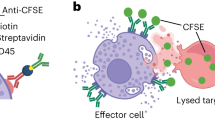
Abstract
We have developed a method exploiting the phenomenon of trogocytosis to detect lymphocytes reacting specifically with target cells by flow cytometry. Trogocytosis is a process by which lymphocytes capture fragments of the plasma membrane from the antigen-presenting cells (APCs) expressing their cognate antigen. For this method, a label (such as a fluorescent lipid or biotin) is first incorporated in the membrane of APCs. These labeled cells are then co-cultured for a few hours with a population of cells containing the lymphocytes to be detected. After this period of stimulation, lymphocytes that have performed trogocytosis are identified by their acquisition of the label initially present on the APC membrane using flow cytometry. A major advantage of this method is its compatibility with the simultaneous detection of phenotypic and/or functional markers on the lymphocytes. Furthermore, cells can be recovered alive and active after detection of trogocytosis, and are therefore available for further characterization or even conceivably for therapeutic purposes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman, J.D. et al. Phenotypic analysis of antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Science 274, 94–96 (1996).
Kohrt, H.E. et al. Rapid assessment of recognition efficiency and functional capacity of antigen-specific T-cell responses. J. Immunother. 28, 297–305 (2005).
Betts, M.R. et al. Sensitive and viable identification of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by a flow cytometric assay for degranulation. J. Immunol. Methods 281, 65–78 (2003).
Rubio, V. et al. Ex vivo identification, isolation and analysis of tumor-cytolytic T cells. Nat. Med. 9, 1377–1382 (2003).
Chattopadhyay, P.K., Yu, J. & Roederer, M. A live-cell assay to detect antigen-specific CD4+ T cells with diverse cytokine profiles. Nat. Med. 11, 1113–1117 (2005).
Hudrisier, D., Riond, J., Garidou, L., Duthoit, C. & Joly, E. T Cell activation correlates with an increased proportion of antigen among the materials acquired from target cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 35, 2284–2294 (2005).
Huang, J.F. et al. TCR-mediated internalization of peptide-MHC complexes acquired by T cells. Science 286, 952–954 (1999).
Tomaru, U. et al. Detection of virus-specific T cells and CD8(+) T-cell epitopes by acquisition of peptide-HLA-GFP complexes: analysis of T-cell phenotype and function in chronic viral infections. Nat. Med. 9, 469–476 (2003).
Wetzel, S., McKeithan, T. & Parker, D. Peptide-specific intercellular transfer of MHC Class II to CD4 T cells directly from the immunological synapse upon cellular dissociation. J. Immunol. 174, 80–89 (2005).
Batista, F.D., Iber, D. & Neuberger, M.S. B cells acquire antigen from target cells after synapse formation. Nature 411, 489–494 (2001).
Joly, E. & Hudrisier, D. What is trogocytosis and what is its purpose? Nat. Immunol. 4, 815 (2003).
Hudrisier, D., Riond, J., Mazarguil, H., Gairin, J.E. & Joly, E. Cutting edge: CTLs rapidly capture membrane fragments from target cells in a TCR signaling-dependent manner. J. Immunol. 166, 3645–3649 (2001).
Beadling, C. & Slifka, M. Quantifying viable virus-specific T cells without a priori knowledge of fine epitope specificity. Nat. Med. 12, 1208–1212 (2006).
Puaux, A. et al. A very rapid and simple assay based on trogocytosis to detect and measure specific T and B cells reactivity by flow cytometry. Eur. J. Immunol. 36, 779–788 (2006).
Machlenkin, A. et al. Membrane capture by tumour-reactive T cells: a novel concept in detection and isolation of functional cytotoxic lymphocytes. in European Congress of Immunology Institute, Paris (2006).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from the ANR (TEAAVAC project, to E.J.), the Région Midi-Pyrénées (to D.H.), the Ligue Régionale Contre le Cancer (to E.J.) and the CNRS. We thank the European Journal of Immunology for permitting us to use figures from the manuscript by Puaux et al.14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.D. and A.-L.P. contributed equally to this work. E.J. and D.H. contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daubeuf, S., Puaux, AL., Joly, E. et al. A simple trogocytosis-based method to detect, quantify, characterize and purify antigen-specific live lymphocytes by flow cytometry, via their capture of membrane fragments from antigen-presenting cells. Nat Protoc 1, 2536–2542 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.400
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.400
This article is cited by
-
Extracellular vesicle-mediated MHC cross-dressing in immune homeostasis, transplantation, infectious diseases, and cancer
Seminars in Immunopathology (2018)
-
Fas stimulation of T lymphocytes promotes rapid intercellular exchange of death signals via membrane nanotubes
Cell Research (2010)
-
Trans-SILAC: sorting out the non-cell-autonomous proteome
Nature Methods (2010)
-
Intercellular Exchange of Surface Molecules and its Physiological Relevance
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.