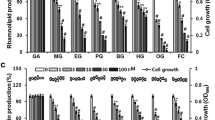
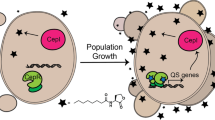
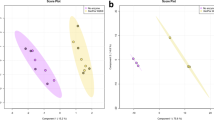
Abstract
This article will introduce the reader to protocols intended for (i) identification of quorum sensing (QS) inhibitors (QSIs), (ii) characterization of these compounds in vitro and (iii) evaluation of these compounds in animal models. Traditional antimicrobial drugs are designed against planktonic bacteria and not against bacterial biofilms. In biofilms, bacteria are highly resistant to otherwise lethal treatments and they communicate with each other, thus enabling coordinated group behavior. For many years, we have focused on interference with cell to cell communication, also known as QS, with the aim of disabling the expression of virulence and reduction of antibiotic tolerance. Here we present protocols for screening and testing for acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL)-dependent QS inhibition. We also present protocols for the in vivo validation of QSIs as possible drug candidates. The presented methods allow the evaluation of QS inhibition by a potential drug candidate within 2–3 weeks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fuqua, W.C., Winans, S.C. & Greenberg, E.P. Quorum sensing in bacteria: the LuxR-LuxI family of cell density-responsive transcriptional regulators. J. Bacteriol. 176, 269–275 (1994).
Hentzer, M. et al. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 22, 3803–3815 (2003).
Bjarnsholt, T. et al. Garlic blocks quorum sensing and promotes rapid clearing of pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Microbiology 151, 3873–3880 (2005).
Bjarnsholt, T. et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa tolerance to tobramycin, hydrogen peroxide and polymorphonuclear leukocytes is quorum-sensing dependent. Microbiology 151, 373–383 (2005).
Christensen, L.D. et al. Impact of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing on biofilm persistence in an in vivo intraperitoneal foreign-body infection model. Microbiology 153, 2312–2320 (2007).
Jensen, P.O. et al. Rapid necrotic killing of polymorphonuclear leukocytes is caused by quorum-sensing-controlled production of rhamnolipid by Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Microbiology 153, 1329–1338 (2007).
Costerton, J.W., Stewart, P.S. & Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284, 1318–1322 (1999).
Kirketerp-Moller, K. et al. Distribution, organization, and ecology of bacteria in chronic wounds. J Clin. Microbiol. 46, 2717–2722 (2008).
Homoe, P., Bjarnsholt, T., Wessman, M., Sorensen, H.C. & Johansen, H.K. Morphological evidence of biofilm formation in Greenlanders with chronic suppurative otitis media. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. (2009).
Bjarnsholt, T., Tolker-Nielsen, T., Givskov, M., Janssen, M. & Chrsitensen, L. Detection of bacteria by FISH in culture-negative soft tissue filler lesions. Dermatol. Surg. in press. (2009).
Bjarnsholt, T. et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in the respiratory tract of cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 44, 547–558 (2009).
Neut, D., van, H., Jr., van Kooten, T.G., van der Mei, H.C. & Busscher, H.J. Detection of biomaterial-associated infections in orthopaedic joint implants. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 261–268 (2003).
Givskov, M. et al. Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signalling. J. Bacteriol. 178, 6618–6622 (1996).
Wu, H. et al. Synthetic furanones inhibit quorum-sensing and enhance bacterial clearance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in mice. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 53, 1054–1061 (2004).
Rasmussen, T.B. et al. Identity and effects of quorum sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillum species. Microbiology 151, 1325–1340 (2005).
Skindersoe, M.E. et al. Quorum sensing antagonism from marine organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. (NY) 10, 56–63 (2008).
Rasmussen, T.B. et al. Screening for quorum sensing inhibitors using a novel genetic system—the QSI selector. J. Bacteriol. 187, 1799–1814 (2005).
Skindersoe, M.E. et al. Effects of antibiotics on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 3648–3663 (2008).
Yang, L. et al. Computer-aided identification of recognized drugs as Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53, 2432–2443 (2009).
Ravn, L., Christensen, A.B., Molin, S., Givskov, M. & Gram, L. Methods for detecting acylated homoserine lactones produced by Gram-negative bacteria and their application in studies of AHL-production kinetics. J Microbiol. Methods 44, 239–251 (2001).
Hentzer, M. et al. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 148, 87–102 (2002).
Pedersen, S.S., Shand, G.H., Hansen, B.L. & Hansen, G.N. Induction of experimental chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection with P. aeruginosa entrapped in alginate microspheres. APMIS 98, 203–211 (1990).
Wu, H. et al. Detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones in lung tissues of mice infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Microbiology 146 (Pt 10): 2481–2493 (2000).
Buret, A., Ward, K.H., Olson, M.E. & Costerton, J.W. An in vivo model to study the pathobiology of infectious biofilms on biomaterial surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 25, 865–874 (1991).
van, G.M. et al. Inactivation of the rhlA gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa prevents rhamnolipid production, disabling the protection against polymorphonuclear leukocytes. APMIS 117, 537–546 (2009).
Kohler, T., van Delden, C., Curty, L.K., Hamzehpour, M.M. & Pechere, J.C. Overexpression of the MexEF-OprN multidrug efflux system affects cell-to-cell signaling in Pseudomonas aeruginosa . J. Bacteriol. 183, 5213–5222 (2001).
Høiby, N. Epidemiological investigations of the respiratory tract bacteriology in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta. Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. B Microbiol. Immunol. 82, 541–550 (1974).
Acknowledgements
We thank Anne Kirstine Nielsen for her contribution to experimental setups.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed extensively to developing and writing the protocols presented in this paper.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bjarnsholt, T., van Gennip, M., Jakobsen, T. et al. In vitro screens for quorum sensing inhibitors and in vivo confirmation of their effect. Nat Protoc 5, 282–293 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.205
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2009.205
This article is cited by
-
Plant growth-promoting activity and quorum quenching-mediated biocontrol of bacterial phytopathogens by Pseudomonas segetis strain P6
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia AHL-Degrading Strains Isolated from Marine Invertebrate Microbiota Attenuate the Virulence of Pectobacterium carotovorum and Vibrio coralliilyticus
Marine Biotechnology (2019)
-
Reconstruction of the metabolic network of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to interrogate virulence factor synthesis
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Reducing Virulence and Biofilm of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Potential Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Carotenoid: Zeaxanthin
Microbial Ecology (2017)
-
Mechanism of azithromycin inhibition of HSL synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Scientific Reports (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.