Abstract
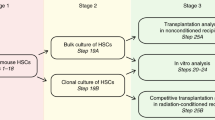
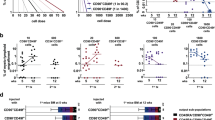
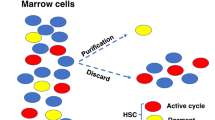
Mouse hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the best-studied stem cells because functional assays for mouse HSCs were established earliest and purification techniques for mouse HSCs have progressed furthest. Here we describe our current protocols for the purification of CD34−/lowc-Kit+Sca-1+lineage marker− (CD34−KSL) cells, the HSC population making up approximately 0.005% of bone marrow cells in adult C557BL/6 mice. Purified HSCs have been characterized at cellular and molecular levels. Since clonal analysis is essential for the study of self-renewal and lineage commitment in HSCs, here we present our single-cell colony assay and single-cell transplantation procedures. We also introduce our immunostaining procedures for small numbers of HSCs, which are useful for signal transduction analysis. The purification of CD34−KSL cells requires approximately 6 h. Initialization of single-cell culture requires approximately 1 h. Single-cell transplantation requires approximately 6 h. Single-cell immunostaining requires approximately 2 d.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Micklem, H.S., Ford, C.E., Evans, E.P., Ogden, D.A. & Papworth, D.S. Competitive in vivo proliferation of foetal and adult haematopoietic cells in lethally irradiated mice. J. Cell. Physiol. 79, 293–298 (1972).
Harrison, D.E., Jordan, C.T., Zhong, R.K. & Astle, C.M. Primitive hemopoietic stem cells: direct assay of most productive populations by competitive repopulation with simple binomial, correlation and covariance calculations. Exp. Hematol. 21, 206–219 (1993).
Szilvassy, S.J., Humphries, R.K., Lansdorp, P.M., Eaves, A.C. & Eaves, C.J. Quantitative assay for totipotent reconstituting hematopoietic stem cells by a competitive repopulation strategy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 8736–8740 (1990).
Osawa, M., Hanada, K.-I., Hamada, H. & Nakauchi, H. Long-term lymphohematopoietic reconstitution by a single CD34-low/negative hematopoietic stem cell. Science 273, 242–245 (1996).
Ema, H. et al. Quantification of self-renewal capacity in single hematopoietic stem cells from normal and Lnk-deficient mice. Dev. Cell 8, 907–914 (2005).
Ivanova, N.B. et al. A stem cell molecular signature. Science 298, 601–604 (2002).
Ramalho-Santos, M., Yoon, S., Matsuzaki, Y., Mulligan, R.C. & Melton, D.A. 'Stemness': transcriptional profiling of embryonic and adult stem cells. Science 298, 597–600 (2002).
Park, I.-K. et al. Differential gene expression profiling of adult murine hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 99, 488–498 (2002).
Forsberg, E.C. et al. Differential expression of novel potential regulators in hematopoietic stem cells. PLoS Genet. 1, e28 (2005).
Kiel, M.J. et al. SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell 121, 1109–1121 (2005).
Visser, J.W., Bauman, J.G., Mulder, A.H., Eliason, J.F. & de Leeuw, A.M. Isolation of murine pluripotent hemopoietic stem cells. J. Exp. Med. 159, 1576–1590 (1984).
Spangrude, G.J., Heimfeld, S. & Weissman, I.L. Purification and characterization of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. Science 241, 58–62 (1988).
Sitnicka, E. et al. Key role of flt3 ligand in regulation of the common lymphoid progenitor but not in maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool. Immunity 17, 463–472 (2002).
Forsberg, E.C., Serwold, T., Kogan, S., Weissman, I.L. & Passegue, E. New evidence supporting megakaryocyte-erythrocyte potential of flk2/flt3+ multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. Cell 126, 415–426 (2006).
Uchida, N., Dykstra, B., Lyons, K.J., Leung, F.Y.K. & Eaves, C.J. Different in vivo repopulating activities of purified hematopoietic stem cells before and after being stimulated to divide in vitro with the same kinetics. Exp. Hematol. 31, 1338–1347 (2003).
Benveniste, P., Cantin, C., Hyam, D. & Iscove, N.N. Hematopoietic stem cells engraft in mice with absolute efficiency. Nat. Immunol. 4, 708–713 (2003).
Matsuzaki, Y., Kinjo, K., Mulligan, R.C. & Okano, H. Unexpectedly efficient homing capacity of purified murine hematopoietic stem cells. Immunity 20, 87–93 (2004).
Camargo, F.D., Chambers, S.M., Drew, E., McNagny, K.M. & Goodell, M.A. Hematopoietic stem cells do not engraft with absolute efficiencies. Blood 107, 501–507 (2006).
Ema, H. & Nakauchi, H. Self-renewal and lineage restriction of hematopoietic stem cells. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 13, 508–512 (2003).
Rosendaal, M., Hodgson, G.S. & Bradley, T.R. Organization of haemopoietic stem cells: the generation-age hypothesis. Cell Tissue Kinet. 12, 17–29 (1979).
Goodell, M.A., Brose, K., Paradis, G., Conner, A.S. & Mulligan, R.C. Isolation and functional properties of murine hematopoietic stem cells that are replicating in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 183, 1797–1806 (1996).
Goodell, M.A. et al. Dye efflux studies suggest that hematopoietic stem cells expressing low or undetectable levels of CD34 antigen exist in multiple species. Nat. Med. 3, 1337–1345 (1997).
Morita, Y., Ema, H., Yamazaki, S. & Nakauchi, H. Non-side-population hematopoietic stem cells in mouse bone marrow. Blood 108, 2850–2856 (2006).
Balazs, A.B., Fabian, A.J., Esmon, C.T. & Mulligan, R.C. Endothelial protein C receptor (CD201) explicitly identifies hematopoietic stem cells in murine bone marrow. Blood 107, 2317–2321 (2006).
Ema, H., Suda, T., Miura, Y. & Nakauchi, H. Colony formation of clone-sorted human hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 75, 1941–1946 (1990).
Takano, H., Ema, H., Sudo, K. & Nakauchi, H. Asymmetric division and lineage commitment at the level of hematopoietic stem cells: inference from differentiation in daughter cell and granddaughter cell pairs. J. Exp. Med. 199, 295–302 (2004).
Yamazaki, S. et al. Cytokine signals modulated via lipid rafts mimic niche signals and induce hibernation in hematopoietic stem cells. EMBO J. 25, 3515–3523 (2006).
Seita, J. et al. Lnk negatively regulates self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells by modifying thrombopoietin-mediated signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA (2007) in the press.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank A. S. Knisely for critically reviewing the manuscript. The work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ema, H., Morita, Y., Yamazaki, S. et al. Adult mouse hematopoietic stem cells: purification and single-cell assays. Nat Protoc 1, 2979–2987 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.447
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.447
This article is cited by
-
Chemically defined cytokine-free expansion of human haematopoietic stem cells
Nature (2023)
-
PI(18:1/18:1) is a SCD1-derived lipokine that limits stress signaling
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Aneuploidy-inducing gene knockdowns overlap with cancer mutations and identify Orp3 as a B-cell lymphoma suppressor
Oncogene (2020)
-
Long-term ex vivo expansion of mouse hematopoietic stem cells
Nature Protocols (2020)
-
High Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Activity Sensitizes Murine Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells to DNA Damage
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.