Abstract
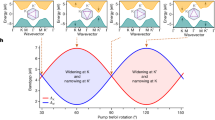
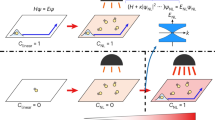
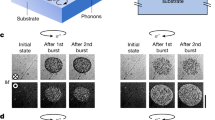
The study of non-Hermitian systems with parity–time (PT) symmetry is a rapidly developing frontier. Realized in recent experiments, PT-symmetric classical optical systems with balanced gain and loss hold great promise for future applications. Here we report the experimental realization of passive PT-symmetric quantum dynamics for single photons by temporally alternating photon losses in the quantum walk interferometers. The ability to impose PT symmetry allows us to realize and investigate Floquet topological phases driven by PT-symmetric quantum walks. We observe topological edge states between regions with different bulk topological properties and confirm the robustness of these edge states with respect to PT-symmetry-preserving perturbations and PT-symmetry-breaking static disorder. Our results contribute towards the realization of quantum mechanical PT-synthetic devices and suggest exciting possibilities for the exploration of the topological properties of non-Hermitian systems using discrete-time quantum walks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender, C. M. & Boettcher, S. Real spectra in non-Hermitian Hamiltonians having PT symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 5243–5246 (1998).
Bender, C. M., Brody, D. C. & Jones, H. F. Complex extension of quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 270401 (2002).
Bender, C. M. Making sense of non-Hermitian Hamiltonians. Rep. Prog. Phys. 70, 947–1018 (2007).
Klaiman, S., Günther, U. & Moiseyev, N. Visualization of branch points in PT-symmetric waveguides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 080402 (2008).
Guo, A. et al. Observation of PT-symmetry breaking in complex optical potentials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 093902 (2009).
Rüter, C. E. et al. Observation of parity–time symmetry in optics. Nat. Phys. 6, 192–195 (2010).
Chong, Y. D., Ge, L. & Stone, A. D. PT-symmetry breaking and laser-absorber modes in optical scattering systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 093902 (2011).
Liertzer, M. et al. Pump-induced exceptional points in lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 173901 (2012).
Schomerus, H. Topologically protected midgap states in complex photonic lattices. Opt. Lett. 38, 1912–1914 (2013).
Brandstetter, M. et al. Reversing the pump dependence of a laser at an exceptional point. Nat. Commun. 5, 4034 (2014).
Poli, C., Bellec, M., Kuhl, U., Mortessagne, F. & Schomerus, H. Selective enhancement of topologically induced interface states in a dielectric resonator chain. Nat. Commun. 6, 6710 (2015).
Zeuner, J. M. et al. Observation of a topological transition in the bulk of a non-Hermitian system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 040402 (2015).
Weimann, S. et al. Topologically protected bound states in photonic parity–time-symmetric crystals. Nat. Mater. 16, 433–438 (2017).
Feng, L. et al. Nonreciprocal light propagation in a silicon photonic circuit. Science 333, 729–733 (2011).
Feng, L. et al. Experimental demonstration of a unidirectional reflectionless parity–time metamaterial at optical frequencies. Nat. Mater. 12, 108–113 (2013).
Peng, B. et al. Parity-time-symmetric whispering-gallery microcavities. Nat. Phys. 10, 394–398 (2014).
Chang, L. et al. Parity-time symmetry and variable optical isolation in active-passive-coupled microresonators. Nat. Photon. 8, 524–529 (2014).
Feng, L., Wong, Z. J., Ma, R. M., Wang, Y. & Zhang, X. Single-mode laser by parity–time symmetry breaking. Science 346, 972–975 (2014).
Hodaei, H. et al. Parity–time-symmetric microring lasers. Science 346, 975–978 (2014).
Regensburger, A. et al. Parity–time synthetic photonic lattices. Nature 488, 167–171 (2012).
Regensburger, A. et al. Observation of defect states in PT-symmetric optical lattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 223902 (2013).
Schreiber, A. et al. Photons walking the line: a quantum walk with adjustable coin operations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 050502 (2010).
Schreiber, A. et al. A 2D quantum walk simulation of two-particle dynamics. Science 336, 55–58 (2012).
Ambainis, A. Quantum walks and their algorithmic applications. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 1, 507–518 (2003).
Childs, A. M. et al. Proceedings of the 35th ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing 59–68 (ACM, 2003).
Childs, A. M., Gosset, D. & Webb, Z. Universal computation by multiparticle quantum walk. Science 339, 791–794 (2013).
Schreiber, A. et al. Decoherence and disorder in quantum walks: from ballistic spread to localization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 180403 (2011).
Kitagawa, T. et al. Observation of topologically protected bound states in photonic quantum walks. Nat. Commun. 3, 882 (2012).
Crespi, A. et al. Anderson localization of entangled photons in an integrated quantum walk. Nat. Photon. 7, 322–328 (2013).
Genske, M. et al. Electric quantum walks with individual atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 190601 (2013).
Xue, P. et al. Experimental quantum-walk revival with a time-dependent coin. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 140502 (2015).
Mochizuki, K., Kim, D. & Obuse, H. Explicit definition of PT symmetry for nonunitary quantum walks with gain and loss. Phys. Rev. A 93, 062116 (2016).
Jeong, Y.-C., Di Franco, C., Lim, H.-T., Kim, M. S. & Kim, Y.-H. Experimental realization of a delayed-choice quantum walk. Nat. Commun. 4, 2471 (2013).
Kim, D., Mochizuki, K., Kawakami, N. & Obuse, H. Floquet Topological phases driven by PT symmetric nonunitary time evolution. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.09650 (2016).
Kitagawa, T., Rudner, M. S., Berg, E. & Demler, E. Exploring topological phases with quantum walks. Phys. Rev. A 82, 033429 (2010).
Asbóth, J. K. & Obuse, H. Bulk-boundary correspondence for chiral symmetric quantum walks. Phys. Rev. B 88, 121406(R) (2013).
Pasek, M. & Chong, Y. D. Network models of photonic Floquet topological insulators. Phys. Rev. B 89, 075113 (2014).
Mostafazadeh, A. Pseudo-unitary operators and pseudo-unitary quantum dynamics. J. Math. Phys. 45, 932–946 (2004).
Mochizuki, K. & Obuse, H. Effects of disorder on non-unitary PT symmetric quantum walks. Interdiscip. Inf. Sci. 23, 95–103 (2017).
Mostafazadeh, A. Pseudo-Hermiticity versus PT symmetry: the necessary condition for the reality of the spectrum of a non-Hermitian Hamiltonian. J. Math. Phys. 43, 205–214 (2002).
Khanikaev, A. B. et al. Photonic topological insulators. Nat. Mater. 12, 233–239 (2013).
Rechtsman, M. C. et al. Photonic Floquet topological insulators. Nature 496, 196–200 (2013).
Lu, L., Joannopoulos, J. D. & Soljačić, M. Topological photonics. Nat. Photon. 8, 821–829 (2014).
Süsstrunk, R. & Huber, S. D. Observation of phononic helical edge states in a mechanical topological insulator. Science 349, 47–50 (2015).
Fleury, R., Khanikaev, A. B. & Alù, A. Floquet topological insulators for sound. Nat. Commun. 7, 11744 (2016).
Xiao, M., Zhang, Z. Q. & Chan, C. T. Surface impedance and bulk band geometric phases in one-dimensional systems. Phys. Rev. X 4, 021017 (2014).
Harari, G. et al. Topological insulators in PT-symmetric lattices. Conf. Lasers Electro-Opt. (CLEO) paper FTh3D.3 1–2 (Optical Society of America, 2015).
Esaki, K., Sato, M., Hasebe, K. & Kohmoto, M. Edge states and topological phases in non-Hermitian systems. Phys. Rev. B 84, 205128 (2011).
Hu, Y. C. & Hughes, T. L. Absence of topological insulator phases in non-hermitian PT-symmetric Hamiltonians. Phys. Rev. B 84, 153101 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11474049, 11674056, 11374283 and 11522545) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK20160024). W.Y. acknowledges support from the National Key R&D Program (Grant No. 2016YFA0301700) and the ‘Strategic Priority Research Program(B)’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB01030200). N.K. and H.O. were supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas ‘Topological Materials Science’ (Grant Nos JP15H05855, JP15K21717 and JP16H00975) and JSPS KAKENHI (Grant No. JP16K17760). B.C.S. acknowledges the 1000-Talent Plan and NSFC (Grant No. GG2340000241) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.X., X.Z., Z.H.B. and K.K.W. performed the experiments. K.M., D.K., N.K. and H.O. performed the theoretical analysis. W.Y., H.O. and B.C.S. wrote part of the paper. P.X. designed the experiments, analysed the data and wrote most of the paper. All the authors participated in the discussions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 1866 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, L., Zhan, X., Bian, Z. et al. Observation of topological edge states in parity–time-symmetric quantum walks. Nature Phys 13, 1117–1123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys4204
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys4204
This article is cited by
-
Third-order exceptional line in a nitrogen-vacancy spin system
Nature Nanotechnology (2024)
-
Floquet parity-time symmetry in integrated photonics
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Divergence and flutter instabilities of a non-conservative axial lattice under non-reciprocal interactions
Archive of Applied Mechanics (2024)
-
Demonstration of \(\mathcal{P}\mathcal{T}\)-symmetric quantum state discrimination
Quantum Information Processing (2024)
-
Entanglement entropy in a certain nonlinear discrete quantum walk model
Quantum Information Processing (2024)