Abstract
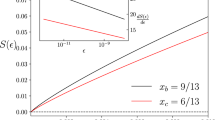
What is the maximum rate at which digital information can be communicated without error using electromagnetic signals, such as radio communication? According to Shannon theory this rate is the capacity of the communication channel, which is obtained by maximizing the mutual information between the channel's input and output. Shannon theory, however, has been developed within classical physics, whereas electromagnetic signals are, ultimately, quantum-mechanical entities. To account for this fact, the capacity must be expressed in terms of a complicated optimization of the Holevo information, but explicit solutions are still unknown for arguably the most elementary electromagnetic channel, the one degraded by additive thermal noise. We place bounds on the thermal channel's Holevo information that determine the capacity up to corrections that are insignificant for practical scenarios such as those with high noise or low transmissivity. Our results apply to any bosonic thermal-noise channel, including electromagnetic signalling at any frequency.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shannon, C. E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Technol. J. 27, 9–423, 623–656 (1948).
Caves, C. M. & Drummond, P. D. Quantum limits on bosonic communication rates. Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 481–537 (1994).
Holevo, A. S. & Giovannetti, V. Quantum channels and their entropic characteristics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 75, 046001 (2012).
König, R. & Smith, G. Classical capacity of quantum thermal noise channels to within 1.45 Bits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 040501 (2013).
König, R. & Smith, G. Limits on classical communication from quantum entropy power inequalities. Nature Photon. 7, 142–146 (2013).
Holevo, A. S. & Werner, R. F. Evaluating capacities of bosonic Gaussian channels. Phys. Rev. A 63, 032312 (2001).
Giovannetti, V. et al. Classical capacity of the lossy bosonic channel: the exact solution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 027902 (2004).
Giovannetti, V., Guha, S., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L. & Shapiro, J. H. Minimum output entropy of bosonic channels: a conjecture. Phys. Rev. A 70, 032315 (2004).
Shirokov, M. E. The Holevo capacity of infinite dimensional channels and the additivity problem. Commun. Math. Phys. 262, 137–159 (2006).
Shirokov, M. E. On entropic quantities related to the classical capacity of infinite dimensional quantum channels. Proc. SPIE 5833, 222–228 (2005).
Holevo, A. S. & Shirokov, M. E. Continuous ensembles and the χ-capacity of infinite-dimensional channels. Theory Probab. Appl. 50, 86–96 (2006).
Hiroshima, T. Additivity and multiplicativity properties of some Gaussian channels for Gaussian inputs. Phys. Rev. A 73, 012330 (2006).
Giovannetti, V., Holevo, A. S., Lloyd, S. & Maccone, L. Generalized minimal output entropy conjecture for Gaussian channels: definitions and some exact results. J. Phys. A 43, 415305 (2010).
Shapiro, J. H., Guha, S. & Erkmen, B. I. Ultimate channel capacity of free-space optical communications. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 4, 501–516 (2005).
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L. & Shor, P. W. Entanglement assisted capacity of the broadband lossy channel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 047901 (2003).
Hastings, M. B. A counterexample to additivity of minimum output entropy. Nature Phys. 5, 255–257 (2009).
Holevo, A. S. The capacity of the quantum channel with general signal states. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 44, 269–273 (1998).
Schumacher, B. & Westmoreland, M. D. Sending classical information via noisy quantum channels. Phys. Rev. A 56, 131–138 (1997).
Horodecki, M., Shor, P. W. & Ruskai, M. B. Entanglement breaking channels. Rev. Math. Phys. 15, 629–641 (2003).
Holevo, A. S. Entanglement-breaking channels in infinite dimensions. Probl. Inf. Transm. 44, 171–184 (2008).
Shor, P. W. Additivity of the classical capacity of entanglement-breaking quantum channels. J. Math. Phys. 43, 4334–4340 (2002).
Giovannetti, V. et al. Minimum bosonic channel output entropies. AIP Conf. Proc. 734, 21–24 (2004).
Garcia-Patron, R., Navarrete-Benlloch, C., Lloyd, S., Shapiro, J. H. & Cerf, N. J. Majorization theory approach to the Gaussian channel minimum entropy conjecture. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 110505 (2012).
Zy˙czkowski, K. Rényi extrapolation of Shannon entropy. Open Syst. Inf. Dyn. 10, 297–310 (2003).
Beck, C. & Schlögl, F. Thermodynamics of Chaotic Systems (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1993).
Giovannetti, V. & Lloyd, S. Additivity properties of a Gaussian bosonic channel. Phys. Rev. A 69, 062307 (2004).
Acknowledgements
V.G. acknowledges support from the Italian Ministry of Instruction, University and Research (MIUR) through FIRB-IDEAS project no. RBID08B3FM, and L.M. from European project COQUIT (Collective Quantum Operations for Information Technologies). S.L. and J.H.S. acknowledge support from a US Office of Naval Research (ONR) Basic Research Challenge grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the derivation and writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 427 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S., Maccone, L. et al. Electromagnetic channel capacity for practical purposes. Nature Photon 7, 834–838 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.193
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.193
This article is cited by
-
A Solution of Gaussian Optimizer Conjecture for Quantum Channels
Communications in Mathematical Physics (2015)
-
Ultimate classical communication rates of quantum optical channels
Nature Photonics (2014)
-
Quantum state majorization at the output of bosonic Gaussian channels
Nature Communications (2014)