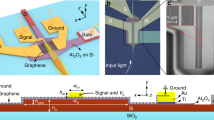
Abstract
Optical interconnects are becoming attractive alternatives to electrical wiring in intra- and interchip communication links. Particularly, the integration with silicon complementary metal–oxide semiconductor (CMOS) technology has received considerable interest because of the ability of cost-effective integration of electronics and optics on a single chip1. Although silicon enables the realization of optical waveguides2 and passive components3, the integration of another, optically absorbing, material is required for photodetection. Traditionally, germanium4 or compound semiconductors5 are used for this purpose; however, their integration with silicon technology faces major challenges. Recently, graphene6 emerged as a viable alternative for optoelectronic applications7, including photodetection8. Here, we demonstrate an ultra-wideband CMOS-compatible photodetector based on graphene. We achieved a multigigahertz operation over all fibre-optic telecommunication bands beyond the wavelength range of strained germanium photodetectors9, the responsivity of which is limited by their bandgap. Our work complements the recent demonstration of a CMOS-integrated graphene electro-optical modulator10, and paves the way for carbon-based optical interconnects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jalali, B. & Fathpour, S. Silicon photonics. J. Lightwave Technol. 24, 4600–4615 (2004).
Vlasov, Y. A. & McNab, S. J. Losses in single-mode silicon-on-insulator strip waveguides and bends. Opt. Express 12, 1622–1631 (2004).
Bogaerts, W. et al. Compact wavelength-selective functions in silicon-on-insulator photonic wires. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 12, 1394–11401 (2006).
Chen, L. & Lipson, M. Ultra-low capacitance and high speed germanium photodetectors on silicon. Opt. Express 17, 7901–7906 (2009).
Park, H. et al. A hybrid AlGaInAs–silicon evanescent waveguide photodetector. Opt. Express 15, 6044–6052 (2007).
Novoselov, K. S. et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306, 666–669 (2004).
Bonaccorso, F., Sun, Z., Hasan, T. & Ferrari, A. C. Graphene photonics and optoelectronics. Nature Photon. 4, 611–622 (2010).
Mueller, T., Xia, F. & Avouris, P. Graphene photodetectors for high-speed optical communications. Nature Photon. 4, 297–301 (2010).
Liu, J. et al. High-performance, tensile-strained Ge p–i–n photodetectors on a Si platform. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 103501 (2005).
Liu, M. et al. A graphene-based broadband optical modulator. Nature 474, 64–67 (2011).
Lee, E. J. H., Balasubramanian, K., Weitz, R. T., Burghard, M. & Kern, K. Contact and edge effects in graphene devices. Nature Nanotech. 3, 486–490 (2008).
Xia, F. et al. Photocurrent imaging and efficient photon detection in a graphene transistor. Nano Lett. 9, 1039–1044 (2009).
Park, J., Ahn, Y. H. & Ruiz-Vargasv, C. Imaging of photocurrent generation and collection in single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 9, 1742–1746 (2009).
Xu, X. et al. Photo-thermoelectric effect at a graphene interface junction. Nano Lett. 10, 562–566 (2010).
Lemme, M. C. et al. Gate-activated photoresponse in a graphene p–n junction. Nano Lett. 11, 4134–4137 (2010).
Gabor, N. M. et al. Hot carrier-assisted intrinsic photoresponse in graphene. Science 334, 648–652 (2011).
Freitag, M., Low, T., Xia, F., & Avouris, P. Photoconductivity of biased graphene. Nature Photon. 7, 53–59 (2013).
Song, J. C. W., Rudner, M. S., Marcus, C. M. & Levitov, L. S. Hot carrier transport and photocurrent response in graphene. Nano Lett. 11, 4688–4692 (2011).
Xia, F., Mueller, T., Lin, Y.-M., Valdes-Garcia, A. & Avouris, P. Ultrafast graphene photodetector. Nature Nanotech. 4, 839–843 (2009).
Echtermeyer, T. J. et al. Strong plasmonic enhancement of photovoltage in graphene. Nature Commun. 2, 458 (2011).
Liu, Y. et al. Plasmon resonance enhanced multicolour photodetection by graphene. Nature Commun. 2, 579 (2011).
Furchi, M. et al. Microcavity-integrated graphene photodetector. Nano Lett. 12, 2773–2777 (2012).
Konstantatos, G. et al. Hybrid graphene–quantum dot phototransistors with ultrahigh gain. Nature Nanotech. 7, 363–368 (2012).
Yan, J. et al. Dual-gated bilayer graphene hot-electron bolometer. Nature Nanotech. 7, 472–478 (2012).
Vicarelli, L. et al. A. Graphene field-effect transistors as room-temperature terahertz detectors. Nature Mater. 11, 865–871 (2012).
Liu, M., Yin, X. & Zhang, X. Double-layer graphene optical modulator. Nano Lett. 12, 1482–1485 (2012).
Lee, C.-C., Suzuki, S., Xie, W. & Schibli, T. R. Broadband graphene electro-optic modulators with sub-wavelength thickness. Opt. Express 20, 5264–5269 (2012).
Koester, S. J. & Li, M. High-speed waveguide-coupled graphene-on-graphene optical modulators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 171107 (2012).
Li, Z. Q. et al. Dirac charge dynamics in graphene by infrared spectroscopy. Nature Phys. 4, 532–535 (2008).
Wang, F. et al. Gate-variable optical transitions in graphene. Science 320, 206–209 (2008).
Kim, K., Choi, J.-Y., Kim, T., Cho, S.-H. & Chung, H.-J. A role for graphene in silicon-based semiconductor devices. Nature 479, 338–344 (2011).
Bruna, M. & Borini, S. Optical constants of graphene layers in the visible range. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 031901 (2009).
Assefa, S. et al. CMOS-integrated high-speed MSM germanium waveguide photodetector. Opt. Express 18, 4986–4999 (2010).
Freitag, M., Low, T. & Avouris, P. Increased responsivity of suspended graphene photodetectors. Nano Lett. 13, 1644–1648 (2013).
Urich, A. et al. Silver nanoisland enhanced Raman interaction in graphene. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 153113 (2012).
Geis, M. W. et al. CMOS-compatible all-Si high-speed waveguide photodiodes with high responsivity in near-infrared communication band. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 19, 152–154 (2007).
Su, S. et al. GeSn p–i–n photodetector for all telecommunication bands detection. Opt. Express 19, 6400–6405 (2011).
Koester, S. J., Li, H. & Li, M. Switching energy limits of waveguide-coupled graphene-on-graphene optical modulators. Opt. Express 20, 20330–20341 (2012).
Bae, S. et al. Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nature Nanotech. 5, 574–578 (2010).
Ma, H., Jen, A. K.-Y. & Dalton, L. R. Polymer-based optical waveguides: materials, processing, and devices. Adv. Mater. 14, 1339–1365 (2002).
Ferrari, A. C. et al. Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 187401 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge discussions with W. Schrenk and K. Unterrainer. We thank H. Arthaber for lending us a sampling oscilloscope and K. Unterrainer, J. Darmo and D. Dietze for providing access to their femtosecond fibre laser. This work was supported by the Austrian Science Fund FWF (START Y-539) and the Austrian Research Promotion Agency FFG (NIL-Graphene, PLATON-SiN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.M. conceived and designed the experiments. A.P. and M.H. fabricated the samples. A.P. carried out the measurements. T.M. and M.H. performed the simulations. M.M.F. and D.B. contributed to the development of the measurement set-ups. R.G. and T.F. contributed to the sample fabrication. A.P. and T.M. analysed the data. T.M. wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pospischil, A., Humer, M., Furchi, M. et al. CMOS-compatible graphene photodetector covering all optical communication bands. Nature Photon 7, 892–896 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.240
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.240
This article is cited by
-
On-chip optoelectronic logic gates operating in the telecom band
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Highly efficient tunable photodetector with a bipolar response in van der Waals heterojunctions
Science China Technological Sciences (2024)
-
Experimental comparison between Nb2O5- and TiO2-based photoconductive and photogating GFET UV detector
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Polarization-induced photocurrent switching effect in heterojunction photodiodes
Nano Research (2023)
-
All solution-processed SnO2/1D-CsAg2I3 heterojunction for high-sensitivity self-powered visible-blind UV photodetector
Science China Materials (2023)