Abstract
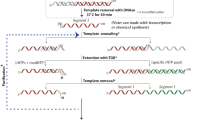
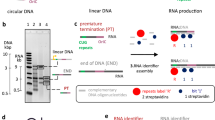
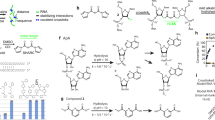
RNA structure determination by solution NMR spectroscopy is often restricted to small RNAs (<15 kDa) owing to the problem of chemical shift degeneracy. A fruitful coupling of novel NMR techniques with segmental RNA labeling methodologies could be a powerful tool to overcome the molecular mass limitation of RNA NMR spectroscopy. Herein, we describe a time- and cost-effective procedure to prepare and purify segmentally labeled large RNAs. Two sets of RNA fragments with complementary labeling schemes, such as one fragment 13C- and the other 15N-labeled, are prepared by in vitro transcription from a single plasmid DNA. The desired RNA fragments are excised from the primary transcript by two cis-acting hammerhead ribozymes, yielding the required engineered ends for subsequent, complementary ligation. The resulting RNA oligonucleotides display NMR spectra with greatly reduced resonance overlap and thus enable NMR studies of smaller labeled RNA segments within the native context of a large RNA. The procedure is expected to take 3–4 weeks to implement.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varani, G., Aboul-Ela, F. & Allain, F. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 29, 51–127 (1996).
Furtig, B., Richter, C., Wohnert, J. & Schwalbe, H. NMR spectroscopy of RNA. ChemBioChem 4, 936–962 (2003).
Latham, M.P., Brown, D.J., McCallum, S.A. & Pardi, A. NMR methods for studying the structure and dynamics of RNA. Chembiochem 6, 1492–1505 (2005).
Tjandra, N. & Bax, A. Direct measurement of distances and angles in biomolecules by NMR in a dilute liquid crystalline medium. Science 278, 1111–1114 (1997).
Zhou, H., Vermeulen, A., Jucker, F.M. & Pardi, A. Incorporating residual dipolar couplings into the NMR solution structure determination of nucleic acids. Biopolymers 52, 168–180 (1999).
Hansen, M.R., Hanson, P. & Pardi, A. Filamentous bacteriophage for aligning RNA, DNA, and proteins for measurement of nuclear magnetic resonance dipolar coupling interactions. Methods Enzymol. 317, 220–240 (2000).
Mollova, E.T. & Pardi, A. NMR solution structure determination of RNAs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 10, 298–302 (2000).
Lukavsky, P.J. & Puglisi, J.D. Structure determination of large biological RNAs. Methods Enzymol. 394, 399–416 (2005).
Lukavsky, P.J., Kim, I., Otto, G.A. & Puglisi, J.D. Structure of HCV IRES domain II determined by NMR. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10, 1033–1038 (2003).
D'Souza, V., Dey, A., Habib, D. & Summers, M.F. NMR structure of the 101-nucleotide core encapsidation signal of the Moloney murine leukemia virus. J. Mol. Biol. 337, 427–442 (2004).
Chen, Y. et al. Structure of stem-loop IV of Tetrahymena telomerase RNA. EMBO J. 25, 3156–3166 (2006).
Kim, I., Lukavsky, P.J. & Puglisi, J.D. NMR study of 100 kDa HCV IRES RNA using segmental isotope labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 9338–9339 (2002).
Tzakos, A.G., Easton, L.E. & Lukavsky, P.J. Complementary segmental labeling of large RNAs: economic preparation and simplified NMR spectra for measurement of more RDCs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 13344–13345 (2006).
Ferbeyre, G., Bourdeau, V., Pageau, M., Miramontes, P. & Cedergren, R. Distribution of hammerhead and hammerhead-like RNA motifs through the GenBank. Genome Res. 10, 1011–1019 (2000).
Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3406–3415 (2003).
Tiedge, H., Zhou, A., Thorn, N.A. & Brosius, J. Transport of BC1 RNA in hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal axons. J. Neurosci. 13, 4214–4219 (1993).
Batey, R.T., Battiste, J.L. & Williamson, J.R. Preparation of isotopically enriched RNAs for heteronuclear NMR. Methods Enzymol. 261, 300–322 (1995).
Li, Y., Wang, E. & Wang, Y. A modified procedure for fast purification of T7 RNA polymerase. Protein Expr. Purif. 16, 355–358 (1999).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual 3rd edn. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 2001).
Ausubel, F.M. et al. (eds). Short Protocols in Molecular Biology: A Compedium of Methods. (John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, 2002).
Tanner, N.K. et al. A three-dimensional model of hepatitis delta virus ribozyme based on biochemical and mutational analyses. Curr. Biol. 4, 488–498 (1994).
Guo, H.C. & Collins, R.A. Efficient trans-cleavage of a stem–loop RNA substrate by a ribozyme derived from neurospora VS RNA. EMBO J. 14, 368–376 (1995).
Acknowledgements
A.G.T. is grateful for an EMBO long-term fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzakos, A., Easton, L. & Lukavsky, P. Preparation of large RNA oligonucleotides with complementary isotope-labeled segments for NMR structural studies. Nat Protoc 2, 2139–2147 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.306
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.306
This article is cited by
-
Isotope labeling for studying RNA by solid-state NMR spectroscopy
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2018)
-
Isotope labeling strategies for NMR studies of RNA
Journal of Biomolecular NMR (2010)
-
The preparation of site-specifically modified riboswitch domains as an example for enzymatic ligation of chemically synthesized RNA fragments
Nature Protocols (2008)
-
Purification and characterization of transcribed RNAs using gel filtration chromatography
Nature Protocols (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.