Abstract
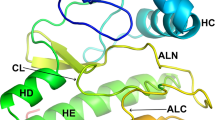
Protein kinases are essential effectors of cellular signaling. Surprisingly, using bioinformatics tools, we predicted protein kinase structure and function for proteins of unknown function (FAM69 family) coded by five related human genes and their Metazoan homologues. Analysis of three-dimensional structure models and conservation of the classic catalytic motifs of protein kinases in four of human FAM69 proteins suggests they might have retained catalytic phosphotransferase activity. The FAM69 genes, FAM69A, FAM69B, FAM69C, C3ORF58 and CXORF36, are by large uncharacterized molecularly, yet linked to several neurological disorders in genetics studies. An EF-hand Ca2+-binding domain in FAM69A and FAM69B proteins, inserted within the structure of the kinase domain, suggests they function as Ca2+-dependent kinases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dudkiewicz, M., Lenart, A. & Pawłowski, K. A novel predicted calcium-regulated kinase family implicated in neurological disorders . Nat Prec (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.7015.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.7015.1