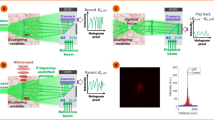
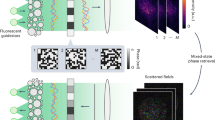
Abstract
The ability to steer and focus light inside scattering media has long been sought for a multitude of applications. At present, the only feasible strategy to form optical foci inside scattering media is to guide photons by using either implanted1 or virtual2,3,4 guide stars, which can be inconvenient and limits the potential applications. Here we report a scheme for focusing light inside scattering media by employing intrinsic dynamics as guide stars. By adaptively time-reversing the perturbed component of the scattered light, we show that it is possible to focus light to the origin of the perturbation. Using this approach, we demonstrate non-invasive dynamic light focusing onto moving targets and imaging of a time-variant object obscured by highly scattering media. Anticipated applications include imaging and photoablation of angiogenic vessels in tumours, as well as other biomedical uses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




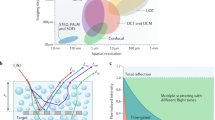
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vellekoop, I. M., van Putten, E. G., Lagendijk, A. & Mosk, A. P. Demixing light paths inside disordered metamaterials. Opt. Express 16, 67–80 (2008).
Xu, X., Liu, H. & Wang, L. V. Time-reversed ultrasonically encoded optical focusing into scattering media. Nature Photon. 5, 154–157 (2011).
Si, K., Fiolka, R. & Cui, M. Fluorescence imaging beyond the ballistic regime by ultrasound-pulse-guided digital phase conjugation. Nature Photon. 6, 657–661 (2012).
Wang, Y. M., Judkewitz, B., DiMarzio, C. A. & Yang, C. Deep-tissue focal fluorescence imaging with digitally time-reversed ultrasound-encoded light. Nature Commun. 3, 928 (2012).
Ntziachristos, V. Going deeper than microscopy: the optical imaging frontier in biology. Nature Methods 7, 603–614 (2010).
Vellekoop, I. M. & Mosk, A. P. Focusing coherent light through opaque strongly scattering media. Opt. Lett. 32, 2309–2311 (2007).
Katz, O., Small, E., Bromberg, Y. & Silberberg, Y. Focusing and compression of ultrashort pulses through scattering media. Nature Photon. 5, 372–377 (2011).
Popoff, S., Lerosey, G., Fink, M., Boccara, A. C. & Gigan, S. Image transmission through an opaque material. Nature Commun. 1, 81 (2010).
Chaigne, T. et al. Controlling light in scattering media non-invasively using the photoacoustic transmission matrix. Nature Photon. 8, 58–64 (2014).
Tay, J. W., Lai, P., Suzuki, Y. & Wang, L. V. Ultrasonically encoded wavefront shaping for focusing into random media. Sci. Rep. 4, 3918 (2014).
Yaqoob, Z., Psaltis, D., Feld, M. S. & Yang, C. Optical phase conjugation for turbidity suppression in biological samples. Nature Photon. 2, 110–115 (2008).
Hsieh, C-L., Pu, Y., Grange, R., Laporte, G. & Psaltis, D. Imaging through turbid layers by scanning the phase conjugated second harmonic radiation from a nanoparticle. Opt. Express 18, 20723–20731 (2010).
Vellekoop, I. M., Cui, M. & Changhuei, Y. Digital optical phase conjugation of fluorescence in turbid tissue. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 081108 (2012).
Judkewitz, B., Wang, Y. M., Horstmeyer, R., Mathy, A. & Yang, C. Speckle-scale focusing in the diffusive regime with time reversal of variance-encoded light (TROVE). Nature Photon. 7, 300–305 (2013).
Wang, L. V. & Hu, S. Photoacoustic tomography: in vivo imaging from organelles to organs. Science 335, 1458–1462 (2012).
Briers, D. et al. Laser speckle contrast imaging: theoretical and practical limitations. J. Biomed. Opt. 18, 066018 (2013).
Bertolotti, J. et al. Non-invasive imaging through opaque scattering layers. Nature 491, 232–234 (2012).
Yang, X., Pu, Y. & Psaltis, D. Imaging blood cells through scattering biological tissue using speckle scanning microscopy. Opt. Express 22, 3405–3413 (2014).
Fienup, J. R. Reconstruction of an object from the modulus of its Fourier transform. Opt. Lett. 3, 27–29 (1978).
Anderson, D. Z., Feinberg, J. & Lininger, D. M. Optical tracking novelty filter. Opt. Lett. 12, 123–125 (1987).
Cudney, R., Pierce, R. & Feinberg, J. The transient detection microscope. Nature 332, 424–426 (1988).
Brooks, R. E., Heflinger, L. O. & Wuerker, R. F. Pulsed laser holograms. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2, 275–279 (1966).
Liu, R., Qin, J. & Wang, R. K. Motion-contrast laser speckle imaging of microcirculation within tissue beds in vivo. J. Biomed. Opt. 18, 060508 (2013).
Miccio, L. et al. Particle tracking by full-field complex wavefront subtraction in digital holography microscopy. Lab Chip 14, 1129–1134 (2014).
Fouda, A. E. & Teixeira, F. L. Imaging and tracking of targets in clutter using differential time reversal techniques. Wave Random Complex 22, 66–108 (2012).
Brady, D. J. et al. Multiscale gigapixel photography. Nature 486, 386–389 (2012).
Jin, Y., Jia, C., Huang, S-W., O'Donnell, M. & Gao, X. Multifunctional nanoparticles as coupled contrast agents. Nature Commun. 1, 41 (2010).
Peterka, D. S., Takahashi, H. & Yuste, R. Imaging voltage in neurons. Neuron 69, 9–21 (2011).
Rust, M. J., Bates, M. & Zhuang, X. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nature Methods 3, 793–796 (2006).
Patterson, G. H. & Lippincott-Schwartz, J. A Photoactivatable GFP for selective photolabeling of proteins and cells. Science 297, 1873–1877 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank F. Zhou for assistance on the flow-control system, L. Wang for discussion on the experimental design, Y. Zhou for assistance on the dye-solution preparation and J. Ballard for editing the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants DP1 EB016986 (NIH Director's Pioneer Award) and R01 CA186567 (NIH Director's Transformative Research Award).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.M. and L.V.W. initiated the project. C.M. and X.X. implemented the DOPC-based system. C.M., X.X. and Y.L. designed and ran the experiments. C.M. wrote the codes for the experiments and simulation, and processed the experimental results. L.V.W. provided overall supervision. All authors were involved in writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2063 kb)
Supplementary Movie 1
Supplementary Movie 1 (MOV 5633 kb)
Supplementary Movie 2
Supplementary Movie 2 (MOV 501 kb)
Supplementary Movie 3
Supplementary Movie 3 (MOV 681 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, C., Xu, X., Liu, Y. et al. Time-reversed adapted-perturbation (TRAP) optical focusing onto dynamic objects inside scattering media. Nature Photon 8, 931–936 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.251
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.251
This article is cited by
-
Phase conjugation with spatially incoherent light in complex media
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
High-gain and high-speed wavefront shaping through scattering media
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
Transfer learning in infrared light imaging with upconversion through different disordered media
Applied Physics B (2023)
-
Enhance the delivery of light energy ultra-deep into turbid medium by controlling multiple scattering photons to travel in open channels
Light: Science & Applications (2022)
-
Focusing light into scattering media with ultrasound-induced field perturbation
Light: Science & Applications (2021)