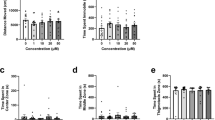
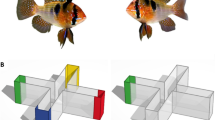
Abstract
This protocol describes conditioned place preference (CPP) in zebrafish following a single exposure to a substance. In the CPP paradigm, animals show a preference for an environment that has previously been associated with a substance (drug), thus indicating the positive-reinforcing qualities of that substance. The test tank consists of two visually distinct compartments separated by a central alley. The protocol involves three steps: the determination of initial preference, one conditioning session and the determination of final preference. This procedure is carried out in ∼2 d; other reported CPP protocols take up to 2 weeks. An increase in preference for the drug-associated compartment is observed after a single exposure. Establishment of this high-throughput protocol in zebrafish makes it possible to investigate the molecular and cellular basis of choice behavior, reward and associative learning. The protocol is also a tool for testing psychoactive compounds in the context of a vertebrate brain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tzschentke, T.M. Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm: update of the last decade. Addict. Biol. 12, 227–462 (2007).
Grunwald, D.J. & Eisen, J.S. Headwaters of the zebrafish—emergence of a new model vertebrate. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3, 717–724 (2002).
Fetcho, J.R. & Liu, K.S. Zebrafish as a model system for studying neuronal circuits and behavior. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 860, 333–345 (1998).
Guo, S. Linking genes to brain, behavior and neurological diseases: what can we learn from zebrafish? Genes Brain Behav. 3, 63–74 (2004).
White, R.M. et al. Transparent adult zebrafish as a tool for in vivo transplantation analysis. Cell Stem Cell. 2, 183–189 (2008).
Mattioli, R., Nelson, C.A., Huston, J.P. & Spieler, R.E. Conditioned place-preference analysis in the goldfish with the H1 histamine antagonist chlorpheniramine. Brain Res. Bull. 45, 41–44 (1998).
Serra, E.L., Medalha, C.C. & Mattioli, R. Natural preference of zebrafish (Danio rerio) for a dark environment. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 32, 1551–1553 (1999).
Gerlai, R., Lahav, M., Guo, S. & Rosenthal, A. Drinks like a fish: zebra fish (Danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 67, 773–782 (2000).
Maximino, C., Marques de Brito, T., Dias, C.A., Gouveia, A. Jr. & Morato, S. Scototaxis as anxiety-like behavior in fish. Nat. Protoc. 5, 209–216 (2010).
Darland, T. & Dowling, J.E. Behavioral screening for cocaine sensitivity in mutagenized zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11691–11696 (2001).
Ninkovic, J. et al. Genetic identification of AChE as a positive modulator of addiction to the psychostimulant D-amphetamine in zebrafish. J. Neurobiol. 66, 463–475 (2006).
Braida, D. et al. Hallucinatory and rewarding effect of salvinorin A in zebrafish: kappa-opioid and CB1-cannabinoid receptor involvement. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 190, 441–448 (2007).
Kily, L.J. et al. Gene expression changes in a zebrafish model of drug dependency suggest conservation of neuro-adaptation pathways. J. Exp. Biol. 211, 1623–1634 (2008).
Parmar, A., Parmar, M. & Brennan, C.H. Zebrafish conditioned place preference models of drug reinforcement and relapse to drug seeking. In Zebrafish Neurobehavioral Protocols. Vol. 51 (eds. Kalueff, A.V. & Cachat, J.M.) (Humana Press, 2011).
Lau, B., Bretaud, S., Huang, Y., Lin, E. & Guo, S. Dissociation of food and opiate preference by a genetic mutation in zebrafish. Genes Brain Behav. 5, 497–505 (2006).
Mathur, P., Berberoglu, M.A. & Guo, S. Preference for ethanol in zebrafish following a single exposure. Behav. Brain Res. 217, 128–133 (2011).
Bevins, R. The reference-dose place conditioning procedure yields a graded dose-effect function. Int. J. Comp. Psychol. 18, 101–111 (2005).
Dworkin, S. & Smith., J. Molecular mechanisms of drug reinforcement—current status. NIDA Res. Monogr. 90, 266–274 (1988).
Everitt, B.J. & Robbins, T.W. Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1481–1489 (2005).
Robinson, T.E. & Berridge, K.C. The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res. Rev. 18, 247–291 (1993).
Ninkovic, J. & Bally-Cuif, L. The zebrafish as a model system for assessing the reinforcing properties of drugs of abuse. Methods 39, 262–274 (2006).
Cunningham, C.L., Ferree, N.K. & Howard, M.A. Apparatus bias and place conditioning with ethanol in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 170, 409–422 (2003).
Cunningham, C.L., Gremel, C.M. & Groblewski, P.A. Drug-induced conditioned place preference and aversion in mice. Nat. Protoc. 1, 1662–1670 (2006).
Cunningham, C.L., Clemans, J.M. & Fidler, T.L. Injection timing determines whether intragastric ethanol produces conditioned place preference or aversion in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 72, 659–668 (2002).
Cunningham, C.L. & Prather, L.K. Conditioning trial duration affects ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Anim. Learn. Behav. 20, 187–194 (1992).
Li, L. & Dowling, J.E. A dominant form of inherited retinal degeneration caused by a non-photoreceptor cell-specific mutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 11645–11650 (1997).
Dlugos, C.A. & Rabin, R.A. Ethanol effects on three strains of zebrafish: model system for genetic investigations. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 74, 471–480 (2003).
Naidong, W. et al. Simultaneous assay of morphine, morphine-3-glucuronide and morphine-6-glucuronide in human plasma using normal-phase liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with a silica column and an aqueous organic mobile phase. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 735, 255–269 (1999).
Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book: A Guide for the Laboratory use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). 10.26 (University of Oregon Press, 2007).
Van Raaij, M.T.M., Pit, D.S.S., Balm, P.H., Steffens, A.B. & van der Thillart, G.E.E. Behavioral strategy and the physiological stress response in rainbow trout exposed to severe hypoxia. Horm. Behav. 30, 85–92 (1996).
Lockwood, B., Bjerke, S., Kobayashi, K. & Guo, S. Acute effects of alcohol on larval zebrafish: a genetic system for large-scale screening. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 77, 647–654 (2004).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Department of Neurology, Alcohol and Addiction research program at the University of California San Francisco, the Sandler Family Foundation, the Packard Foundation and NIH AA016021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.M., B.L. and S.G. designed experiments. P.M. and B.L. collected data and carried out data analyses. P.M. and S.G. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathur, P., Lau, B. & Guo, S. Conditioned place preference behavior in zebrafish. Nat Protoc 6, 338–345 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2010.201
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2010.201
This article is cited by
-
Working for food is related to range use in free-range broiler chickens
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Fatty ethanolamide of Bertholletia excelsa triglycerides (Brazil nuts): anti-inflammatory action and acute toxicity evaluation in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Inflammopharmacology (2021)
-
Increased Response to 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) Reward and Altered Gene Expression in Zebrafish During Short- and Long-Term Nicotine Withdrawal
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Nurture is above nature: nursery experience determines habitat preference of red sea bream Pagrus major juveniles
Journal of Ethology (2019)
-
Effects of Bothrops alternatus venom in zebrafish: a histopathological study
Inflammopharmacology (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.