Abstract
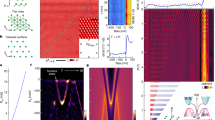
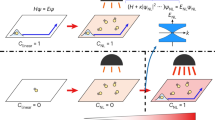
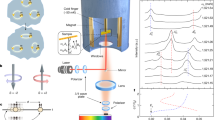
Ring exchange is an elementary interaction for modelling unconventional topological matter. Here, we report the observation of four-body ring-exchange interactions and the topological properties of anyonic excitations within an ultracold atom system. A minimum toric-code Hamiltonian, in which the ring exchange is the dominant term, was implemented in disconnected four-spin plaquette arrays formed by two orthogonal superlattices. The ring-exchange interactions were resolved from the dynamical evolutions of the spin orders in each plaquette, matching well with the predicted energy gaps between two anyonic excitations of the spin system. A braiding operation was applied to the spins in the plaquettes and an induced phase 1.00(3)π in the four-spin state was observed, confirming 1/2 mutual statistics. This work offers new prospects for the quantum simulation of topological phases by engineering many-body interactions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nielsen, M. & Chuang, I. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2000).
Steane, A. M. Error correcting codes in quantum theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 793–797 (1996).
Knill, E. Quantum computing with realistically noisy devices. Nature 434, 39–44 (2005).
Kitaev, A. Fault-tolerant quantum computation by anyons. Ann. Phys. 303, 2–30 (2003).
Wilczek, F. Quantum mechanics of fractional-spin particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 957–959 (1982).
Han, Y.-J., Raussendorf, R. & Duan, L.-M. Scheme for demonstration of fractional statistics of anyons in an exactly solvable model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 150404 (2007).
Müller, M., Hammerer, K., Zhou, Y. L., Roos, C. F. & Zoller, P. Simulating open quantum systems: from many-body interactions to stabilizer pumping. New J. Phys. 13, 085007 (2011).
Marcos, D. et al. Two-dimensional lattice gauge theories with superconducting quantum circuits. Ann. Phys. 351, 634–654 (2014).
Paredes, B. & Bloch, I. Minimum instances of topological matter in an optical plaquette. Phys. Rev. A 77, 023603 (2008).
Büchler, H. P., Hermele, M., Huber, S. D., Fisher, M. P. A. & Zoller, P. Atomic quantum simulator for lattice gauge theories and ring exchange models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 040402 (2005).
Aguado, M., Brennen, G. K., Verstraete, F. & Cirac, J. I. Creation, manipulation, and detection of Abelian and non-Abelian anyons in optical lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 260501 (2008).
Weimer, H., Müller, M., Lesanovsky, I., Zoller, P. & Büchler, H. P. A Rydberg quantum simulator. Nat. Phys. 6, 382–388 (2010).
Wiese, U.-J. Ultracold quantum gases and lattice systems: quantum simulation of lattice gauge theories. Ann. Phys. 525, 777–796 (2013).
Tagliacozzo, L., Celi, A., Orland, P., Mitchell, M. W. & Lewenstein, M. Simulation of non-Abelian gauge theories with optical lattices. Nat. Commun. 4, 3615 (2013).
Banerjee, D. et al. Atomic quantum simulation of U(N) and SU(N) non-Abelian lattice gauge theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 125303 (2013).
Zohar, E., Cirac, J. I. & Reznik, B. Quantum simulations of lattice gauge theories using ultracold atoms in optical lattices. Rep. Prog. Phys. 79, 014401 (2016).
Lu, C.-Y. et al. Demonstrating anyonic fractional statistics with a six-qubit quantum simulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 030502 (2009).
Pachos, J. K. et al. Revealing anyonic features in a toric code quantum simulation. New J. Phys. 11, 083010 (2009).
Feng, G., Long, G. & Laflamme, R. Experimental simulation of anyonic fractional statistics with an nmr quantum-information processor. Phys. Rev. A 88, 022305 (2013).
Park, A. J., McKay, E., Lu, D. & Laflamme, R. Simulation of anyonic statistics and its topological path independence using a seven-qubit quantum simulator. New J. Phys. 18, 043043 (2016).
Barreiro, J. T. et al. An open-system quantum simulator with trapped ions. Nature 470, 486–491 (2011).
Jiang, L. et al. Anyonic interferometry and protected memories in atomic spin lattices. Nat. Phys. 4, 482–488 (2008).
Jaksch, D., Bruder, C., Cirac, J. I., Gardiner, C. W. & Zoller, P. Cold bosonic atoms in optical lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 3108–3111 (1998).
Bloch, I., Dalibard, J. & Zwerger, W. Many-body physics with ultracold gases. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 885–964 (2008).
Simon, J. et al. Quantum simulation of antiferromagnetic spin chains in an optical lattice. Nature 472, 307–312 (2011).
Fukuhara, T. et al. Quantum dynamics of a mobile spin impurity. Nat. Phys. 9, 235–241 (2013).
Nascimbène, S. et al. Experimental realization of plaquette resonating valence-bond states with ultracold atoms in optical superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 205301 (2012).
Aidelsburger, M. et al. Realization of the Hofstadter Hamiltonian with ultracold atoms in optical lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 185301 (2013).
Miyake, H., Siviloglou, G. A., Kennedy, C. J., Burton, W. C. & Ketterle, W. Realizing the Harper Hamiltonian with laser-assisted tunneling in optical lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 185302 (2013).
Jotzu, G. et al. Experimental realization of the topological Haldane model with ultracold fermions. Nature 515, 237–240 (2014).
Fukuhara, T. et al. Spatially resolved detection of a spin-entanglement wave in a Bose–Hubbard chain. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 035302 (2015).
Islam, R. et al. Measuring entanglement entropy in a quantum many-body system. Nature 528, 77–83 (2015).
Dai, H.-N. et al. Generation and detection of atomic spin entanglement in optical lattices. Nat. Phys. 12, 783–787 (2016).
Trotzky, S. et al. Time-resolved observation and control of superexchange interactions with ultracold atoms in optical lattices. Science 319, 295–299 (2008).
Brown, R. C. et al. Two-dimensional superexchange-mediated magnetization dynamics in an optical lattice. Science 348, 540–544 (2015).
Dutta, O. et al. Non-standard Hubbard models in optical lattices: a review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 78, 066001 (2015).
Bakr, W. S. et al. Probing the superfluid-to-Mott insulator transition at the single-atom level. Science 329, 547–550 (2010).
Sherson, J. F. et al. Single-atom-resolved fluorescence imaging of an atomic Mott insulator. Nature 467, 68–72 (2010).
Chin, C., Grimm, R., Julienne, P. & Tiesinga, E. Feshbach resonances in ultracold gases. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 1225–1286 (2010).
Eckardt, A., Weiss, C. & Holthaus, M. Superfluid–insulator transition in a periodically driven optical lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 260404 (2005).
Kitagawa, T., Berg, E., Rudner, M. & Demler, E. Topological characterization of periodically driven quantum systems. Phys. Rev. B 82, 235114 (2010).
Trebst, S., Schollwöck, U., Troyer, M. & Zoller, P. d-wave resonating valence bond states of fermionic atoms in optical lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 250402 (2006).
Wen, X.-G. Quantum Field Theory of Many-Body Systems (Oxford Univ. Press, 2004).
Altman, E. & Auerbach, A. Plaquette Boson–Fermion model of cuprates. Phys. Rev. B 65, 104508 (2002).
Kitaev, A. Anyons in an exactly solved model and beyond. Ann. Phys. 321, 2–111 (2006).
Duan, L.-M., Demler, E. & Lukin, M. D. Controlling spin exchange interactions of ultracold atoms in optical lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 090402 (2003).
Zhang, C., Scarola, V. W., Tewari, S. & Das Sarma, S. Anyonic braiding in optical lattices. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 18415–18420 (2007).
Dusuel, S., Schmidt, K. P. & Vidal, J. Creation and manipulation of anyons in the Kitaev model. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 177204 (2008).
Nayak, C., Simon, S. H., Stern, A., Freedman, M. & Das Sarma, S. Non-Abelian anyons and topological quantum computation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1083–1159 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank A. J. Leggett, P. Zoller and B. Zhao for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFA0301600), National Natural Science Foundation of China (91421305, 11521063), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.-A.C., Z.-S.Y. and J.-W.P. initiated and designed this research project. H.-N.D., B.Y., A.R., X.-F.X. and Z.-S.Y. set up the experiment. H.-N.D., B.Y., A.R. and H.S. performed the measurement and analysed the data. All authors contributed to manuscript preparation. Z.-S.Y. and J.-W.P. supervised the whole project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 577 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, HN., Yang, B., Reingruber, A. et al. Four-body ring-exchange interactions and anyonic statistics within a minimal toric-code Hamiltonian. Nature Phys 13, 1195–1200 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys4243
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys4243
This article is cited by
-
Realizing a 1D topological gauge theory in an optically dressed BEC
Nature (2022)
-
Protocol designs for NOON states
Communications Physics (2022)
-
Realization of a bosonic antiferromagnet
Nature Physics (2021)
-
Large-scale Ising emulation with four body interaction and all-to-all connections
Communications Physics (2020)
-
Nagaoka ferromagnetism observed in a quantum dot plaquette
Nature (2020)