An inducible mouse model of colon carcinogenesis for the analysis of sporadic and inflammation-driven tumor progression. Nat. Protoc. 2, 1998–2004 (2007).
Wirtz, S., Neufert, C., Weigmann, B. & Neurath, M.F. Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat. Protoc. 2, 541–546 (2007).
Strober, W., Fuss, I.J. & Blumberg, R.S. The immunology of mucosal models of inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 495–549 (2002).
Alencar, H., Mahmood, U., Kawano, Y., Hirata, T. & Weissleder, R. Novel multiwavelength microscopic scanner for mouse imaging. Neoplasia 7, 977–983 (2005).
Riol-Blanco, L. et al. Immunological synapse formation inhibits, via NF-kappaB and FOXO1, the apoptosis of dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 10, 753–760 (2009).
Massberg, S., Eisenmenger, S., Enders, G., Krombach, F. & Messmer, K. Quantitative analysis of small intestinal microcirculation in the mouse. Res. Exp. Med. (Berl) 198, 23–35 (1998).
Gompels, L.L. et al. In vivo fluorescence imaging of E-selectin: quantitative detection of endothelial activation in a mouse model of arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 63, 107–117 (2011).
Beer, A. & Schwaiger, M. Imaging of integrin alphavbeta3 expression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27, 631–644 (2008).
Eisenblatter, M., Holtke, C., Persigehl, T. & Bremer, C. Optical techniques for the molecular imaging of angiogenesis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 37 (Suppl 1): S127–S137 (2010).
Wang, K. et al. In vivo imaging of tumor apoptosis using histone H1-targeting peptide. J. Controlled Release 148, 283–291 (2010).
Baish, J.W. & Jain, R.K. Cancer, angiogenesis and fractals. Nat. Med. 4, 984 (1998).
Baish, J.W. & Jain, R.K. Fractals and cancer. Cancer Res. 60, 3683–3688 (2000).
Neurath, M.F. & Kiesslich, R. Is chromoendoscopy the new standard for cancer surveillance in patients with ulcerative colitis? Nat. Clin. Pract. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 134–135 (2009).
Danese, S. et al. Narrow-band imaging endoscopy to assess mucosal angiogenesis in inflammatory bowel disease: a pilot study. World J. Gastroenterol. 16, 2396–2400 (2010).
Emura, F., Saito, Y. & Ikematsu, H. Narrow-band imaging optical chromocolonoscopy: advantages and limitations. World J. Gastroenterol. 14, 4867–4872 (2008).
Rogart, J.N. et al. Narrow-band imaging without high magnification to differentiate polyps during real-time colonoscopy: improvement with experience. Gastrointest. Endosc. 68, 1136–1145 (2008).
Yoshida, N. et al. Efficacy of magnifying endoscopy with flexible spectral imaging color enhancement in the diagnosis of colorectal tumors. J. Gastroenterol. 46, 65–72 (2011).
Hoffman, A. et al. High definition colonoscopy combined with i-Scan is superior in the detection of colorectal neoplasias compared with standard video colonoscopy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy 42, 827–833 (2010).
Acknowledgements
M.F.N. and M.J.W. were supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the Graduiertenkolleg 1043; M.F.N., S.W. and C.B. were supported by the DFG within the FOR527. M.F.N. received funding from the European Community's seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement no. 202230, acronym GENINCA. M.F.N. was supported by the United European Gastroenterology Foundation Research Prize.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.J.W., S.W., C.N. and C.B. conducted experiments. M.J.W. and M.F.N. analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and implications and commented on the manuscript at all stages.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
M.F.N. provides expert scientific advice to Pentax. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waldner, M., Wirtz, S., Neufert, C. et al. Confocal laser endomicroscopy and narrow-band imaging-aided endoscopy for in vivo imaging of colitis and colon cancer in mice. Nat Protoc 6, 1471–1481 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.377
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2011.377
This article is cited by
-
Surgical polarimetric endoscopy for the detection of laryngeal cancer
Nature Biomedical Engineering (2023)
-
Targeted detection of cancer at the cellular level during biopsy by near-infrared confocal laser endomicroscopy
Nature Communications (2022)
-
An “expressionistic” look at serrated precancerous colorectal lesions
Diagnostic Pathology (2021)
-
Machine Learning-Based Classification of the Health State of Mice Colon in Cancer Study from Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Colonoscopy-based colorectal cancer modeling in mice with CRISPR–Cas9 genome editing and organoid transplantation
Nature Protocols (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.