Abstract
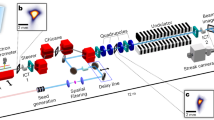
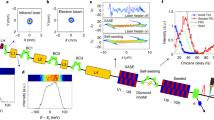
Free-electron lasers (FELs) are promising devices for generating light with laser-like properties in the extreme ultraviolet and X-ray spectral regions. Recently, FELs based on the self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) mechanism have allowed major breakthroughs in diffraction and spectroscopy applications, despite the relatively large shot-to-shot intensity and photon-energy fluctuations and the limited longitudinal coherence inherent in the SASE mechanism. Here, we report results on the initial performance of the FERMI seeded FEL, based on the high-gain harmonic generation configuration, in which an external laser is used to initiate the emission process. Emission from the FERMI FEL-1 source occurs in the form of pulses carrying energy of several tens of microjoules per pulse and tunable throughout the 65 to 20 nm wavelength range, with unprecedented shot-to-shot wavelength stability, low-intensity fluctuations, close to transform-limited bandwidth, transverse and longitudinal coherence and full control of polarization.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maiman, T. H. Stimulated optical radiation in ruby. Nature 187, 493–494 (1960).
Als-Nielsen, J. & McMorrow, D. Elements of Modern X-ray Physics (Wiley, 2001).
Madey, J. M. J. Stimulated emission of bremsstrahlung in a periodic magnetic field. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 1906–1913 (1971).
Elias, L. R., Fairbank, W. M., Madey, J. M. J., Schwettman, H. A. & Smith, T. I. Observation of stimulated emission of radiation by relativistic electrons in a spatially transverse magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 36, 717–720 (1976).
Deacon, D. A. G. et al. First operation of a free electron laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 38, 892–894 (1977).
Kondratenko, A. M. & Saldin, E. L. Generation of coherent radiation by a relativistic electron beam in an undulator. Part. Accel. 10, 207–216 (1980).
Bonifacio, R., Pellegrini, C. & Narducci, L. Collective instabilities and high gain regime in a free electron laser. Opt. Commun. 50, 373–378 (1984).
Saldin, E. L., Schneidmiller, E. A. & Yurkov, M. V. The Physics of Free Electron Lasers (Springer, 2000).
Hogan, M. J. et al. Measurements of gain larger than 105 at 12 µm in a self amplified spontaneous emission free electron laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 4867–4871 (1998).
Milton, S. et al. Exponential gain and saturation of a self amplified spontaneous emission free electron laser. Science 292, 2037–2041 (2001).
Ayvazyan, V. et al. Generation of GW radiation pulses from VUV free-electron laser operating in the femtosecond regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 104802 (2002).
Ackermann, W. et al. Operation of a free-electron laser from the extreme ultraviolet to the water window. Nature Photon. 1, 336–342 (2007).
Emma, P. et al. First lasing and operation of an angstrom-wavelength free-electron laser. Nature Photon. 4, 641–647 (2010).
Ishikawa, I. et al. A compact X-ray free-electron laser emitting in the sub-ångström region. Nature Photon. 6, 540–544 (2012).
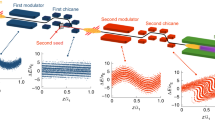
Yu, L. H. Generation of intense UV radiation by subharmonically seeded single-pass free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. A 44, 5178–5193 (1991).
Yu, L. H. et al. High-gain harmonic-generation free-electron laser. Science 289, 932–934 (2000).
Xiang, D. et al. Demonstration of the echo-enabled harmonic generation technique for short-wavelength seeded free electron lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 114801 (2010).
Zhao, Z. T. et al. First lasing of an echo-enabled harmonic generation free-electron laser. Nature Photon. 6, 360–363 (2012).
Čutić, N. et al. Vacuum ultraviolet circularly polarized coherent femtosecond pulses from laser seeded relativistic electrons. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 14, 030706 (2011).
Labat, M. et al. High-gain harmonic-generation free-electron laser seeded by harmonics generated in gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 224801 (2011).
De Ninno G. et al. Generation of ultrashort coherent vacuum ultraviolet pulses using electron storage rings: a new bright light source for experiments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 053902 (2008).
Labat, M. et al. Coherent harmonic generation experiments on UVSOR-II storage ring. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 593, 1–5 (2008).
Bocchetta, C. J. et al. FERMI@Elettra FEL Conceptual Design Report (Sincrotrone Trieste, 2007).
Bonifacio, R. et al. Physics of the high-gain FEL and superradiance. Rivista del Nuovo Cimento 13(9), 1–69 (1990).
Kim, K. J. Three-dimensional analysis of coherent amplification and self-amplified spontaneous emission in free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 57, 1871–1874 (1986).
Saldin, E. L., Schneidmiller, E. A. & Yurkov, M. V. Statistical properties of radiation from VUV and X-ray free electron laser. Opt. Commun. 148, 383–403 (1998).
Allaria, E. et al. The FERMI@Elettra free-electron-laser source for coherent X-ray physics: photon properties, beam transport system and applications. New J. Phys. 12, 075002 (2010).
Sasaki, S. Analyses for a planar variably-polarizing undulator. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 347, 83–86 (1994).
Bonifacio, R., De Salvo Souza, L. & Pierini, P. Generation of XUV light by resonant frequency tripling in a two-wiggler FEL amplifier. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 296, 787–790 (1990).
Freund, H. P., Biedron, S. G. & Milton, S. V. Nonlinear harmonic generation in free-electron lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 36, 275–281 (2000).
Huang, Z. & Kim, K. J. Three-dimensional analysis of harmonic generation in high-gain free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. E 62, 7295–7308 (2000).
Spezzani, C. et al. Coherent light with tunable polarization from single-pass free-electron lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 084801 (2011).
Kokole, M. et al. Magnetic characterization of the FEL-1 undulators for the FERMI@ELETTRA free-electron laser. Proc. FEL 2010, 664–666 (2010).
Ferianis, M. et al. The copper free FERMI timing system: implementation and results. Proc. Beam Instrumentation Workshop 398–402 (2010).
Ben-Zvi, I., Yang, K. M. & Yu, L. H. The ‘fresh-bunch’ technique in FELS. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 318, 726–729 (1992).
Allaria, E. & De Ninno, G. Soft-X-ray coherent radiation using a single-cascade free-electron laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 014801 (2007).
Fawley, W. M. A user manual for GINGER and its post-processor XPLOTGIN, LBNL Technical Report LBNL-49625 (2002).
Xie, M. Exact and variational solutions of 3D eigenmodes in high gain FELs. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 445, 59–66 (2000).
Saldin, E. L., Schneidmiller, E. A. & Yurkov, M. V. Coherence properties of the radiation from X-ray free electron laser. Opt. Commun. 281, 1179–1188 (2008).
Singer, A. et al. Transverse-coherence properties of the free-electron-laser FLASH at DESY. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 254801 (2008).
Lambert, G. et al. Injection of harmonics generated in gas in a free-electron laser providing intense and coherent extreme-ultraviolet light. Nature Phys. 4, 296–300 (2008).
Allaria, E., Danailov, M. D. & De Ninno, G. Tunability of a seeded free-electron laser through frequency pulling. Eur. Phys. Lett. 89, 064005 (2010).
Ratner, D., Fry, A., Stupakov, G. & White, W. Laser phase errors in seeded free electron lasers. Phys. Rev. ST Accel. Beams 15, 030702 (2012).
Welch, J. et al. FEL spectral measurements at LCLS. Proc. FEL 2011, 461–464 (2011).
Stupakov, G. Using the beam-echo effect for generation of short-wavelength radiation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 074801 (2009).
Feldhaus, J., Saldin, E. L., Schneider, J. R., Schneidmiller, E. A. & Yurkov, M. V. Possible application of X-ray optical elements for reducing the spectral bandwidth of an X-ray SASE FEL. Opt. Commun. 140, 341–352 (1997).
Geloni, G., Kocharyan, V. & Saldin, E. A novel self-seeding scheme for hard X-ray FELs. J. Mod. Opt. 58, 1391–1403 (2011).
Amann, J. et al. Demonstration of self-seeding in a hard X-ray free-electron laser. Nature Photon. 6, http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2012.180 (2012).
Zangrando, M. et al. PADReS: the photon analysis delivery and reduction system at the FERMI@Elettra FEL user facility. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80, 113110 (2009).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the many people at Sincrotrone Trieste who contributed to this project, including the accelerator operations group, the electron and systems controls groups, the undulator systems design, X-ray diagnostics/optics, RF engineering, all engineering support teams, procurement and administration. Thanks are also extended to colleagues at Kyma S.r.l. for the timely construction and delivery of the undulators used in the present study. The resources that made possible the construction of FERMI were obtained and managed by G. Comelli, A. Franciosi and C. Rizzuto. The authors acknowledge support from the Italian Government, the Regional Government of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, the European Commission, the European Research Council and the European Investment Bank.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.A. and G.D.N. co-wrote the first draft of the paper. All authors co-developed the FERMI concept, designed, constructed and tested the accelerator and FEL systems, performed experiments and analysed the data. S.V.M. was the FERMI project director in the first phase of the project. M.S. is the current FERMI project director.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allaria, E., Appio, R., Badano, L. et al. Highly coherent and stable pulses from the FERMI seeded free-electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet. Nature Photon 6, 699–704 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2012.233
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2012.233
This article is cited by
-
Bright continuously tunable vacuum ultraviolet source for ultrafast spectroscopy
Communications Physics (2024)
-
Ultrafast demagnetization in bulk nickel induced by X-ray photons tuned to Ni M3 and L3 absorption edges
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Ultrafast electronic relaxation pathways of the molecular photoswitch quadricyclane
Nature Chemistry (2024)
-
Finding the semantic similarity in single-particle diffraction images using self-supervised contrastive projection learning
npj Computational Materials (2023)
-
Progress and prospects in nonlinear extreme-ultraviolet and X-ray optics and spectroscopy
Nature Reviews Physics (2023)