Abstract
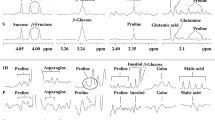
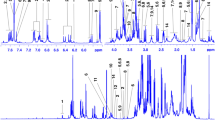
Metabolite fingerprinting provides a powerful method for discriminating between biological samples on the basis of differences in metabolism caused by such factors as growth conditions, developmental stage or genotype. This protocol describes a technique for acquiring metabolite fingerprints from samples of plant origin. The preferred method involves freezing the tissue rapidly to stop metabolism, extracting soluble metabolites using perchloric acid (HClO4) and then obtaining a fingerprint of the metabolic composition of the sample using 1D 1H NMR spectroscopy. The spectral fingerprints of multiple samples may be analyzed using either unsupervised or supervised multivariate statistical methods, and these approaches are illustrated with data obtained from the developing seeds of two genotypes of sunflower (Helianthus annuus). Preparation of plant extracts for analysis takes 2–3 d, but multiple samples can be processed in parallel and subsequent acquisition of NMR spectra takes ∼30 min per sample, allowing 24–48 samples to be analyzed in a week.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roessner, U., Willmitzer, L. & Fernie, A.R. Metabolic profiling and biochemical phenotyping of plant systems. Plant Cell Rep. 21, 189–196 (2002).
Sumner, L.W., Mendes, P. & Dixon, R.A. Plant metabolomics: large-scale phytochemistry in the functional genomics era. Phytochemistry 62, 817–836 (2003).
Weckwerth, W. Metabolomics in systems biology. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 54, 669–689 (2003).
Bino, R.J. et al. Potential of metabolomics as a functional genomics tool. Trends Plant Sci. 9, 418–425 (2004).
Fernie, A.R., Trethewey, R.N., Krotzky, A.J. & Willmitzer, L. Metabolite profiling: from diagnostics to systems biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 763–769 (2004).
Kopka, J., Fernie, A., Weckwerth, W., Gibon, Y. & Stitt, M. Metabolite profiling in plant biology: platforms and destinations. Genome Biol. 5, 109 (2004).
Krishnan, P., Kruger, N.J. & Ratcliffe, R.G. Metabolite fingerprinting and profiling in plants using NMR. J. Exp. Bot. 56, 255–265 (2005).
Ratcliffe, R.G. & Shachar-Hill, Y. Revealing metabolic phenotypes in plants: inputs from NMR analysis. Biol. Rev. 80, 27–43 (2005).
Bhalla, R., Narasimhan, K. & Swarup, S. Metabolomics and its role in understanding cellular responses in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 24, 562–571 (2005).
Hall, R.D. Plant metabolomics: from holistic hope, to hype, to hot topic. New Phytol. 169, 453–468 (2006).
Holmes, E., Tang, H., Wang, Y. & Seger, C. The assessment of plant metabolite profiles by NMR-based methodologies. Planta Med. 72, 771–785 (2006).
Schauer, N. & Fernie, A.R. Plant metabolomics: towards biological function and mechanism. Trends Plant Sci. 11, 508–516 (2006).
Dixon, R.A. et al. Applications of metabolomics in agriculture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 54, 8984–8994 (2006).
Last, R.L., Jones, A.D. & Shachar-Hill, Y. Towards the plant metabolome and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 167–174.
Ward, J.L., Baker, J.M. & Beale, M.H. Recent applications of NMR spectroscopy in plant metabolomics. FEBS J. 274, 1126–1131 (2007).
Colquhoun, I.J. Use of NMR for metabolic profiling in plant systems. J. Pestic. Sci. 32, 200–212 (2007).
Seger, C. & Sturm, S. Analytical aspects of plant metabolite profiling platforms: current standings and future aims. J. Proteome Res. 6, 480–497 (2007).
Verpoorte, R., Choi, Y.H. & Kim, H.K. NMR-based metabolomics at work in phytochemistry. Phytochem. Rev. 6, 3–14 (2007).
Kruger, N.J. & Ratcliffe, R.G. Metabolic organization in plants: a challenge for the metabolic engineer. in Advances in Plant Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Vol. 1. Bioengineering and Molecular Biology of Plant Pathways (eds. Bohnert, H.J., Nguyen, H. & Lewis, N.G.) 1–27 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2008).
Belton, P.S. et al. Application of chemometrics to the 1H NMR spectra of apple juices: discrimination between apple varieties. Food Chem. 61, 207–213 (1998).
Pereira, G.E. et al. 1H NMR metabolite fingerprints of grape berry: comparison of vintage and soil effects in Bordeaux grapevine growing areas. Anal. Chim. Acta 563, 346–352 (2006).
Bailey, N.J. et al. Prediction of anti-plasmodial activity of Artemisia annua extracts: application of 1H NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 35, 117–126 (2004).
Noteborn, H.P.J.M., Lommen, A., van der Jagt, R.C. & Weseman, J.M. Chemical fingerprinting for the evaluation of unintended secondary metabolic changes in transgenic food crops. J. Biotechnol. 77, 103–114 (2000).
Charlton, A. et al. NMR profiling of transgenic peas. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2, 27–35 (2004).
Choi, H.K. et al. Metabolic fingerprinting of wild type and transgenic tobacco plants by 1H NMR and multivariate analysis technique. Phytochemistry 65, 857–864 (2004).
Catchpole, G.S. et al. Hierarchical metabolomics demonstrates substantial compositional similarity between genetically modified and conventional potato crops. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 14458–14462 (2005).
Baker, J.M. et al. A metabolomic study of substantial equivalence of field-grown genetically modified wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 4, 381–392 (2006).
Wu, L., van Winden, W.A., van Gulik, W.M. & Heijnen, J.J. Application of metabolome data in functional genomics: a conceptual study. Metab. Eng. 7, 302–310 (2005).
Ott, K.H., Araníbar, N., Singh, B. & Stockton, G.W. Metabonomics classifies pathways affected by bioactive compounds. Artificial neural network classification of NMR spectra of plant extracts. Phytochemistry 62, 971–985 (2003).
Kruger, N.J., Huddleston, J.E., Le Lay, P., Brown, N.D. & Ratcliffe, R.G. Network flux analysis: impact of 13C-substrates on metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspension cultures. Phytochemistry 68, 2176–2188 (2007).
Wishart, D.S. Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. Trends Analyt. Chem. 27, 228–237 (2008).
Fiehn, O. et al. Minimum reporting standards for plant biology context information in metabolomic studies. Metabolomics 3, 195–201 (2007).
Rubtsov, D. et al. Proposed reporting requirements for the description of NMR-based metabolomics experiments. Metabolomics 3, 223–229 (2007).
Goodacre, R. et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for data analysis in metabolomics. Metabolomics 3, 231–241 (2007).
Fiehn, O. et al. Quality control for plant metabolomics: reporting MSI-compliant studies. Plant J. 53, 691–704 (2008).
Trygg, J., Holmes, E. & Lunsdstedt, T. Chemometrics in metabonomics. J. Proteome Res. 6, 469–479 (2007).
Kemsley, E.K. et al. Multivariate techniques and their application in nutrition: a metabolomics case study. Br. J. Nutr. 98, 1–14 (2007).
Gartland, K.P. et al. Pattern recognition analysis of high resolution 1H NMR spectra of urine. A nonlinear mapping approach to the classification of toxicological data. NMR Biomed. 3, 166–172 (1990).
Tikunov, Y. et al. A novel approach for nontargeted data analysis for metabolomics. Large-scale profiling of tomato fruit volatiles. Plant Physiol. 139, 1125–1137 (2005).
Goodacre, R., York, E.V., Heald, J.K. & Scott, I.M. Chemometric discrimination of unfractionated plant extracts profiled by flow-injection electrospray mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry 62, 859–863 (2003).
Eriksson, L. et al. Multi- and Megavariate Data Analysis 2nd edn. (Umetrics Academy, Umeå, Sweden, 2006).
Jonsson, P. et al. Extraction, interpretation and validation of information for comparing samples in metabolic LC/MS data sets. Analyst 130, 701–707 (2005).
Cloarec, O. et al. Evaluation of the orthogonal projection on latent structure model limitations caused by chemical shift variability and improved visualization of biomarker changes in 1H NMR spectroscopic metabonomic studies. Anal. Chem. 77, 517–526 (2005).
Bylesjö, M. et al. OPLS discriminant analysis: combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. J. Chemometrics 20, 341–351 (2006).
Forshed, J. et al. A comparison of methods for alignment of NMR peaks in the context of cluster analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 38, 824–832 (2005).
Craig, A., Cloarec, O., Holmes, E., Nicholson, J.K. & Lindon, J.C. Scaling and normalization effects in NMR spectroscopic metabonomic data sets. Anal. Chem. 78, 2262–2267 (2006).
van den Berg, R.A., Hoefsloot, H.C., Westerhuis, J.A., Smilde, A.K. & van der Werf, M.J. Centering, scaling, and transformations: improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genomics 7, 142 (2006).
Akoka, S., Barantin, L. & Trierweiler, M. Concentration measurement by proton NMR using the ERETIC method. Anal. Chem. 71, 2554–2557 (1999).
Wiklund, S. et al. Visualization of GC/TOF-MS-based metabolomics data for identification of biochemically interesting compounds using OPLS class models. Anal. Chem. 80, 115–122 (2008).
Bieleski, R.L. The problem of halting enzyme action when extracting plant tissues. Anal. Biochem. 9, 431–442 (1964).
ap Rees, T. Pathways of carbohydrate breakdown in plants. in MTP International Review of Science, Biochemistry Series 1, Vol. XI. Plant Biochemistry (ed. Northcote, D.H.) 89–127 (Butterworth, London, 1974).
Passonneau, J.V. & Lowry, O.H. Enzymatic Analysis: A Practical Guide (Humana Press, Totowa, New Jersey, 1993).
Wollenberger, A., Ristau, O. & Schoffa, G. Eine einfache Technik der extrem schnellen Abkühlung größerer Gewebestücke. Pflügers Arch. 270, 399–412 (1960).
Leidenfrost, J.G. De Aquae Communis Nonnullis Qualitatibus Tractatus (A Tract About Some Qualities of Common Water), Duisburg, (1756); Section translated into English by Wares, C. On the fixation of water in diverse fire. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 9, 1153–1166 (1966).
Gullberg, J., Jonsson, P., Nordstrom, A., Sjostrom, M. & Moritz, T. Design of experiments: an efficient strategy to identify factors influencing extraction and derivatization of Arabidopsis thaliana samples in metabolomic studies with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 331, 283–295 (2004).
Lin, C., Wu, H., Tjeerdema, R. & Viant, M. Evaluation of metabolite extraction strategies from tissue samples using NMR metabolomics. Metabolomics 3, 55–67 (2007).
Le Gall, G., Colquhoun, I.J., Davis, A.L., Collins, G.J. & Verhoeyen, M.E. Metabolite profiling of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) using 1H NMR spectroscopy as a tool to detect potential unintended effects following a genetic modification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 51, 2447–2456 (2003).
Roessner, U., Wagner, C., Kopka, J., Trethewey, R.N. & Willmitzer, L. Simultaneous analysis of metabolites in potato tuber by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Plant J. 23, 131–142 (2000).
Keun, H.C. et al. Analytical reproducibility in 1H NMR-based metabonomic urinalysis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 15, 1380–1386 (2002).
Nguyen, B.D., Meng, X., Donovan, K.J. & Shaka, A.J. SOGGY: solvent-optimized double gradient spectroscopy for water suppression. A comparison with some existing techniques. J. Magn. Reson. 184, 263–274 (2007).
Becker, E.D., Ferretti, J.A. & Gambhir, P.N. Selection of optimum parameters for pulse Fourier-transform nuclear magnetic-resonance. Anal. Chem. 51, 1413–1420 (1979).
Lindon, J.C. & Nicholson, J.K. Analytical technologies for metabonomics, and multi-omic information recovery. Trends Analyt. Chem. 27, 194–204 (2008).
Lommen, A., Weseman, J.M., Smith, G.O. & Noteborn, H.P.J.M. On the detection of environmental effects on complex matrices combining off-line liquid chromatography and 1H NMR. Biodegradation 9, 513–525 (1998).
Defernez, M. & Colquhoun, I.J. Factors affecting the robustness of metabolite fingerprinting using 1H NMR spectra. Phytochemistry 62, 1009–1017 (2003).
Larsen, F.H., van den Berg, F. & Engelsen, S.B. An exploratory chemometric study of 1H NMR spectra of table wines. J. Chemometrics 20, 198–208 (2006).
Yazdisamadi, B., Rinne, R.W. & Seif, R.D. Components of developing soybean seeds—oil, protein, sugars, starch, organic acids, and amino acids. Agron. J. 69, 481–486 (1977).
Borisjuk, L. et al. Spatial analysis of plant metabolism: Sucrose imaging within Vicia faba cotyledons reveals specific developmental patterns. Plant J. 29, 521–530 (2002).
Hill, L.M., Morley-Smith, E.R. & Rawsthorne, S. Metabolism of sugars in the endosperm of developing seeds of oilseed rape. Plant Physiol. 131, 228–236 (2003).
Weschke, W. et al. The role of invertases and hexose transporters in controlling sugar ratios in maternal and filial tissues of barley caryopses during early development. Plant J. 33, 395–411 (2003).
Lisec, J., Schauer, N., Kopka, J., Willmitzer, L. & Fernie, A.R. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling in plants. Nat. Protoc. 1, 387–396 (2006).
Beckonert, O. et al. Metabolic profiling, metabolomic and metabonomic procedures for NMR spectroscopy of urine, plasma, serum and tissue extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2, 2692–2703 (2007).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council of the United Kingdom (grant # B17210), the Spanish 'Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia' and FEDER project AGL2005-00100 and funding from the Programa CSIC-I3P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kruger, N., Troncoso-Ponce, M. & Ratcliffe, R. 1H NMR metabolite fingerprinting and metabolomic analysis of perchloric acid extracts from plant tissues. Nat Protoc 3, 1001–1012 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.64
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.64
This article is cited by
-
Unrevealing metabolomics for abiotic stress adaptation and tolerance in plants
Journal of Crop Science and Biotechnology (2021)
-
Optimizing 1D 1H-NMR profiling of plant samples for high throughput analysis: extract preparation, standardization, automation and spectra processing
Metabolomics (2019)
-
Simultaneous untargeted and targeted metabolomics profiling of underivatized primary metabolites in sulfur-deficient barley by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Plant Methods (2018)
-
Aluminium-induced excessive ROS causes cellular damage and metabolic shifts in black gram Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper
Protoplasma (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.