Abstract
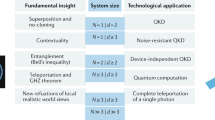
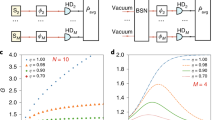
The wave–particle duality of light has led to two different encodings for optical quantum information processing. Several approaches have emerged based either on particle-like discrete-variable states (that is, finite-dimensional quantum systems) or on wave-like continuous-variable states (that is, infinite-dimensional systems). Here, we demonstrate the generation of entanglement between optical qubits of these different types, located at distant places and connected by a lossy channel. Such hybrid entanglement, which is a key resource for a variety of recently proposed schemes, including quantum cryptography and computing, enables information to be converted from one Hilbert space to the other via teleportation and therefore the connection of remote quantum processors based upon different encodings. Beyond its fundamental significance for the exploration of entanglement and its possible instantiations, our optical circuit holds promise for implementations of heterogeneous network, where discrete- and continuous-variable operations and techniques can be efficiently combined.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kok, P. et al. Linear optical quantum computing with photonic qubits. Rev. Mod. Phys. 79, 135–174 (2007).
Braunstein, S. L. & Pati, A. (eds) Continuous Variable Quantum Information (Kluwer Academic, 2003).
Ralph, T. C. & Pryde, G. J. Optical quantum computation. Prog. Opt. 54, 209–269 (2010).
O'Brien, J. L., Furusawa, A. & Vucković, J. Photonic quantum technologies. Nature Photon. 3, 687–695 (2009).
Knill, E., Laflamme, R. & Milburn G. J. A scheme for efficient quantum computation with linear optics. Nature 409, 46–52 (2001).
Van Loock, P. Optical hybrid approaches to quantum information. Laser Photon. Rev. 5, 167–200 (2011).
Jeong, H. & Kim, M. S. Efficient quantum computation using coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 65, 042305 (2002).
Ralph, T. C., Gilchrist, A., Milburn, G. J., Munro, W. J. & Glancy, S. Quantum computation with optical coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042319 (2003).
Sangouard, N. et al. Quantum repeaters with entangled coherent states. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27, 137–145 (2010).
Brask, J. B. et al. A hybrid long-distance entanglement distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 160501 (2010).
Lund, A. P., Ralph, T. C. & Haselgrove, H. L. Fault-tolerant optical quantum computing with small-amplitude coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 030503 (2008).
Park, K. & Jeong, H. Entangled coherent states versus entangled photon pairs for practical quantum-information processing. Phys. Rev. A 82, 062325 (2010).
Lee, S.-W. & Jeong, H. Near-deterministic quantum teleportation and resource-efficient quantum computation using linear optics and hybrid qubits. Phys. Rev. A 87, 022326 (2013).
Morin O. et al. Witnessing trustworthy single-photon entanglement with local homodyne measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 130401 (2013).
Kreis, K. & van Loock, P. Classifying, quantifying, and witnessing qudit–qumode hybrid entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 85, 032307 (2012).
Rigas, J., Gühne, O. & Lütkenhaus, N. Entanglement verification for quantum-key-distribution systems with an underlying bipartite qubit-mode structure. Phys. Rev. A 73, 012341 (2006).
Wittmann, C. et al. Witnessing effective entanglement over a 2 km fiber channel. Opt. Express 18, 4499–4509 (2010).
Spiller, T. P. et al. Quantum computation by communication. New J. Phys. 8, 30 (2006).
Van Loock, P. et al. Hybrid quantum computation in quantum optics. Phys. Rev. A 78, 022303 (2008).
Van Loock, P. et al. Hybrid quantum repeater using bright coherent light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 240501 (2006).
Jeong, H. Using weak nonlinearity under decoherence for macroscopic entanglement generation and quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 72, 034305 (2005).
Duan, L.-M., Lukin, M. D., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Long-distance quantum communication with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Nature 414, 413–418 (2001).
Ourjoumtsev, A., Ferreyrol, F., Tualle-Brouri, R. & Grangier, P. Preparation of non-local superpositions of quasi-classical light states. Nature Phys. 5, 189–192 (2009).
Marek, P. & Fiurášek, J. Elementary gates for quantum information with superposed coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 82, 014302 (2010).
Morin, O., Fabre, C. & Laurat, J. Experimentally accessing the optimal temporal mode of traveling quantum light states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 213602 (2013).
Ourjoumtsev, A., Tualle-Brouri, R., Laurat, J. & Grangier P. Generating optical Schrödinger kittens for quantum information processing. Science 312, 83–86 (2006).
Neergard-Nielsen, J. S., Nielsen, B. M., Hettich, C., Molmer, K. & Polzik, E. S. Generation of a superposition of odd photon number states for quantum information networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 083604 (2006).
Wakui, K., Takahashi, H., Furusawa, A. & Sasaki, M. Controllable generation of highly nonclassical states from nearly pure squeezed vacua. Opt. Express 15, 3568–3574 (2007).
Lee, N. et al. Teleportation of nonclassical wave packets of light. Science 332, 330–333 (2011).
Morin, O., D'Auria, V., Fabre C. & Laurat, J. High-fidelity single-photon source based on a type-II optical parametric oscillator. Opt. Lett. 37, 3738–3740 (2012).
D'Auria, V., Lee, N., Amri, T., Fabre, C. & Laurat, J. Quantum decoherence of single-photon counters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 050504 (2011).
D'Auria, V., Morin, O., Fabre, C. & Laurat, J. Effect of the heralding detector properties on the conditional generation of single-photon states. Eur. Phys. J. D 66, 249 (2012).
Van Enk, S. J., Lütkenhaus, N. & Kimble, H. J. Experimental procedures for entanglement verification. Phys. Rev. A 75, 052318 (2007).
Lvovksy, A. I. & Raymer, M. G. Continuous-variable optical quantum-state tomography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 299–332 (2009).
Vidal, G. & Werner, R. F. A computable measure of entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032314 (2002).
Park, K., Lee, S.-W. & Jeong, H. Quantum teleportation between particlelike and fieldlike qubits using hybrid entanglement under decoherence effects. Phys. Rev. A 86, 062301 (2012).
Nielsen, A. E. B. & Molmer, K. Transforming squeezed light into a large-amplitude coherent-state superposition. Phys. Rev. A 76, 043840 (2007).
Morin, O. et al. Quantum state engineering of light with continuous-wave optical parametric oscillators. J. Visualized Experiments 87, e51224 10.3791/51224(2014).
Marsili, F. et al. Detecting single infrared photons with 93% system efficiency. Nature Photon. 7, 210–214 (2013).
Andersen, U. L. & Neergaard-Nielsen, J. S. Heralded generation of a micro–macro entangled state. Phys. Rev. A 88, 022337 (2013).
Lvovsky, A. I., Ghobadi, R., Chandra, A., Prasad, A. S. & Simon, C. Observation of micro–macro entanglement of light. Nature Phys. 9, 541–544 (2013).
Bruno, N. et al. Displacement of entanglement back and forth between the micro and macro domains. Nature Phys. 9, 545–548 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank N. Sangouard for discussions and V. D'Auria and F. A. S. Barbosa for their valuable contributions in the early stage of the experiment. This work is supported by the ERA-Net CHIST-ERA (QScale) and by the European Research Council (ERC) starting grant HybridNet. K.H. acknowledges support from the Foundation for the Author of National Excellent Doctoral Dissertation of China (PY2012004) and the China Scholarship Council. C.F. and J.L. are members of the Institut Universitaire de France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. and O.M. conceived the experiment. O.M., K.H., J.Liu and H.L.J. carried out the experiment and analysed the data, under the supervision of J.L. O.M, K.H., H.L.J., C.F. and J.L. contributed to discussing the implementation and the results. O.M., K.H. and J.L. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 762 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morin, O., Huang, K., Liu, J. et al. Remote creation of hybrid entanglement between particle-like and wave-like optical qubits. Nature Photon 8, 570–574 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.137
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.137
This article is cited by
-
Quantum secure direct communication with hybrid entanglement
Frontiers of Physics (2024)
-
Converting qubits
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
A random optical parametric oscillator
Nature Communications (2023)
-
A quantum-bit encoding converter
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
Controllable shaping of CV–DV entanglement between CV states of certain parity and delocalized photon
Pramana (2023)