Abstract
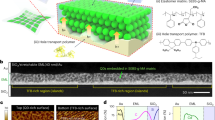
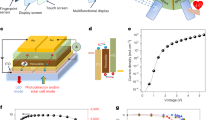
We report a full series of blue, green and red quantum-dot-based light-emitting devices (QD-LEDs), all with high external quantum efficiencies over 10%. We show that the fine nanostructure of quantum dots—especially the composition of the graded intermediate shell and the thickness of the outer shell—plays a very important role in determining QD-LED device performance due to its effects on charge injection, transport and recombination. These simple devices have maximum current and external quantum efficiencies of 63 cd A−1 and 14.5% for green QD-LEDs, 15 cd A−1 and 12.0% for red devices, and 4.4 cd A−1 and 10.7% for blue devices, all of which are well maintained over a wide range of luminances from 102 to 104 cd m−2. All the QD-LEDs are solution-processed for ease of mass production, and have low turn-on voltages and saturated pure colours. The green and red devices exhibit lifetimes of more than 90,000 and 300,000 h, respectively.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekimov, A. I. & Onushchenko, A. A. Quantum size effect in 3-dimensional microscopic semiconductor crystals. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 34, 345–349 (1981).
Efros, A. L. Interband absorption of light in a semiconductor sphere. Sov. Phys. Semicond. 16, 772–775 (1982).
Brus, L. E. A simple model for the ionization potential, electron affinity, and aqueous redox potentials of small semiconductor crystallites. J. Chem. Phys. 79, 5566–5571 (1983).
Brus, L. Electronic wave-functions in semiconductor clusters—experiment and theory. J. Phys. Chem. 90, 2555–2560 (1986).
Alivisatos, A. P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 271, 933–937 (1996).
Lim, J. et al. Perspective on synthesis, device structures, and printing processes for quantum dot displays. Opt. Mater. Express 2, 594–628 (2012).
Shirasaki, Y., Supran, G. J., Bawendi, M. G. & Bulovic, V. Emergence of colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting technologies. Nature Photon. 7, 13–23 (2012).
Coe, S., Woo, W. K., Bawendi, M. & Bulovic, V. Electroluminescence from single monolayers of nanocrystals in molecular organic devices. Nature 420, 800–803 (2002).
Sun, Q. et al. Bright, multicoloured light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature Photon. 1, 717–722 (2007).
Caruge, J. M., Halpert, J. E., Wood, V., Bulovic, V. & Bawendi, M. G. Colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with metal-oxide charge transport layers. Nature Photon. 2, 247–250 (2008).
Cho, K. S. et al. High-performance crosslinked colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nature Photon. 3, 341–345 (2009).
Kim, T. H. et al. Full-colour quantum dot displays fabricated by transfer printing. Nature Photon. 5, 176–182 (2011).
Qian, L., Zheng, Y., Xue, J. & Holloway, P. H. Stable and efficient quantum-dot light-emitting diodes based on solution-processed multilayer structures. Nature Photon. 5, 543–548 (2011).
Kwak, J. et al. Bright and efficient full-color colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes using an inverted device structure. Nano Lett. 12, 2362–2366 (2012).
Lee, K. H. et al. Highly efficient, color-pure, color-stable blue quantum dot light-emitting devices. ACS Nano 7, 7295–7302 (2013).
Mashford, B. S. et al. High-efficiency quantum-dot light-emitting devices with enhanced charge injection. Nature Photon. 7, 407–412 (2013).
Lee, K. H. et al. Over 40 cd/A efficient green quantum dot electroluminescent device comprising uniquely large-sized quantum dots. ACS Nano 8, 4893–4901 (2014).
Dai, X. et al. Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature 515, 86–89 (2014).
Adachi, C., Baldo, M. A., Thompson, M. E. & Forrest, S. R. Nearly 100% internal phosphorescence efficiency in an organic light-emitting device. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 5048–5051 (2001).
Baldo, M. A., Lamansky, S., Burrows, P. E., Thompson, M. E. & Forrest, S. R. Very high-efficiency green organic light-emitting devices based on electrophosphorescence. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 4–6 (1999).
Baldo, M. A. et al. Highly efficient phosphorescent emission from organic electroluminescent devices. Nature 395, 151–154 (1998).
Wang, X. et al. Non-blinking semiconductor nanocrystals. Nature 459, 686–689 (2009).
Mahler, B. et al. Towards non-blinking colloidal quantum dots. Nature Mater. 7, 659–664 (2008).
Chen, O. et al. Compact high-quality CdSe–CdS core–shell nanocrystals with narrow emission linewidths and suppressed blinking. Nature Mater. 12, 445–451 (2013).
Li, J. et al. Large-scale synthesis of nearly monodisperse CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals using air-stable reagents via successive ion layer adsorption and reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 12567–12575 (2003).
Shen, H. et al. High quality synthesis of monodisperse zinc-blende CdSe and CdSe/ZnS nanocrystals with a phosphine-free method. CrystEngComm 11, 1733–1738 (2009).
Pal, B. N. et al. ‘Giant’ CdSe/CdS core/chell nanocrystal quantum dots as efficient electroluminescent materials: strong influence of shell thickness on light-emitting diode performance. Nano Lett. 12, 331–336 (2011).
Jha, P. P. & Guyot-Sionnest, P. Photoluminescence switching of charged quantum dot films. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 15440–15445 (2007).
Woo, W. K. et al. Reversible charging of CdSe nanocrystals in a simple solid-state device. Adv. Mater. 14, 1068–1071 (2002).
Htoon, H. et al. Highly emissive multiexcitons in steady-state photoluminescence of individual ‘giant’ CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 10, 2401–2407 (2010).
Jin, S., Song, N. & Lian, T. Suppressed blinking dynamics of single QDs on ITO. ACS Nano 4, 1545–1552 (2010).
Wu, X. & Yeow, E. K. L. Charge-transfer processes in single CdSe/ZnS quantum dots with p-type NiO nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 46, 4390–4392 (2010).
Bae, W. K., Char, K., Hur, H. & Lee, S. Single-step synthesis of quantum dots with chemical composition gradients. Chem. Mater. 20, 531–539 (2008).
Li, S., Steigerwald, M. L. & Brus, L. E. Surface states in the photoionization of high-quality CdSe core/shell nanocrystals. ACS Nano 3, 1267–1273 (2009).
Cherniavskaya, O., Chen, L. W., Islam, M. A. & Brus, L. Photoionization of individual CdSe/CdS core/shell nanocrystals on silicon with 2-nm oxide depends on surface band bending. Nano Lett. 3, 497–501 (2003).
Wei, S. & Zunger, A. Calculated natural band offsets of all II–VI and III–V semiconductors: chemical trends and the role of cation d orbitals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 2011–2013 (1998).
Bae, W. K., Nam, M. K., Char, K. & Lee, S. Gram-scale one-pot synthesis of highly luminescent blue emitting Cd1−xZnxS/ZnS nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 20, 5307–5313 (2008).
Bae, W. K. et al. Highly efficient green-light-emitting diodes based on CdSe@ZnS quantum dots with a chemical-composition gradient. Adv. Mater. 21, 1690–1694 (2009).
Dabbousi, B. O. et al. (CdSe)ZnS core–shell quantum dots: synthesis and characterization of a size series of highly luminescent nanocrystallites. J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 9463–9475 (1997).
Qian, L. et al. Electroluminescence from light-emitting polymer/ZnO nanoparticle heterojunctions at sub-bandgap voltages. Nano Today 5, 384–389 (2010).
Pandey, A. K. & Nunzi, J. M. Rubrene/fullerene heterostructures with a half-gap electroluminescence threshold and large photovoltage. Adv. Mater. 19, 3613–3617 (2007).
Pechstedt, K., Whittle, T., Baumberg, J. & Melvin, T. Photoluminescence of colloidal CdSe/ZnS quantum dots: the critical effect of water molecules. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 12069–12077 (2010).
Cordero, S. R., Carson, P. J., Estabrook, R. A., Strouse, G. F. & Buratto, S. K. Photo-activated luminescence of CdSe quantum dot monolayers. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 12137–12142 (2000).
Dembski, S. et al. Photoactivation of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots embedded in silica colloids. Small 4, 1516–1526 (2008).
Zhang, J., Li, D., Wu, W., Wu, H. & Zhu, W. Lifetime prediction of white OLED based on MLE under lognormal distribution. J. Test. Eval. 41, 398–402 (2013).
Kim, L. et al. Contact printing of quantum dot light-emitting devices. Nano Lett. 8, 4513–4517 (2008).
Haverinen, H. M., Myllyla, R. A. & Jabbour, G. E. Inkjet printed RGB quantum dot-hybrid LED. J. Disp. Technol. 6, 87–89 (2010).
Forrest, S. R., Bradley, D. D. C. & Thompson, M. E. Measuring the efficiency of organic light-emitting devices. Adv. Mater. 15, 1043–1048 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the US National Science Foundation (NSF; SBIR Phase I award no. 1248863 and Phase II award no. 1353411) and the Florida High-Tech Corridor Council (FHTCC). Assistance with data collection and reduction by R. Zhou and J. Mudrick (Materials Science and Engineering, University of Florida) is acknowledged. The authors also acknowledge Shanghai Tianma Micro-Electronics Group for assistance with AM QD-LED fabrication. J.X. acknowledges financial support from the NSF Major Research Instrumentation Program for the acquisition of the PHI XPS instrument.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Y. and Y.Z. synthesized material, fabricated devices, collected performance data and postulated mechanisms to explain the performance of the QD-LEDs. W.C. carried out the TEM and XPS measurements. A.T. and J.H. carried out the lifetime test and fabrication of the 4.3-inch AM QD-LED prototypes. J.R.M. carried out the XRD measurement and device efficiency distribution statistics. J.X., P.H.H. and L.Q. supervised the synthesis of materials and devices, directed the collection of performance data, designed tests for the postulated mechanism, and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare competing financial interests. Y.Y., A.T., J.H. and J.R.M. are employees of NanoPhotonica Inc., and Y.Z. and L.Q. are Founders of NanoPhotonica Inc., which is the provider of the QD-LEDs display technique and related materials.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 865 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Zheng, Y., Cao, W. et al. High-efficiency light-emitting devices based on quantum dots with tailored nanostructures. Nature Photon 9, 259–266 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2015.36
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2015.36
This article is cited by
-
Stable and efficient pure blue quantum-dot LEDs enabled by inserting an anti-oxidation layer
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Blue light-emitting diodes based on colloidal quantum dots with reduced surface-bulk coupling
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Giant room-temperature nonlinearities in a monolayer Janus topological semiconductor
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Anomalous efficiency elevation of quantum-dot light-emitting diodes induced by operational degradation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Minimizing heat generation in quantum dot light-emitting diodes by increasing quasi-Fermi-level splitting
Nature Nanotechnology (2023)